Green Solvent for Synthesis and Catalysis
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Chemistry |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1760 words | ✅ Published: 24 Jan 2018 |
- Adnan S/OAbdul Qayyum
- Title
Green Solvent for synthesis and catalysis: Room Temperature Ionic Liquids.
- Abstract
This proposal describes a research project to synthesis the ionic liquids; the alternative green, non-volatile solvent to harmful volatile organic solvent and chemical industries in the future. The ionic liquids, whose properties can be predicted before their synthesis. The already known properties enable to gain required result for different applications. This has versatile the range of applications of Ionic’s liquids. The properties of I.Ls are affected by a no. of factors such as lattice energy, electrostatic potential between cation and anion, charges of ions, separation between the charges, symmetry & hydrophobicity. Currently scientists are working not only on synthesis of new ionic liquids but also elevating their applications in different fields including solar cells, lubricants, green organic solvents etc. Because of significant properties attributed to these new classes of compounds, which have been classified as new compounds only a decade ago, we started studies towards the synthesis of ionic liquids. We attempted to prepare different types of ionic liquids. i) Imidazole based ionic liquids ii) Caffeine based ionic liquids.
- Introduction
“The term ionic liquid implies a material that is fluid at (or close to) ambient temperature, is colorless, has a low viscosity and is easily handled.” (Sheldon)
“Room temperature ionic liquids are generally salts of organic cations, e.g. tetraalkylammonium, tetraalkylphosphonium, N-alkylpyridinium, 1,3-dialkylimidazolium and trialkylsulfoniumcations.” (Sheldon)
“Most basic definition of a room temperature ionic liquid is a salt that has a melting point at or near room temperature.” (Handy)
“Organic salts with melting points below ambient or reaction temperature.” (Maio)
“Ionic liquid is a salt with a melting temperature below the boiling point of water.” (Wilkes)
- Ionic liquids are defined as molten salt composed entirely of ions without any neutral molecules and having low melting point (usually ~100ËšC)

The properties of the ionic liquids are mentioned below.
- Problem or Need
In this knowledge era, science has changed our world by discovering new methods to be the beneficial for human being but simultaneously it also pollutes our environment. Therefore these methods and chemicals have also become somehow harmful to the human beings. So this is how, these chemicals, which polluting our environment have become a problem for the common people. Organic solvents are widely used in the laboratory and industries, which are volatile and used in huge amounts, i.e. Solvents are the most damaging chemicals. That is why, our research project is about finding some green alternative to the most damaging solvents. The new alternative solvent will be non-volatile, less toxic, biodegradable, air and moisture stable and economically viable to large scale process.
- Objectives and Expected Significance:
We have prepared project to give alternative solution to above mention problems. After synthesizing the green non-volatile, non-toxic solvent, the pollution could be reduced to great extent. Not only this, ionic liquid may have a lot of benefits and may be used as in batteries, propellants, lubricant, storage media for toxic gases, performance additives in pigments and many more.
- Methodology
6.1. Imidazole based ionic liquids.
Room temperature ionic liquids are generally salts of organic cations, e.g. tetraalkylammonium, tetraalkylphosphonium, N-alkylpyridinium, 1, 3-dialkylimidazolium and trialkylsulfoniumcations. Imidazole has a unique property to stabilization a positive charge on nitrogen that’s why we use it as a substrate. Two nitrogens in imidazole stabilize quaternary nitrogen charge therefore the weaker the charge so it form ionic liquid which is liquid in room temperature. General reaction of imidazole based ionic liquid is
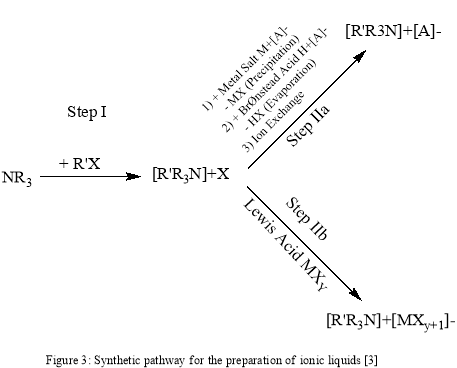
6.2. Caffeine based ionic liquids
Caffeine has been chosen due analogy of its structure with imidazole. Since five membered-ring that is fused with a six membered ring possessing amide and imide moieties, must behave like imidazole which has extensively been used in the synthesis of ionic liquids. For this reaction, first we prepared alkyl caffenium halides by treated of caffeine with different alkyl halide (i.e. methyl iodide, ethyl iodide and hexyl bromide) and taken tetrahydrofuran as a solvent, alkyl caffenium halide is obtained as a white crystals. We also tried to prepared caffeine based ILs due to its similar analogy structure with imidazole. Caffeine is relatively less expensive and is easily available in abundance. ILs become cheaper and its applications enhanced due to the use of caffeine.

