Capacity Planning and Supply Chain Management
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Business |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1791 words | ✅ Published: 13 Sep 2017 |
Answer 1: CAPACITY
- Capacity planning is the ways of defining the make capacity required by an organisation meet the upcoming future limit capacity requirement for its items. Capacity planning of an operation management is the maximum level of significant value included action over a timeframe that the procedure can reach under normal operating condition. This process has many long term concerns with regards to operation management given the long term responsibilities of assets.
- Three factors that are to be taken into consideration in terms of effective capacity management and design in Call-Us Plumbing supply company:
- Facilities: the measurement and condition of work range for development are the main plan of facilities. Others facility component include like transport expense, work assets goes under area of office. The format of the work zone terms how easily function can be achieved.
- Human factor: to perform tasks which are required for specific employments in the organisation, human activities included staff preparation, ability and experience required for successful work and actual result. In this factor include the workers motivation; participation records and work cost are all influence the organisation output rate.
- External factor:
- Calculating capacity utilization rate of production
Design capacity= 5500,000
Actual capacity= 300,000
Utilization= Actual output/ Design Capacity*100
= 300,000/5500, 000*100
Utilization=5.45%
- Three capacity or production planning strategies:
- Lead strategy
- Match strategy
- Adjustment strategy
- Lead strategy: In lead strategy, which include capacity in expectation of a rise in demand. It is a forceful strategy with the objective of customers far from the organisation’s competitors by enhancing the provision level and decreasing lead time. It is also expanding the company’s capacity in hope of an increase in demand.
- Lag strategy: it is opposite of lead strategy. It is mainly focuses on increasing capacity by actual increase in the demand whereas the operation is working at complete steam.it decrease a company’s risk.
- Match strategy: In this strategy we include capacity in small addition in capacity of the changing market situation. It is lies in the middle of the above two strategy.
- Three capacity or production planning strategies to call-us plumbing:
- Lean planning: In this strategy the primary concentration is to achieving occasional demand instead of the real order and ends the waste and drag products which are popular.
- Make an order: As per as this strategy, the goods are produced in advance to the order being placed by the customer. The retail environment is the best suited example.
- Technology: Because of technology change, business will run efficient and successfully to the item the things. It helps the business to make the productive result.
Answer 2: INVENTORY
2.1 Two reasons keep a supply of inventory:
- Expecting the Unexpected: Any inventory manager is expected to overcome is changing customer demand. A business need must dependably be having the capacity to meet its consumer benefit target. It means having the capacity to supply its consumer with the goods and services they need just when they need them.
- Capitalizing on low cost offer: Since time to time producers or providers will offer great closeout and advertisement offer with very smart discounts. Bring down purchasing costs for the business expanse to lesser selling expense to consumer. This pulls in and wins over new customers, additionally offers the business a distinct aggressive edge.
2.2: Calculate the present total annual stocking cost
D= 10,000
Q= 400
H= 0.40
S= 5.50
Total Annual Stock Cost= 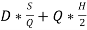
= 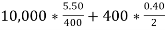
= 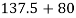
Total Annual Stock Cost = $217.5
2.3 Calculate EOQ (economic order quantity)
EOQ= 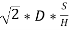
=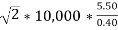
=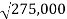
EOQ= 524.40 units.
2.4 Calculate the Total amount of stocking cost
Total cost of EOQ= Setup Cost + Holding Cost
= 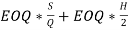
= 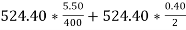
= 
Total amount of stocking cost= $112.10
2.5 The estimate savings in stocking costs
Total annual cost- Total amount of stocking costs
=217.5-112.10
=$105.4
2.6 Calculate the POQ
D= 10,000
Q= 400
D= 40
S= 5.50
C= 0.40
P= 120
POQ= 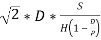
= 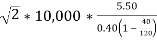
= 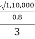
= 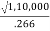
= 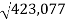
= 650.44units
2.7 Calculate total annual stocking cost
Total annual stocking cost= 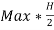
= 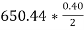
= $130.08
2.8 The estimated savings in total annual stocking cost
EOQ= 112.10
POQ= 130.08
= POQ-EOQ
= 130.08- 112.10
= $17.98
2.9 In fixed order inventory management system, the order is placed from time to time but every time of various quantities. While in variable period inventory management system, the request duration is variable and regular. The fixed amount of stock can be renewed when the stock level achieves the auto set reorder fact or the least stock level. (jargons)
2.10
- Just- in- Time: – According to this idea the products are produced and obtained just a couple of hours before they are put to utilize. This concept was evolved in Japan. The just- in- time framework is received by the organisation, to diminish the unnecessary burden of inventory management, just in case the demand is not as much as the inventory raised. For example: this production model shown has been received by Toyota creation framework (jargons)
- Kanban: it is an inventory management system where the organisation is allowed to stock the necessary parts (goods, labours) for the development and manufacture process. Example can be acknowledged with ‘push’ system which is administered with Kanban ethics.it is mainly to enhance producing productivity, for example, work in process inventory, over burdening avoiding in produce system. (Wikipedia)
2.11
Answer 3: SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
3.1 Supply chain management: The supply chain management of the movement of goods and services. It includes the capacity of raw material of work in process inventory, and of completed products from purpose of utilization. It has been defined as the design, planning, execution and control. (Kinsella, 2010)
The different process involved in the supply chain management:
- Planning
- Purchasing
- Processing
- Distribution
- Planning: it is a process of activity concerned with the essential objectives for an organisation’s instruction to achieve the objectives. To get together the objectives, managements improve the strategies for example: business plans and marketing key ideas.
