Uses of Herbal Medicine: An Overview
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Chemistry |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1864 words | ✅ Published: 28 Nov 2017 |
1 Folk medicine
According to WHO- ‘Traditional medicine is the sum total of the knowledge, skills, and practices based on the theories, beliefs, and experiences indigenous to different cultures, whether explicable or not, used in the maintenance of health as well as in the prevention, diagnosis, improvement or treatment of physical and mental illness.’ (Qi, 2014)
Generally traditional medicines, alternative medicine, indigenous medicine, complementary medicine, or natural medicine, folk medicine are all different names of locally found medicines.
1.1 Herbal Medicines
An herb is a plant or plant part used for its scent, flavour, or therapeutic properties. Medical science in which use of plants for medicinal purposes is studied, is called ‘Herbology’. Herbal medicines include:  (Qi, 2014) (Herbalism, n.d.)
(Qi, 2014) (Herbalism, n.d.)
2 Ayurvedic medicine
Ayurveda, is one of the most ancient and comprehensive systems of healthcare. It is the science of life and system of traditional medicine native to Indian subcontinent. It is believed that Lord Brahma the creator of universe was first preacher of Ayurveda. Four Vedas, composed between 5000 -1000BC have info on treatment by plants and natural resources. However, till 1000 BC Ayurvedic system was fully developed, into Caraka SamhitÄ and SuÅ›ruta SamhitÄ (books on Ayurveda written in systematic manner); these two books included 8(Aá¹£á¹Äá¹…ga) major clinical specialities: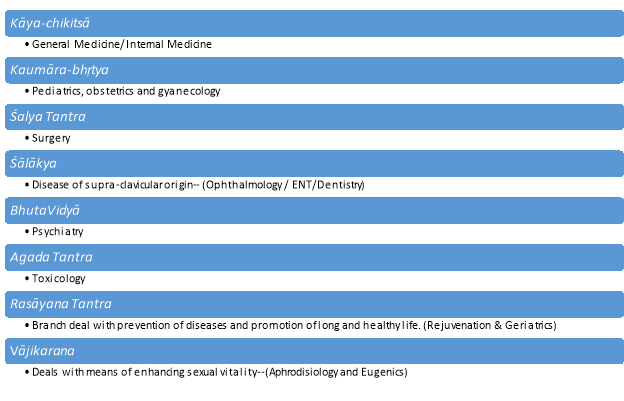 (Ayurvedic Medicine, n.d.) (CCRA)
(Ayurvedic Medicine, n.d.) (CCRA)
3 Herbal Antibiotic Medicines
An antibiotic is an antibacterial agent that curbs bacterial growth or kills bacteria. Antibiotics if are used frequently for things they can’t treat—like colds or other viral infections—they can stop working efficiently against bacterial infections, this development is called as antibiotic resistance. (Bruno, 2014)
3.1 Echinacea
3.1.1 Introduction
Echinacea is a group of herbaceous flowering plants (in daisy family), it contains nine species generally called as coneflowers. (Echinacea, n.d.)
3.1.2 Geographical Availability
Are generally found in eastern and central North America. (Echinacea, n.d.)
3.1.3 Medicinal Effects/Uses
It is called as granddaddy of all immune- enhancing herbs. It is an immune stimulant, is excellent in preventing and treating colds and influenza. Research reveals that it affirms the immune system by actuating white blood cells (WBCs-lymphocytes and macrophages. (Bruno, 2014) (Literature Education Series On Dietary Supplements )
3.1.4 Dosage
General dosage range for Echinacea extract is 200-300 mg; for acute infections (e.g. Cold or flu) could be increased to 900-1200mg. (Bruno, 2014)
3.2 Andrographis paniculata
3.2.1 Introduction & Geographical Availability
Also called as ‘king of bitters’, ‘kalmegh—‘Dark Cloud’’, ‘Bhuneem– neem of ground’. It is an annual herbaceous plant in the family Acanthaceae, native to India and Sri Lanka; widely cultivated in south and south-east Asia. Mostly the leaves and roots are used for medicinal purposes. (Andrographis paniculata, n.d.)
