Negative Externality: Pakistan’s Carbon Tax
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Economics |
| ✅ Wordcount: 2952 words | ✅ Published: 09 Oct 2017 |
Table of Contents (Jump to)
Introduction
The assignment is based on the concept of negative externalities. A negative externality normally is a cost that is incurred to the third party as a result of an economic transaction. The assignment is based on the case study of Pakistan’s policy for implementing the carbon tax. This way the government of Pakistan has taken a positive step towards dealing with the negative externality – pollution and green house gas emission. Later the assignment covers the other steps that must be considered by the Pakistan government to deal with the problem ad reduce the impact of negative externalities.
Answer 1
Negative Externalities: It can be defined as the action of products on consumers that has the negative impact on the third party. Negative externalities are mainly concerned with the environmental effects of producing and consuming a product (Laffont, 2008). The main examples of negative externalities are air pollution, water pollution, noise pollution, systematic risk etc.
A negative externality normally is a cost that is incurred to the third party as a result of an economic transaction. In this type of economic transaction, consumer and producer are the first and second party, and the third party is comprised of organization, individual, resource or property owner that get indirectly affected due to that transaction (Caplan, 2008). The negative externality is also known as external cost in economics.
Some common negative externalities are:
- The smokers ignore the fact of the harmful impact of the passive smoking for the non smokers around them.
- Air pollution caused by the traffic impacts the lungs of the people who are not even travelling on the road
- The food wastage
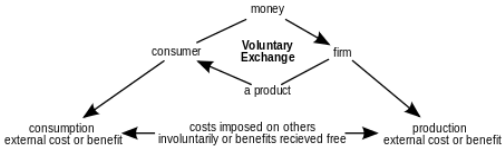
(Source: Buchanan, James, “Externality”.Economical)
Negative externalities normally occur in the situations where property ownership of the assets and resources are not properly allocated and are uncertain. For instance, there is no owner of the oceans or the forests, so anybody can pollute them without any fear of getting sued by the owner. External cost like the cost of pollution makes the marginal social cost curve mush higher than the marginal private cost.
 (Source: Economicsonline.co.uk)
(Source: Economicsonline.co.uk)
Government Intervention to correct the negative Externalities:
The environmental concerns are the most important challenge in front of government now days. They are taking up many steps to deal with the negative externalities and eradicate its harmful effects from the third party. The most common among them are the:
Environmental tax:
This is the most common approach of adjusting the negative externalities. This is also referred to as the “making of polluters day”. This tax increases the private tax of production or consumption with the aim of reducing the overall demand for the product that is causing the negative externality. For instance: money collected from the congestion charge of a vehicle that is entering a busy road. The environmental taxes include – the landfill tax, the congestion charges, vehicle excise duty and plastic bag tax.
Problems with environmental taxes: Pollution tax has the following related problems:
- Assignment of the right level of taxation
- Consumer welfare effects
- Investment and employment consequences.
Carbon Tax:
Carbon tax refers to the tax that is imposed on the fuels’ carbon content (Holler, 1991). All the hydrocarbon fuel contains the carbon content in it like petroleum, natural gas and coal. They release the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere when they are burnt. Carbon taxes are formed to reduce the green house effects of gas emission through cost effective means (Gupta, 2007). . Carbon taxes are very regressive and impact the lower income group largely. The impact of carbon taxes can be addressed using the tax revenue for the lower income groups. The features of carbon tax are:
- This is a direct tax on the content of carbon in fossil fuel.
- It is considered as the most economical and efficient means for conveying the price signals that are crucial for reducing the carbon content
- It can be structured for softening the impact of the additional cost by distributing to the households.
- Carbon tax is supported by economists, public officials, environmental leaders and citizens.
The carbon tax policies of government are significant for taking the global effort to fight the climatic changes. Pricing carbon is a positive step towards it.
The government may interfere through the use of laws and regulations. For example, theHealth and Safety at Work Actcovers all public and private sector businesses. Local Councils can take action against noisy, unruly neighbors and can pass by-laws preventing the public consumption of alcohol.
Answer 2
Case Study – Overview
Pakistan has recently considered taxing the carbon emission from the big fossil fuel industry and reduces its negative impact on the world’s climate. This was declared in the national climate change strategy. They emphasize on the use of renewable resources. The government will “consider introducing carbon tax on the use of environmentally detrimental energy generation from fossil fuels”, said the plan, launched at an event in Islamabad. (Reuters Point Carbon)
The Pakistan government in their policy announced the tax on carbon at the rate of Pakistani Rupee 25 per ton. It started from 1 July 2012 with the objective of changing the policy later to market based emission trading scheme (Gillard, 2010). Pakistani economy suffered slow-down due to the climatic changes. Climate change refers to situation that reflects the significant changes in the patters on weather conditions over the particular time period. Climate changes are caused by various factors such as solar radiation variations, biotic process and volcanic eruptions. The human activities are also responsible for the severe climatic changes that have lead to global warming (Edward & Miller, 2001). These severe climatic changes have the adverse impact on the overall cycle of earth’s process. Evidence for recording the climate changes has been taken from various resources that were used to reconstruct the past climates. The changes have affected the entire world and Pakistan has faced the significant economic impacts due to this. It has affected the infrastructure, coastal communities, and agriculture and water security in Pakistan.
