Methods of Studying the Brain
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Biology |
| ✅ Wordcount: 3559 words | ✅ Published: 12 Jun 2018 |
History of brain treatments
Trepanning is a surgical procedure where a hold is drilled into the skull using a surgical tool, in the 17th and 19th century. The process involved drilling into the skull and removing a piece of bone. In ancient times trepanning was done as a tribal ritual to let evil spirts ‘escape’ out of the head. It was performed to cure, headaches, and many mental illness for instance; Huntington’s, Parkinson, schizophrenia and epilepsy.
Lobotomy is a surgical procedure in which the nerve pathways in a lobes of the brain are severed from those in other areas. The procedure was used as a radical therapeutic measure distributed patients, who had mental illnesses.
Moreover, lobotomy was used in mental institutions where the patients wouldn’t understand and known it is been done. (ETHICS)
Also, the patients would often could out of the procedure with black eyes from the surgery and they would be given darken glasses to cover up the bruising ( ETHICS)
A few years later Thorine a chemical lobotomy was designed which was better as there wasn’t a risk of surgery. 2,900 lobotomies were performed. The last one to be performed was in 1967 due to the patient dying of brain haemorrhage.
EEG stands for electroencephalogram which is a recording of the brains activity. Small sensors are attached to the scalp to pick up the electrical signals produced when brain cells send message to each other. Helped to monitoring and diagnosing conditions affecting the brain.
Invasive methods
Invasive methods are a therapeutic technique that involves breaking the skin. It involves the injection or a placement of a device into the body. Invasive pain management therapies have been used to treat neck and back pain. Invasive methods are done by open surgery or laroscopy.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Increase safety – less trauma to the body and far less blood loss |
Can be time consuming for patient and surgeon |
|
Less scaring – only takes about two stitches to close the womb |
Long recover, some patient might be lucky to start to feel recovered by 6 to 8 weeks but others longer. |
|
You don’t have to stay in hospital very long – most patients get discharged within 24 hours. |
At very high risk of infection |
|
More accurate |
As well as find other damaged areas you might damage that area more or even they might have done the damage. |
|
When doing the surgery you may find other damaged areas and be able to remove or treat it. |
Very expensive |
Non – invasive
Non-invasive is a therapeutic technique which doesn’t involve invading or breaking the skin. Therefore, the produce does not involve tools that can beak the skin or physically enter the body. For example; x-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ECG. Until recent years, exploratory surgery was routinely performed when a patient was critically ill and the source of illness wasn’t known.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
The patient undergo less stress as no time for healing or been under general anaesthetic. |
Some of the scanning can be harmful to the body ad involves radiation |
|
Less time consuming |
Might not see if it damages any other area or if there is any other disease or damage to the brain. |
|
Very quick recovery |
Might not always be an opinion, the surgeon might offer Invasive first |
|
Reduced risk of infection |
Some of the scans may stimulate other parts of the brain |
|
Cheaper |
MRI scanner
X-RAY machine
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep stimulation is a surgical procedure (invasive technique) which is performed under local anaesthetic. It is perform in this situation so that the patient can talk and have brain movement to say the procedure has worked.
Deep stimulation is the main type of surgery used to treat Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s is not cure able however; it may help to control the movement of the symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation involved very fine wires with electrodes at the tip of the brain, which send electrical impulse to the targeted part of the brain. These are connected to extensions that are tunneled under the skin behind the ear and down the neck. They are connected to a pulse generator, which is placed under the skin around the chest.
With Deep Brain Stimulation treating disease of mental health, some people not understand what is mean done and therefore their careers give permission for it to be done and this isn’t technical right the patient themselves hasn’t full agreed to it. Furthermore, the patient isn’t de-brief before the surgery to make sure they full understand what the procedure is and this is all unethical to society.
|
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|
Very accurate |
Increase risk of infection. The implantation of foreign objects entering then body. |
|
Good technique |
Additional surgery may be needed is any of the equipment stops working. Sometimes every 3 to 5 years. |
|
Minimal opening to brain |
Time consuming |
|
Effective techniquie |
Devices which are inserted into the body can sometimes interfere with other devices. |
|
No damage to the brain during the surgery |
Sometimes uncomfortable sensations during stimulation can occur. |
Lesion Production
Brain Lesions can be caused by injury, infection, and problems with immune system. There cause is still unknown. There are several of types and some of the effects can cause great harm to you whereas, some are harmless. In lesions, nerve cells die, leaving behind damages areas of the brain. Then after time the brain function in those parts of the brain decrease. Disease such as; Parkinson’s, huntingsons’ Alzheimer’s and some types of dementia are a group of brain lesions. Some drug additions can be linked to lesions.