3.2.2 Medicinal Effects/Uses
It contains a number of bitter components, which have both immune-stimulating and anti-inflammatory action. Studies have shown that Andrographis may help individuals suffering from the respiratory infection, common cold, and ulcerative colitis. It has an active component Andrographolide, in Andrographis, which is responsible for modulation of various inflammations. (Bruno, 2014) (Literature Education Series On Dietary Supplements )
3.3 Berberine
3.3.1 Introduction & Geographical Availability
It is a quaternary ammonium salt from protoberberine group of isoquinoline alkaloids; bitter in taste, yellow in colour, plant chemical found in the roots of various herbs, including- European barberry (Berberis vulgaris), Oregon grape (Berberis aquifolium)( Mahonia aquifolium)[flowering plant native to western North America], and tree turmeric (Berberis aristata).(Bruno, 2014)
3.3.2 Medicinal Effects/Uses
Plants containing barberine are immune stimulant; also has shown activity against fungal infections, Candida albicans, yeast, parasites, and bacterial/viral infections such as urinary tract infections, chloroquine-resistant malaria, bacterial-induced diarrhoea, treatment of trachoma & leishmaniasis(both in eye).
3.4 Shiitake and AHCC
3.4.1 Introduction & Geographical Availability
Shiitake is native to East Asia (China, Japan, and Korea). In English called as- “Sawtooth oak mushroom”, “black forest mushroom”, “black mushroom”, “golden oak mushroom”, or “oakwood mushroom”. (Shiitake, n.d.)
3.4.2 Medicinal Effects/Uses
Shiitake- is a mushroom used for increasing immunity, making liver healthy and regulating unwanted growth of muted stomach and pancreas cells (Cancer). Active Hexose Correlated Compound (AHCC) – is an α-glucan-rich compound isolated from shiitake. AHCC is the second most popular complementary and alternative medicine used by cancer patients in Japan. (Shiitake, n.d.) AHCC may increase the body’s resistance to pathogen (as resulted in experiments with-influenza virus, West Nile virus, or bacterial infection)
3.5 Pomegranates
3.5.1 Introduction & Geographical Availability
Originated in Iran. It has been mentioned in many ancient texts of Babylon, Quran, Hormeric Hymes, and Books of Exodus. (Pomegranate, n.d.)
3.5.2 Medicinal Effects/Uses
Its juice has better antioxidant activity than red wine and green tea. (Pomegranate, n.d.)
Use in Ayurvedic medicine: Bark of its tree, flower juice is used as remedy to treat diarrhoea, dysentery, internal parasites, stopping nose bleeds, gum bleeds, toning of skin and treating haemorrhoids. The seeds and juice of pomegranates are considered good for the heart and throat. Sweet pomegranate fruit is known as ‘blood builder’. Pomegranate juice is also used as an eye drop, as it is conceived to retard the growth of cataracts.
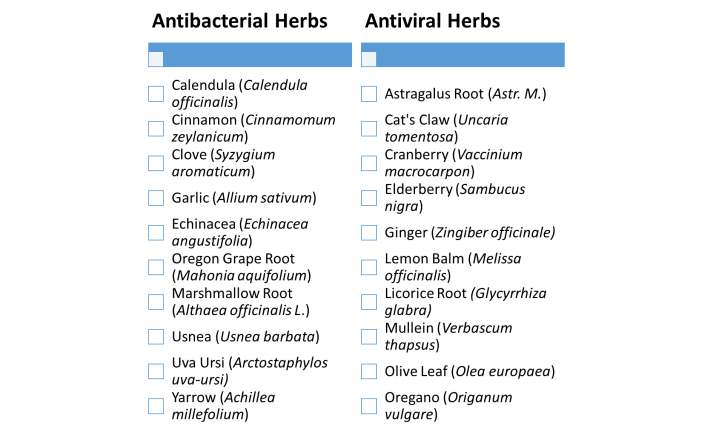
(Nelson, n.d.)