Carbon taxes are important for reducing the negative effects of carbon emission. Carbon taxes are formed to reduce the green house effects of gas emission through cost effective means . Carbon taxes are very regressive and impact the lower income group largely. The impact of carbon taxes can be addressed using the tax revenue for the lower income groups. These taxes provide the incentives for the firms that adopt the environment friendly approach for production process. These are also important for raising the money required for taking the initiatives to save environment. The impacts of carbon tax on the economy of Pakistan are as follows:
Macro economics effects: Pakistan economy promotes the reduction in usage of carbon related energy resources for the industry purpose and switch towards the renewable energy resources. Carbon tax is the cost to the producers that use the carbon efficient energy resources. So in order to reduce the cost and increase the profit, it is important for them to shift towards the other renewable resources of energy. Carbon tax is important for reducing the tax as well as the negative impacts on the environment.

(Source: Self Study)
The left graphs clearly states that the tax will increase the cost of production and decrease the quantity of fuel energy. The will also lead to higher labour cost and also it will lead to increase in fuel prices. The right graph on the contrary shows the benefit of using the renewable resource of energy and increase in production level. So it is seen that carbon tax will impact the business negatively, but at the same time encourage them to use the renewable resources of energy that will have the long term positive impact on environment and business.
Effects on employment: The carbon tax has the direct negative impact on the employment because it will lead to additional burden on the production cost. The trade sector will see the shift towards the non trading sector due to this.
Effects on households: The household will experience the change in cost of the general commodities as the industries will include the cost of carbon tax in total cost of production. This will lead to negative impact and the household income will be reduced.
The government replaces the carbon tax with the direct action plan. The direct action plan includes the incentive program for the industries that reduce the carbon emission rate significantly (Preston, 2006). The key points of the policy are:
- Target of 55 reduction in carbon emission rate
- Scrapping the carbon tax and associated taxes
- Creation of green army for conducting the environment conservation work.
The government released the white paper that has the details about the policy and the working of fund for emission reduction. The labor as well as the coalition supported this policy over the carbon tax. Contrary to the carbon taxes the policy emphasizes on gaining the incentives by reducing the carbon emission in environment. Policy also has the provision for compensation payment to tax payers for reducing the increase in prices. It directs the business to work towards the emission reducing projects.
Pakistan is the largest contributor towards the green house gas emissions, so this policy will help the entire worlds by reducing the carbon emission without imposing any impact on the cost of production. The main feature of the direct action policy is creation of emission reduction fund, which will be $3 billion for four years. The fund will ask the industries to fill the tenders for the emission reduction projects. This will initiate the reverse auction and the industries will compete for reducing the emission rate to win the incentive from the government. The auctions will be held quarterly.
The government is sure about the positive outcomes of the policy in terms of reduction in carbon emission.

(Source: Self Study)
The direct policy has the positive impact on the Pakistan economy. Pakistan actually has the capability of achieving more than the 5% target. Pakistan will achieve the emission reduction project by 2020 in more efficient way. It will contribute towards the global action for addressing the climate change. By reducing the emission amount the economic growth of the Pakistan is expected to be doubled in next few years. It will directly impact the long term projection of the economic growth. Since it has no cost attached to it, it will be beneficial for the business as well as the house hold income. Instead the policy rules of taking the advantage of incentive will direct the business house to reduce the carbon emission without any impact on the cost of production. It is estimated that Pakistan economy will grow by 17% with this project.

(Source:Climate Change Authority, 2013)
The level of the price attached to carbon with incentive plan will reduce the economic cost. There will be no cost passed to the customers in the form of goods and services. It will also regulate the direct income transfer from Pakistan for buying the additional emission from the overseas. This will also reduce the indirect cost. This will have the positive trade effect.
Carbon tax policy as well as the direct action policy aims towards the reduction of the carbon emission in the environment. The base is same but the approach is totally contradictory. The direct action is better than the carbon tax policy because of the below mentioned facts:
- Carbon tax has the cost attached to it which will in return increase the cost of production whereas the direct action has the incentive policy which encourages the industries to reduce the amount of carbon emission without any effect.
- Carbon tax will lead to reduction in employment opportunity due to increased labor cost whereas this will not occur in the case of direct action policy.
- The direct action policy has the better targets and objectives as compared to carbon taxing.
- The carbon tax will reduce the household income due to the increased prices of commodity whereas the direct action plan will not have the negative impact on the household income.
- Carbon taxing policy will lead to increase in fuel prices and the actual efficiency will be reduced whereas the direct action plan will increase the efficiency of the industry and the quality of production.