Symptoms of a brain lesion vary depending on the type, location and size of the lesion. Symptoms include;
- Headache
- Nauseas
- Change of vision
- Memory loss
- Seizures
- Fever
There are different types of Brain lesions. For instance abscesses and Alzheimer’s and other dementias.
Abscesses are areas of infection, including inflamed tissue. This isn’t a common however, they’re life threating. Brain abscesses often occur after an infection. Moreover, it can also appear after an injury or surgery.
Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias – these are another group of brain lesions. In these lesion, the nerve cells die which leaves behind damaged areas to the brain. then
Problems which can occur from brain Lesions are:
- Mood changes
- Personality changes
- Behaviour can change
- Mental ability can change
- A loss of memory
- Having pain in joints and having difficulty to move
Producing lesion is purposely destroying an area on the brain to research and investigate specific areas of the brain. From this you can see exactly which parts do which function.
There are three ways to make an lesion.
- Chemically – to destroy the neurons
- Electrical current – to also destroy the neurons
- Surgically – This involves cutting a part of the brain
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
The whole of the brain been analysed at once therefore a lot of information and research can be gathered. |
Involves surgery – cutting into patients brain could be a lot of blood loss. |
|
The removal of lesion can decrease or even stop seizures |
Recovery could take away |
|
Can look at the size of the lesion and see the damage cause for instance Wernicke’s or Broca’s |
The surgery could cause stress for the patient |
|
Increase risk of infection due to the recovery time and its surgery |
|
|
Removal of a lesion can cause damage in the brain e.g Werneck’s or Broca’s- language and speech centres. |
Carbon nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes are tubes which have a very small diameter for example it can be as small as one nanometer. This is a very new invention and scientists are hoping to build tiny transistors for computer chips and other electronic devices. Each day carbon nanotubes have more research on and so they are very new.
Carbon nanotubes are electrodes which are surrounded by carbon atoms in the shape of a coil. They are really thin! Thinner than a piece of hair.
Nanotechnology is used often as it has a lot of uses. For example; sunscreens, self cleaning glass and clothes with UV protection.
Uses for nanotubes are
- Brain tumour research
- Possibility of using the nanotubes to directly deliver cancer fighting drugs into the brain
- Medical uses for instance; bone scaffolding and cell therapy. This is achieved by drugs or silencing genes
- Carbon nanotubes recently used to control the damage caused by a stroke, dental implants or synthetic muscles.
Ethnics on carbon nanotubes is it is still experimental and we don’t know how it will effect individuals in the long term. It’s still be researched and developed.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Many sectors e.g medical, energy and manufacturing benefit from it |
Newer technology therefore, not much testing been done. |
|
New possible cancer therapy |
Can be difficult to work with |
|
Lots of information on neurones and their responses. |
Very small and can be very expensive to produce. |
|
Future treatments of neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s and strokes |
So far it is only been used in experiments so no long term effects seen |
|
We as humans are carbon based. |
Nobody knows how it will react to the body, will it be compatible |
|
Surgery will still be required and therefore, surgical; risks attached. |
Stereotaxic surgery
Stereotaxic surgery is also called stereotactic. It is brain surgery where a brain tumour is removed with using image if the brain to guild the surgeon to a target within the brain. Neuro-navigation is a technique which may have an external frame attached to the head or imaging markers attached to the scalp to orient the surgeon in his approach. The term stereotactic came from Greek and Latin roots which meant ‘touch in space’.
Stereotaxic surgery is used for many reasons, which include:
- Brain tumors
- Deep Brain Stimulates
- Monitoring activity of brain for instance; scanning
- Monitoring and treating Parkinson’s
Side effects for stereotaxic is that is have very few immediate effects than the normal radiosurgery, as the area being treated is smaller. However, you are likely to have hair loss, feel sick, feel fatigue, dizzy, have headaches or have rashes appear on your skin. These are common side effects of regular external radiotherapy to the brain. Doctor’s normal give does of steroid before the treatment or straight after to help prevent side effects due to swelling in the brain.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
No cutting is involved in |
Could stimulate wrong area of brain therefore different behavior would be seen |
|
Lots of research taking place |
Could damage the brain |
|
Used in Parkinson’s treatment |
Bleeding could be caused |
Function Magnetic Resonance Imaging (FMRI)
FMRI is a technique for measuring the metabolic changes that occur in brain activity. It uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves frequency pulses to produce detailed pictures of soft tissues, bone and other internal body structure. It works by detecting the change in blood oxygenation and flow that occur in response to neural activity. When an area is more active it consumes more oxygen and to meet this increased demand blood flow increase to the active area.
It can be used to examine the brain’s anatomy, determines which part of the brain are handling critical functions, evaluate the effect of stroke or disease. FMRI is the only technique which can detect abnormalities within the brain.