It is reported in literature that Nitrogen containing heterocyclic compounds are used to generate stable carbenes, which were then used to carry out different reactions. One of such reaction is benzoin condensation that may be carried out using carbenes.
- Properties of Ionic Liquids
The properties of ionic liquid differ by the different combinations of cation and anion for particular applications. Some of the important properties of ionic liquids are: melting point, vapour pressure & thermal stability, viscosity, high heat capacity. Due to these properties ionic liquids are widely applicable, as shown in figure 2.
- Melting Point
Ionic liquids are defined as molten salt composed entirely of ions without any neutral molecules and having low melting point (usually ~100ËšC). The chemical and structural composition of an ionic liquid (molten salt) depends upon its melting point. Lowering of melting point is due to the low symmetry of cation and weak intermolecular bonding. By keeping the cation constant we can also use different anions which can affect the melting point. The melting point decreases with increase in the size of anion. [3]
- Vapour Pressure and Thermal Stability
Ionic liquid have no measureable vapour pressure due to this property it can easily separated from reaction mixture by distillation. The thermal stability of an ionic liquid is directly related to the strength of the heteroatom-carbon and heteroatom-hydrogen bonds. Ionic liquids formed from either protonation of amines or phosphanes show significantly restricted thermal stability. [3]

- Density
There is a linear relationship between the density and the N-alkyl chain of cation. The density decreased as the N-alkyl chain increased. [3]
- Viscosity
Ionic liquids are generally more viscous then the classical organic solvents. Cation shows some effect on the viscosity of the ionic liquid. Lower viscosities tend to be a result of small side chains that have sufficient mobility. As side chain increases due to vander waal forces viscosity increases. Temperature is another factor which affects the viscosity of ionic liquid. As temperature increases viscosity decreases. [3]
- Solubility Characteristics
By changing the combination of cations and anions we can tune the solubility of ionic liquid. The solubility of ionic liquid can also depends upon the nature of R group. By increasing the length of alkyl chain the hydrophobicity of the cation increases, as the result its water solubility decreases. [6]
- Solvent Properties
The most common classification used to describe a solvent is polarity of that solvent. Ionic liquids are considered as polar solvent by nature because they can dissolve and stabilize dipolar or charged solutes. [3] They have tendency to dissolve many different many other materials such as organic, inorganic and organometallic materials. [1]
Table1: Comparison of ionic liquids with organic solvents. [5]
|
Property |
Organic Solvents |
Ionic Liquids |
|
Number of solvents |
>1,000 |
>1,000,000 |
|
Applicability |
Single function |
Multifunction |
|
Catalytic ability |
Rare |
Common and tunable |
|
Chirality |
Rare |
Common and tunable |
|
Vapour pressure |
Obeys the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation |
Negligible under normal conditions |
|
Flammability |
Usually flammable |
Usually nonflammable |
|
Salvation |
Weakly solvating |
Strongly solvating |
|
Tunability |
Limited range of solvents available |
Unlimited range means ‘designer solvents’ |
|
Polarity |
Conventional polarity concepts apply |
Polarity concept questionable |
|
Cost |
Normally inexpensive |
2 to 100 times the cost of organic solvents |
|
Recyclability |
Green imperative |
Economic imperative |
- Scope of Ionic liquids
Ionic liquids are attractive, useful, advanced solvents that are a sight of attention by the renowned chemists for its unique and distinct properties. Its tunable components provide a wide range of successful and desire products.