3.6 Garlic
3.6.1 Introduction & Geographical Availability
It was known to Ancient Egyptians, and has been used for both medicinal purposes and culinary. Studies done have found that when it is crushed, it yields allicin-an antibiotic and antifungal compound, sulfur-containing compounds alliin, ajoene, diallyl polysulphides, vinyldithiins, S-ally cysteine, and enzymes, B vitamins, proteins, minerals, saponins, flavonoids etc. (Garlic, n.d.)
3.6.2 Medicinal Effects/Uses
Garlic acts as Diuretic, Flu remedy, Urinary Antiseptic, Antifungal, Antibacterial, Anti asthmatic, immune stimulus etc. It also reduces accumulation of cholesterol, inhibits vascular calcification in patients with high blood cholesterol. Vasodilatory effect (widening of blood vessels) of garlic- probably due to catabolism of garlic-derived polysulfide to hydrogen sulfide in red blood cells (RBCs).
3.7 Ginger
3.7.1 Introduction & Geographical Availability
It is a spice that flourishes in warm and sunny regions like South Asia. Ayurvedic verse says that to enhance digestion everyone should eat fresh ginger just before lunch and dinner. The characteristic odour and taste of ginger is simulated due to a mixture non-volatile phenylpropanoid – zingerone, shogaols and gingerols, volatile oils (called as essential oils) that compose 1-3% of the weight of fresh ginger.
3.7.2 Medicinal Effects/Uses
Study paper on NCBI, ginger inhibits growth and modulates secretion of angiogenic factors in ovarian cancercells. The use of dietary agents such as ginger may have potential in the treatment and prevention of ovarian cancer. (Jennifer Rhode, 2007) In general, ginger enhances the blood flow throughout the body, and stimulates circulation, treat nausea caused by seasickness, morning sickness, digestive disorder, gastric problems, constipation, and colic. Tea brewed from ginger is a common local remedy for treating colds.
3.8 Tulsi (Ocimum tenuiflorum)
3.8.1 Introduction & Geographical Availability
A group of researchers from Central University of Punjab, have done study using Chloroplast genome sequences, and have found that Tulsi is native to North-Central India. (Tulsi, n.d.) Varieties of Tulsi/Holy Basil:
- Krishna or shyama Tulsi (Ocimum sanctum)
- Rama Tulsi (Ocimum sanctum),
- Vana Tulsi (Ocimum gratissimum)
3.8.2 Medicinal Effects/Uses
 In Ayurveda, it is termed as ‘elixir of life’.
In Ayurveda, it is termed as ‘elixir of life’.
(Bhattathiry, n.d.)
3.9 Turmeric
3.9.1 Introduction & Geographical Availability
It is native to tropical Tamil Nadu and South-East Asia. Chemical Composition: Most important group of compounds in turmeric is called curcuminoids. Curcuminoid include curcumin (diferuloylmethane) [3.14% avg.], demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin. It also contain Volatile oils. (Turmeric, n.d.)
3.9.2 Medicinal Effects/Uses
Turmeric is potent antioxidant, powerful anti-inflammatory agent, lowers total cholesterol, anticoagulant, act as antacid, liver protective, anticancer activity, boost immunity and reduces blood sugar.
According to a study paper on NCBI, Curcumin (in turmeric) have shown positive effect on Alzheimer’s disease treatment. (Palanivelu, 2011)

(Synopsis of Turmeric’s Healing Properties, n.d.) (Dr.Jayaprakash, n.d.)
3.10 Aloe Vera
3.10.1 Introduction & Geographical Availability
It is common in India, South Africa, Barbados, Haiti etc. The herb has been regularly mentioned as being used in herbal medicine since first century AD. (Aloe Vera, n.d.) It contains slippery, slimy constituents that have a soothing effect, as well as a wound-healing effect. In Ayurvedic medicines Aloe Vera is commonly used due to its antimicrobial properties. Sapnonin– are the class of chemical compounds found in various plants (including Aloe Vera). It has soap like physical behaviour; it acts as anti-feedant, and protect plant against microbes and fungi. (Sapnonin, n.d.)