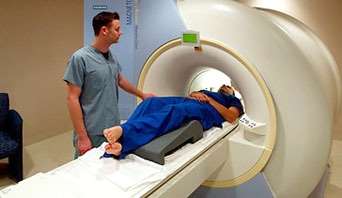
This is a picture of an FMRI scanner, which is a large tube that contains powerful magnets. You lie inside the tube straight and as still as possible during the scan.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Does not use radiation |
Scanners usually expensive |
|
Has no visual risks |
Person needs to be completely still for it to capture a clear image |
|
Evaluate brain function safely and effectively |
Researchers still don’t completely understand how it works. |
|
fMRI is easy to use |
People are in an enclosed space, so people who are claustrophobic are faced with problems with MRI to be done. |
|
MRI scan can provide information about the blood circulation |
The scan involves really loud noises while processing because they involve a really high amount of electric current supple |
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
MEG measures ongoing brain activity with millisecond time resolution. It works by detecting magnetic fields which are created by the brain’s electrical signals. MEG is used for finding out about diseases such as; Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. But also is used for research to measure the time course of brain activity and can detect epilepsy, as well as detect areas of the brain that are most important to avoid during surgery.
MEG has to be carried out in a shielded room often in the night when there are no other electrical devices on. This is because the fields are a billion times smaller than the earth’s magnetic field. The patient will sit inside a helmet of special sensors that detect the tiny magnetic signals produced by the brain, as shown below;
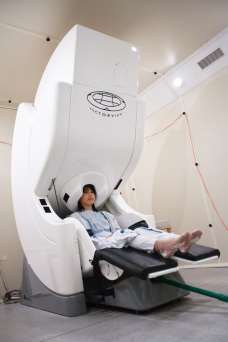
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Makes no noise |
Time consuming takes 2 hours to be performed. |
|
No discomfort for patient |
Needs a special magnetically shield room |
|
Detects areas of normal and abnormal activity in the brain. |
Used to compliment other imaging techniques |
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
TMS is a magnetic method used to stimulate small regions of the brain. During the procedure, a magnetic field generator, or ‘coil’, is placed near the head of the person receiving the treatment. The stimulation take approximately around 20 to 30 minutes. While receiving the stimulations, the patient is normally fully awake, no anaesthetic needed. There are minimal side effects.
TSM is used to treat depression, pain relief, feeling of euphoria of fear and patient who do not response well to antidepressant medication.
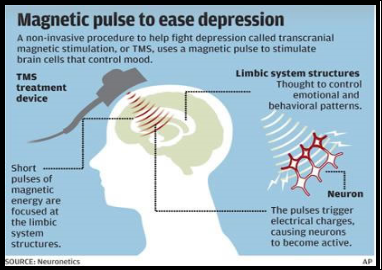
The procedure is associated with mild and minimal side effects, including:
- feelings of light headedness
- temporary hearing problems, due to the sometimes loud magnet noise
- mild headaches
- tingling in the face, jaw, or scalp
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Non- invasive |
Could damage normal brain function |
|
No anaesthetic needed |
Magnetic items must not be worm |
|
Widely available |
Ethics
Informed Consent – disclosure of all significant risks, both those known and those suspected possible.
Potential Benefit must outweigh risk
Equal distribution of risk – Particularly vulnerable patient populations should be avoided.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
PET stands for positron emission tomography. PET scans are images which can clearly show the part of the body which being investigated which could consist of abnormal areas of the body or brain and can highlight how well certain areas of the body are functioning.
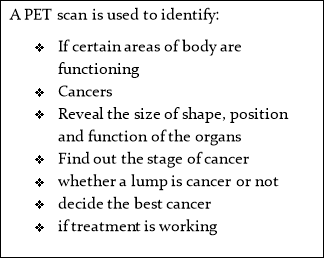
A PET scan works by detecting radiation inside the body, and images are made my passing x-rays through the patient’s body. Radioactive substances are injected into the body. The level of radiation is very small and the radioactive substance has a short decay time and neither of these will damage your body. A PET scan is pain free, and you should are able to return home on the same day without any side effects or restriction function adequately. Scans usually take around 30-60 minutes.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Detect and monitor cancerous growths |
Very expensive |
|
Makes sure functions in the body are working. |
Not widely available only certain hospitals have them in the UK, and you might have to travel a distance to get one. |
|
PET imaging is able to be used as an alternative to biopsy and other exploratory surgeries to determine how much a disease has spread. |
Not as clear as CT or fMRI scans |
|
Reduce the number of unnecessary surgeries performed due to incorrect diagnosis and staging data. |
Tumour growth and inflammation of brain areas are difficult to tell apart. |

Stem Cells
Stem cells are a class of undistinguishable cells that are able to differentiate into specialised cell types. It is most like that stem cells come from two main sources, for example:
- Embryos (embryonic stem cells)
- adult stem cells
Stem cells are unspecialised cells which are restarting themselves through cell division and have the potential to develop into many different cell types which plays a central role in generation and for the generation to come of the body. Stem cells act as an internal repair system, dividing to replace other cells which are lost through wear and tear. Each time a stem cell divides, each new cell may either remain a stem cell or become another type of cell with a more specialised function for example; bone or muscle cells.