Figure2.IL publications (on May 27, 2009) determined from the ISI Web of Science in the last fourteen years.
This is the main reason it is getting huge importance in the field of chemistry now a days. No doubt the immense research work in the field of green chemistry has been an attractive sight for the last few years. [5]By the passage of time many new cations and anions have been reported. The common cations and anions are given below
Common Anions:
BF4; B(CN)4; CH2CHBF3; CF3BF3; C2F5BF3; nC3H7BF3; nC4H9BF3; PF6; CF3CO2; CF3SO3; N(SO2CF3)2; N(COCF3)(SO2CF3); N(SO2F)2; N(CN)2;C(CN)3; SCN; SeCN; CuCl2; AlCl4; OH
Common Cations:

- Timeline
As soon as this project is funded, we import chemicals in first two months while start synthesizing with the available chemicals. Within a one year Insha’Allah, we will complete synthesis about 50 ionic liquids and also check their applications.
- Evaluation
The evaluation will be conducted by PCSIR and HEJ Research institute. This evaluation will be done under the direction of Dr. Nasir-Uddin who has much experience as a professional program evaluator. He had also done the evaluation of several large-scale governmentally funded projects. All chemists already have the experience on this research topic. Every experiment will be done under the supervision of Dr. Imran Ali Hashmi, Ph. D from German on synthetic chemistry.
- Reference Literature Cited
- A review of ionic liquids towards supercritical fluid applications
SedaKeskin, DefneKayrak-Talay, Ug˘urAkman∗, O¨ nerHortac¸su
Department of Chemical Engineering, Bo˘gazi,ci University, Bebek 34342, ˙Istanbul, Turkey
Received 2 August 2006; received in revised form 8 May 2007; accepted 29 May 2007
- Green chemistry ionic liquid –
Useful reaction solvents (TCI)
- Physical Properties of Alcohol Based Deep Eutectic Solvents
Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy by Robert Christopher Harris, University of Leicester, 2008
- Paradigm Confirmed: The First Use of ionic Liquids to Dramatically Influence the Outcome of Chemical Reactions
Organic letters, 2004, Vol. 6, no.5, 707-710
- Review on the Chemical Stabilities of Ionic Liquids
SubbiahSowmiah, VenkatesanSrinivasadesikan, Ming-Chung Tseng and Yen-Ho Chu *
Molecules 2009, 14, 3780-3813; doi: 10.3390/molecules14093780
- Ionic liquids: Innovative fluids for chemical processing
AIChE Journal Volume 47, Issue 11, pages 2384–2389, November 2001
- Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis
Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071-2083
- ACTA UniversitatisOuluensis, Johanna Kärkkäinen
Preparation and characterization of some ionic liquids and their use in the dimerization reaction of 2-methylpropene
- The Design of Polymeric Ionic Liquids for the Preparation of Functional Materials
Journal of Macromolecular Science R _, Part C: Polymer Reviews, 49:339–360, 2009
- Ionic Liquids: Current developments, potential and drawbacks for industrial applications
LenzingerBerichte, 84 (2005) 71-85
- Recent developments of task-specific ionic liquids in organic synthesis
Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews Vol. 4, No. 1, March 2011, 41_54
- Task-Specific Ionic Liquids
James H. Davis, Jr. Chemistry Letters Vol.33, No.9 (2004)
- Wohler, F. Liebig. J. Ann. Pharm. 1832, 3, 249-282
- Lapworth, A. J. J. Chem. Soc. 1903, 83, 995-1005
- Van DenBerg, H. J. J. Mol. Cat. 1943, 51, 1-12
- Suzuki et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8432-8433
- Budget
|
Price |
Quantity |
Total |
|
|
Chemicals |
200000 |
1 |
200000 |
|
H-NMR |
10000 |
50 |
500000 |
|
C13 NMR |
10000 |
50 |
500000 |
|
I.R |
1000 |
50 |
50000 |
|
ESI (+ & – ) |
1000 |
50 |
50000 |
|
MS student |
15000 |
1 year |
180000 |
|
Ph. d student |
20000 |
1 year |
240000 |
|
1,900,000 |
1 | Page
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