3.10.2 Medicinal Effects/Uses
Commercial Use: Yogurts, beverages, health drinks, cosmetic items such as shampoos, soaps, creams, moisturizers etc. Scientific research and clinical trials have found it helpful in treating cancer and certain blood diseases, particularly those associated with low white blood cell counts, such as leukemia; have soothing skin and healing burns, have rashes, frostbite, and severe wounds(due to presence of chrysophanic acid); helpful in treating dandruff, acne, ringworm, gum disease . (Aloe Vera, n.d.)
4 References
- (2014, 05 08). Retrieved from NCHF: http://www.ncfh.org/docs/fs-Folk%20Medicine.pdf
- Aloe Vera. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aloe_vera
- Aloe Vera. (n.d.). Retrieved from howstuffworks: http://health.howstuffworks.com/wellness/natural-medicine/herbal-remedies/aloe-vera-herbal-remedies.htm
- Andrographis paniculata. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andrographis_paniculata
- Ayurvedic Medicine. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ayurvedic_medicine
- Ayurvedic Medicine: An Introduction. (2013, 08). Retrieved from NCCAM: http://nccam.nih.gov/health/ayurveda/introduction.htm
- Berberine. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berberine
- Berberis. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berberis
- Bhattathiry, M. (n.d.). 15 Benefits of the Holy Basil (Tulsi). Retrieved from Hinduism: http://hinduism.about.com/od/ayurveda/a/tulsibenefits.htm
- Bruno, G. (2014, 01 02). Total Health. Retrieved from Herbal Alternatives to Antibiotics: http://www.totalhealthmagazine.com/articles/herbal-medicine/herbal-alternatives-to-antibiotics.html
- CCRA. (n.d.). Ayurveda Introduction. Retrieved from CCRAS: http://www.ccras.nic.in/ayurveda/Chapter-1 Introduction.pdf
- Dr.Jayaprakash. (n.d.). Turmeric – secret ayurvedic recipes. Retrieved from dharmaayurveda: http://www.dharmaayurveda.com/article/2304.html?a
- Echinacea. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Echinacea
- Garlic. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Garlic
- Herbalism. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Herbalism
- Howstuffworks. (n.d.). Retrieved from Ginger: http://health.howstuffworks.com/wellness/natural-medicine/herbal-remedies/ginger-herbal-remedies.htm
- Jennifer Rhode, S. F. (2007). Ginger inhibits cell growth and modulates angiogenic factors in ovarian cancer cells. Retrieved from NCBI: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2241638/
- Literature Education Series On Dietary Supplements . (n.d.). Retrieved from Huntington College of Health Sciences : http://www.hchs.edu/literature/Cold Flu Sinusitus.pdf
- Nelson, N. (n.d.). 20 Antibacterial and Antiviral Herbs and How to Use Them. Retrieved from www.sustainablebabysteps.com/antiviral-herbs.html
- Palanivelu, S. M. (2011). The effect of curcumin (turmeric) on Alzheimer’s disease: An overview. Retrieved from NCBI: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781139/
- Pomegranate. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pomegranate
- Qi, D. Z. (2014). WHO. Retrieved from Traditional and Complementary Medicine: http://www.who.int/medicines/areas/traditional/definitions/en/
- Sapnonin. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saponin#Medical_uses
- Shiitake. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shiitake
- Shiitake. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shiitake
- Synopsis of Turmeric’s Healing Properties. (n.d.). Retrieved from Turmeric: http://www.turmeric.co.in/turmeric_ayurvedic_use.htm
- Tulsi. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ocimum_tenuiflorum
- Turmeric. (n.d.). Retrieved from Wikipedia: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Turmeric
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