Stem cells can give growth to any tissue in the body and, from this it can provide nearly limitless potential for medical applications. Current studies are researching how stem cells may be used to prevent or even cure disease e.g Parkinson’s, diabetes, heart disease and even Alzheimer’s
|
ADVANTAGES |
DISADVANTAGES |
|
Medical benefits for example; therapeutic cloning gets treat chronic illnesses. |
Embryos that are not a patient’s own and the patient’s body may reject them. |
|
Provide an insight to the growth and development of human cells as the understanding of everything about human cells, scientists and researchers would also have a better understanding of disease, and how it comes and what damages the cells which leads them to illness. |
Difficult to find and extract from tissue |
|
Can replace faulty cells with healthy cells, so the individual is well again |
Adult stem cells only produce a few types of cells |
|
No embryo is destroyed so not an ethical issue |
Ethical implications
Embryonic stem cell research poses a moral dilemma. It forces us to choose between two moral principles:
- The duty to prevent suffering
- The duty to respect the value of human life
In the case of embryonic stem cell research, it is impossible to respect both moral principles. To obtain embryonic stem cells, the early embryo has to be destroyed. This means destroying a potential human life. But embryonic stem cell research could lead to the discovery of new medical treatments that would stop the suffering of many people.
There is two issues of stem cells, one that we highly value the duty to prevent suffering and the other the duty to respect the value of human life. A potential humans life is a risk of life or not. It is more ethical to take stem cells from a bone borrow of an individual to help saves someone’s life as to do so it needs constant from the individual for the bone borrow to be given. Whereas, a less ethical view is were a stem cell could be taken from a embolic cord where the mother of the child may have given constant and mean it can go ahead however, the baby might not have wanted that therefore this is morally wrong.
Foetal Brain-tissue Grafting
A method of treating diseases, such as; parkingsons and huntingtons by grafting brain cells from human foetuses onto the affected area of the human brain. Human adults cannot grow new brain cells however, developing unborn foetuses can, this is because, grafting foetal tissue stimulates the growth of new brain cells in affected adult brains.
Use of foetal brain tissue is consequent from aborted embryos or foetuses. The ethical issues related to a therapeutic approach, which is relevantly modern and therefore not only concern the possible side effects for a graft-receiving patient, but also the relationship between the requirements for foetal tissue and the decision-making process for induced abortion.
Although for human embryos and foetuses have been the subject of biomedical studies, and, in principle, their use has therefore not been seen as ethically objectionable, the above points made it necessary to reconsider the moral issues.
Bibliography
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02700424
http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Fetal+tissue+transplantation
History of brain treatments
A good website to go on to first, as it gave an over view of the different methods but also different times e.g the Hippocrates and how life was like for treating the brain then.
https://www.britannica.com/topic/lobotomy
lobotomy surgery and how it is done and why it is done.
http://www.ancient.eu/Trephination/ –
Brothwell, D, Diseases in Antiquity (Charles C Thomas Pub Ltd, 1967).
http://www.imaginis.com/faq/what-does-non-invasive-mean
Invasive and non-invasive
http://www.frca.co.uk/article.aspx?articleid=252
Very good website to start on however no pros or cons one it.
http://internationaljournalofcaringsciences.org/docs/Vol1_Issue3_02_Lavdaniti.pdf
History on the technique
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/304235-overview
Good over view and background information
Deep Brain Stimulation
https://www.parkinsons.org.uk/content/deep-brain-stimulation-surgery-parkinsons
how deep stimulation is used to treat Parkinson’s.
This website explains how deep stimulation can cure certain things and what disorders it helps to cure.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WW-SWAnphFU
video of the deep stimulation back ground information and how it was performed
http://videos.howstuffworks.com/sciencentral/2937-deep-brain-stimulation-video.htm
Another video of how it works and what its done.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25597042
good for information on ethics for DBS. Clearly layout and simple to understand
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12152-015-9240-9
very very complex site and not good for getting information.
http://www.webmd.com/brain/brain-lesions-causes-symptoms-treatments
Lesion Production
http://www.webmd.com/brain/brain-lesions-causes-symptoms-treatments
http://www.emedicinehealth.com/brain_lesions_lesions_on_the_brain/page10_em.htm
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal