Functionalism or Conflict Theory in the Analysis of Social Care Work Professionalization
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Social Work |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1578 words | ✅ Published: 23 Sep 2019 |
Does functionalism or conflict theory provide a more credible explanation of how the professionalization of social care work has developed in Ireland?
Functionalism theory
Functionalist theory is seen as a structuralist theory that focus on society rather than individual because the individual is product of all the social influences on them and shared values and belief shape the individuals and the founder of it is Emile Durkheim (1858-1917) (Allen ,2018).
Conflict theory
Based on the ideas of Karl Marx (1818–1883), looks at society as a battle for limited resources and focus on the inequalities of different groups in society that generate conflict and social change (Allen ,2018).
How professionalization of social care work has developed in Ireland
functionalism vs conflict theory
In the last 20 years in Ireland had been a growth of social work and as well the expansion of the welfare state made a substantial expansion of service sector which created up a conflict about professionalization and its implications for social democracy.
Social care profession definition in Ireland still did not reach the “maturity” as an uncertainty arise and is still under development. For a number of years in Ireland the term of “social care” suited government and agencies for reasons related to salary scales and career structures not to have a specific definition the role of social work and social care are separate professions.
The Health and Social Care Professionals Act 2005 is significant legislation, providing statutory regulation for 17 designated health and social care professions. In the recent years the social care domain has expanded an many educational programs for students entering the field grow considerably. This process has started to occur: within the ongoing development of courses of study (eg. the EirCan model associated with Athlone IT); in the publication of texts and journals; in the regularisation of work-based programs and placement procedures through the IASCE (Gilmore, 2005); and in public debate stimulated by the legislative activity (Share et.al,2005).
In Ireland, Durkheim sociological thinking is more relevant thru the functionalism theory, as his managerial model has contributed the most how Irish society is governed by helping reform, rationalize and improve.
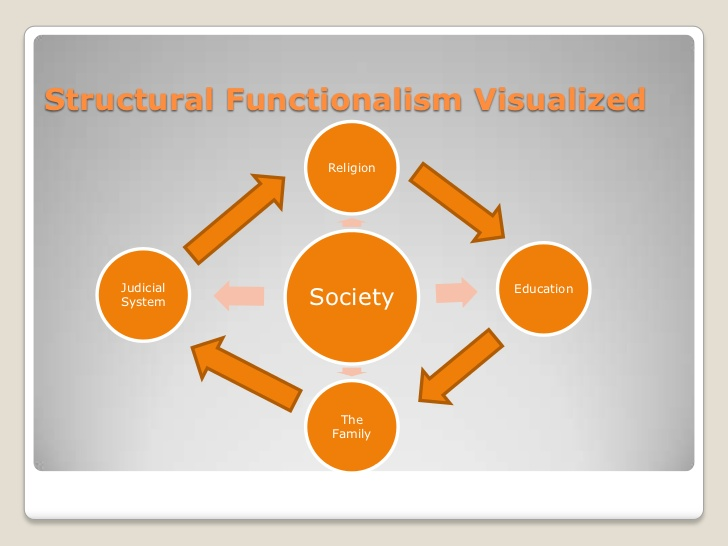
Structural Functionalism viewed by Talcott Parsons (1902-1979) who was considered an advocate of functionalism where religion, education, family and law judicial system have a purpose, an impact over society and where society is a stable arrangement who can influence everything around. In Parsons vision each part contributes to the overall function (Allen, 2018).
Historically, in Ireland a huge impact over society was the Catholic Church which dominated in social care as for example around 1936, education system in Ireland was influenced by religion as government schools were run by 18 religious orders within the Catholic Church. Around 14000 people said that they were abused psychologically, physically and sexually in this schools and this was made public in Ryan report (2009) witch along with the Reformatories and Magdalene laundries scandals contributed the decision of professionalize social care (Lalor and Shane,2013).
According to Share and Lalor (2013) “Modern Social care practice in Ireland was born out of serious deficiencies in the running of children’s centres…pg. 12”
Another two scandals” Cussen Report” (1936) followed by “Kennedy Report” (1970) influenced the aspect of social care in Ireland with its institutionalization through the formation of the Sociological Association of Ireland in 1973 witch later in 1980 generated the professionalization of social care practice. The Sociological Association of Ireland influenced the process of professionalization for the last 40 years through research and studying Irish society that promote the development of sociology. As in functional theory, professions are seen as rational, “stabilizing elements in society” according to Wright (1979) that are an essential and beneficial part for the society.
They “dominate the contemporary scene in such a way as to render obsolescent the primacy of the old issues of authoritarianism and capitalistic exploitation” (Parsons, 1968: 546).