- Purchasing: it is an organisation which includes the goods purchase from supplier. This purchasing activity has been finished by the finance department to make buying request records of the organization.
- Processing: it means work is in procedure on the premise of assets accessibility and association of customers’ demand. It is done the basis of material availability and sales plan.
- Distribution: in this process there should be accessibility of products in the inventory for appropriate coordination with organisation and sales.
3.2 Two reasons keep a supply of inventory:
- Expecting the Unexpected: Any inventory manager is expected to overcome is changing customer demand. A business need must dependably be having the capacity to meet its consumer benefit target. It means having the capacity to supply its consumer with the goods and services they need just when they need them.
- Capitalizing on low cost offer: Since time to time producers or providers will offer great closeout and advertisement offer with very smart discounts. Bring down purchasing costs for the business expanse to lesser selling expense to consumer. This pulls in and wins over new customers, additionally offers the business a distinct aggressive edge. (Mandy, 2015)
3.3 The six current trends in supply chain management:
- Advanced computer technology
- Outsourcing of logistics functions
- Electronic distributions
- Globalization
- Customer centric
- Product and service life cycle
- Advanced computer technology: in this trend people are more mindful about items and services of particular organisation. New elements have been presented, for example: bar coding because of this change in supply chain management coordinated effort amongst consumer and providers relations are most durable.
- Outsourcing of logistic function: this function can improve the consumer services and reduce inventories by various organization purposes. It provides same or better levels of service.
- Electronic Distribution: electronic distribution is a technique that consists of product and services that can be run electronically whether over traditional forms for example- optic cable or through satellite transmission of electronic indicators.
- Globalization: Each business get to be globalize because of communication progress. A global consumers and supply bas has significantly influenced the supply chain. That is the reason supply chain management comes to enhance the global business condition.
- Customer centric: Customer centric is a method for working with customer to become their positive feedback understanding before or after the sale keeping in mind end goal to proceed with business with trustily and benefits.
- Product and service life cycle: it refers to a procedure that supports service companies and helps them identify their gross pay potential. An organisation needs to enhance product and services life cycle to take care of up the consumer demand. For that they have to check the generation execution and monitor the service when they present their new items and services in business market.
3.4 Four supply chain strategy:
- Push Strategy: A push strategy is utilized when product is creating on the base of expected demand. It works when the lead time is long and demand is stable. For example: Canned soup.
- Pull strategy: A pull strategy works when the lead time is short and the demand is high leads to estimate wasteful. For example: Dell.
- Strategic inventory: this strategy analysis and help to deal with how much stock to carry and where. Different strategies are included to keep up the stock.
- Continuous replenishment: In this strategy, the demand is known by the organisation whereas the lead time is short. Providers discharge the shipment on a settled upon frequency to keep up the stock. All through the continuous replenishment, chain management works on push and pull at the retail outlets.
3.5 The most suitable supply chain management is active supply chain. It is most suitable for the huge majority of the company as it responds to the changing customers require and is flexible in nature. When comes to the urgent need in business then it performs more effectively towards customer. With this strategy, vendors are able to reply to the change in customers need and can ask time to supply to improve the act in business limits.
- According to the research, Woolworth is the successful company in New Zealand.
- The performance of the company in terms of supply chain management is highly effective and efficient. All the demands of the supply chain management are estimate according to the creating evaluation of the customer demand. As far as of capacity, the company is highly capable of completing the creation rate and take care of customer demand.
- Call-us plumbing supply helps to manage the plumbing supply business and works according to the demand of the customer. To manage and improve its performance, company is needed to concentrate on the EOQ model to decrease the total holding cost and order costs. The raw material should keep in stock for production base on demand and holding inventories which help to give the goods to consumer according to requirement in time.
References
jargons, B. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://businessjargons.com/just-in-time-system.html#ixzz4bpJERGGG
jargons, B. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://businessjargons.com/fixed-order-quantity.html#ixzz4bpAtA27x
Kinsella, J. (2010). Retrieved from https://www.oxbridgenotes.co.uk/revision_notes/management-university-of-exeter-operations-management/samples/operations-management-supply-chain-planning-and-control-1
Mandy. (2015, October 19). Retrieved from https://www.unleashedsoftware.com/blog/4-very-good-reasons-to-hold-inventory
Wikipedia. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kanban
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