- The direct action policy has the clear targets in terms of reduction of carbon emission whereas it is missing in the carbon tax policy.
For dealing with the negative externalities, the Government of Pakistan has taken a positive step in the form of Carbon tax. This will reduce the green house gas emission and promote the use of renewable resources. This was not only Pakistan but the climate of entire world will get the positive results. Pakistan is taking the considerable steps to reduce the carbon emission in the environment. This is because of the fact that the economy of Pakistan has suffered due to the large amount of green house gas emission. The government introduced the carbon tax and direct action policy for the reduction of carbon emission. The carbon tax policy does not get the enough success and the direct action plan replaced it successfully. By the year 2020 Pakistan is aiming at significant control over the carbon emission in the environment.
Answer 3
The carbon tax is very unique in nature but it is quite effective for reducing the impact of negative externalities. The main purpose of carbon tax is to reduce the carbon dioxide emission and with this save the severe climatic changes. However this is noted that only the carbon tax cannot save the climatic change and reduce the impact of negative externalities. The Pakistan government should also make other policies to reduce the impact of carbon emission in the environment. For this purpose they must make the policies and regulation of reducing the coal usage in industry as it causes lots of pollution and also it is a non renewable resource of energy. The government should compulsorily regulate the use of renewable resources of energy that are natural and reduces the emission of green house gases.
Carbon tax policy is quite cost effective for the Pakistan economy and it is quite easy to switch from the pollution taxes to direct subsidies and promotes the cleaner and greener production technologies. However the impact of these taxes totally depends on how this money is being used for the reducing the impact of negative externalities (Scott, 2005). They must be balanced by decreasing the amount of other taxes by the method of revenue recycling. The green taxes can actually help the overall economy of Pakistan provided it is used in the right direction and the taxes are imposed religiously to achieve the main objective behind them. In the nutshell, it can be said that imposing the carbon tax is a very progressive step of the Pakistan government. However along with this they should also consider the following for dealing with the negative externalities (Bonnieux, 2002):
- Preserving the tropical rain forests in Pakistan
- Limiting the public access to the farm land for their recreational purposes
- Preservation of wet land
- Following the traditional ways of farm building
- Implementing the price-based instruments alter the prices of goods and services to reflect their relative impact.
- Providing the grants to farmers under the Control of Farmyard Pollution Scheme
Conclusion
To conclude, negative externality is a type of economic transaction, consumer and producer are the first and second party, and the third party is comprised of organization, individual, resource or property owner that get indirectly affected due to that transaction. Pakistan Government has decided to impose the carbon tax for dealing with the situation of extreme pollution and green house gas emission through their fossil fuel industry. The level of the price attached to carbon with incentive plan will reduce the economic cost. There will be no cost passed to the customers in the form of goods and services. It will also regulate the direct income transfer from Pakistan for buying the additional emission from the overseas. Main purpose of carbon tax is to reduce the carbon dioxide emission and with this save the severe climatic changes. However this is noted that only the carbon tax cannot save the climatic change and reduce the impact of negative externalities. The Pakistan government should also make other policies to reduce the impact of carbon emission in the environment.
References
Bonnieux, F. and Rainelli, P.( 2002). Economics and the interface between agriculture and nature, in Brouwer, F. and Van der Straaten, J. eds, Nature and Agriculture in the European Union, Cheltenham, Edward Elgar ARTS 338.1094 P2.
Caplan, Bryan(2008).“Externalities”. InDavid R. Henderson(ed.).Concise Encyclopedia of Economics(2nd ed.). Indianapolis:Library of Economics and Liberty.ISBN978-0865976658.OCLC237794267.
Edwards, Paul Geoffrey; Miller, Clark A. (2001).Changing the atmosphere: expert knowledge and environmental governance. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press.ISBN0-262-63219-5.
Gupta, S.et al. (2007).“13.2.1.2 Taxes and charges”.Policies, instruments, and co-operative arrangements. Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (B. Metzet al. Eds.). Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., and New York, N.Y., U.S.A.. This version: IPCC website. Retrieved 2010-03-18.
Hoeller, P. and M. Wallin (1991).OECD Economic Studies No. 17, Autumn 1991. Energy Prices, Taxes and Carbon Dioxide Emissions(PDF). OECD website. p.92. Retrieved 2010-04-23.
J.J. Laffont(2008). “externalities,”The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd Ed.Abstract.
McKibben, Bill (2011). The Global Warming Reader. New York, N.Y.:OR Books.ISBN978-1-935928-36-2.
Preston, B.L.; Jones, R.N. ( 2006).Climate Change Impacts on Australia and the Benefits of Early Action to Reduce Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions.
Scott, S., (2005),Fertiliser Taxes – Implementation Issues, Final Report, Wexford, Environmental Protection Agency.
Williams, C. (1997) ‘Environmental victims: Arguing the costs’,Environmental Values, 6:3-30.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