The first national organization under the name of Association of workers in Care (AWCC) establish in 1972, after named the Irish Association of Social Care Workers (IASCW) is the professional body for the profession that will support with development of new knowledge through research. Under the IASCW was set up the code of practice of the social worker, where social justice, empowerments, dignity, competence are the core values that are promoting the social model of care in Ireland. Nowadays other services in Ireland are adopting the social care model, as will work alongside with the medical model as this functionalist approach point out that for a society’s ability to function is needed good and effective health care (George et.al,2013).
Parsons (1954) makes an interesting and relevant point in suggesting that professional training should culminate in the balance of self and community interest which is vital for the maintenance of social cohesion, which he describes as the maintenance and service of society and community.
In 1999 Gallagher and O’Toole (1999: 78) identified the issue of professionalisation as ‘central to the development of social care work’ but that development of a ‘coherent professional identity’ was stymied by a lack of internal unity, fragmentation across qualification level, diverse client and administrative settings, a changing role and exclusion from key policy making structures within the bureaucratic professional hierarchy of state welfare services (Gallagher and O’Toole, 1999: 83).
Hallstedt and Högström (2005b: 18) suggest that all occupations in the field of welfare ‘are fighting for right to call themselves professions’
By 2005 according to Share and McElwee (2005b: 58), the practitioners were involving with the concept of professionalism and discussing “what it might mean” claiming that ‘it is crucial to the future of social care in Ireland, and this materialised professionalisation onto the agenda for policy-makers in the social care field profession.The functionalist and trait approaches to the sociology of the professions are concerned with defining the characteristics of a profession and identifying the role they fulfil in society.
Professionalization of social care in Ireland have a monopoly of practice in its own field as under the Health and Social Care Professionals Act 2005 as registration of social workers is made with CORU (Health & Social Care Professionals Council). CORU is government controlled and initiated to protect the public by regulating the social care professionals by promoting highest standards of conduct. Functionalism theory focus on institution to maintain an equilibrium, institutions are structures that meets the needs of society and according to Parson institutions always work for the overall benefit of society.
According to Conflict theory discuss that registration, regulation and educational requirements are converted into instruments which will increase earnings and status and will limit the supply of skilled social care workers, where as well the practice of social care worker profession is designated to reduce the supply of services. This come in opposition with CORU´s views that statutory regulation is designated to ensure professional status and increase the provision of services (Farrelly et. O’Doherty,2011).
With the current debate from the Irish parliament relating to the recognition of non-Irish social care qualifications stating that social care labour market is insufficient will influence capitalism. Capitalism is encouraged by globalization where the dominant ideology is transmitted via the social institutions of capitalism, and this can lead to a conflict as according to Marx, capitalists exploit workers for their labor and do not share the fruits of these labors equally.
Conclusion
The professionalization of social care in Ireland is more linked to functionalism theory as it came to life as a functional segment of Irish society, were conflict theory views society as a system of conflict and instability. In this view, the professionalization of social work came as a part of the natural expansion of a social structure associated with modernization.
The long history of child abuse scandals in Ireland generated up by the Catholic Sociological thinking, the authorities would have been unsuccessful in accomplishing the goal of professionalising the social care practice and by marking out this role as a registered practice with ethics and values will never allow such scandals to arise again (Boyd,2013).
References:
- Allen (2018). Major theoretical perspectives in sociology. [online] Slideshare.net. Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/sethallen26/major-theoretical-perspectives-in-sociology-14044354 [Accessed 29 Dec. 2018].
- Farrelly, T., & O’Doherty, C. (2011). Social Care, after the Act–Reflections five years on after the passing of the Health and Social Care Professionals Act 2005. Administration, 59(2), 73-83.
- Finnerty, K. C. (2012). Professional Identity and the Irish Social Care Worker (Doctoral dissertation, University of Leicester).
- Georgina Boyd (2013). History of social care in Ireland
- George, V., & Wilding, P. (2013). Ideology and social welfare. Routledge.
- Lalor, K., & Share, P. (Eds.). (2013). Applied social care: An introduction for students in Ireland. Gill & Macmillan.
- Share, Perry, and N. McElwee. “The professionalisation of social care in Ireland.” Applied social care: an introduction for Irish students. Dublin: Gill and Macmillan Ltd (2005): 42-59.
- Wenocur, S., & Reisch, M. (1983). The social work profession and the ideology of professionalization. J. Soc. & Soc. Welfare, 10, 684.
- Wright, D. K. (1979). Professionalism and social responsibility in public relations. Public Relations Review, 5(3), 20-33.
- https://www.oireachtas.ie/en/debates/debate/dail/2018-12-11/39/
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


