Barleria Prionitis Linn
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Sciences |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1687 words | ✅ Published: 10 Apr 2018 |
Barleria prionitis Linn
Vernacular names
English- common yellow nailo dye plant
Ayurveda Kuruntaka, kurunta, sahachara, vajradanti
Unani Piyaabaansaa
Tamil or siddha: chemmulli
Biological source: It consist of dried whole plant of Barleria prionitis Linn (Acanthaceae)
Geographical source: It found throughout the hotter parts of India. It commonly grown as ornamental plants in gardens
Cultivation
The shrubs prefer a sunny situation on wide variety of well-drained moist soil. They tolerate temperatures only above at least 1°C. It best grows with average annual rainfall between 750-900 mm. The seeds are very light in weight containing 33,000 seeds/kg. Seedlings grow slowly at first i.e. germinated between 13 and 77 days following sowing. However, an established plant grows fast. These shrubs flower from September to December and fruit from January to April.and can be harvested for four years. Natural regeneration generally occurs within 1 or 2 m of the parent plant.
 Description
Description
It is evergreen, is a tender, erect, branching, evergreen shrub with spiny stem nodes, elliptic to oblong, mid-green leaves, and spikes of tubular, yellow to yellow-orange flowers in summer.is a tender, erect, branching, evergreen shrub with spiny stem nodes, elliptic to oblong, mid-green leaves, and spikes of tubular, yellow to yellow-orange flowers in summer.is a tender, erect, branching, evergreen shrub bushy shrub grows up to 1-2 m with spiny stem nodes, elliptic to oblong, mid-green leaves, 6 to 12 centimeters long, narrowed, and pointed at both ends. Flowers are yellow and axillary, with the upper ones in spikes. Bracts and calyx are green, with the outer bract usually foliaceous. Corolla is about 4 centimeters long, flowers in summer.
The stems are terete, glabrous, much branched with cylindrical and tapering branchlet Leaves are smooth, opposite, ovate-elliptic to obovate, acuminate, tapering to base, entire, margin finely ciliate, bristle-tipped and about 6-15 cm long and 4-6 cm wide. The petioles are about 0.5-3 cm long, widely spreading spines present in axils.
The flowers are sessile, yellow in colour and often solitary in lower axils and spictate in the upper axils. Bracts are acute, linear-lanceolate, foliaceous, about 1-1.5 cm long and 0.2-0.8 cm wide with bristle tipped. The corolla is bright, golden yellow in colour with pubescent outside and glabrous inside and about 1.5 cm long. The filaments are hairy and about 2-2.5 cm long, yellowish in colour with 3mm long yellow anthers. The ovary is ovoid and sigma is long, linear, sticky and pinkish in colour.
The fruit is ovoid capsule containing 2 seeds. It is about 1.5-2 cm long and 0.6-0.8 cm wide. The seeds are oval-oblong, covered with silky copper-brown appressed hairs and measuring about 7.4-8.5×6-6.8 mm.
Roots are central tap type, with lateral roots branching in all directions.
Ayurvedic Properties
Rasa – Madhura, Tikta
Guna – Snigdha
Virya – Usna
Vipaka – Katu
Karma – Kaphahara, Keya, Kãsa, Ranjana, Visahara.
Chemical constituents
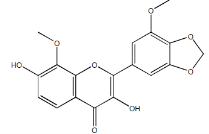
B. prionitis shows presence of glycosides, saponins, flavonoids, steroids and tannins
- Glycosides like prioniside A, prioniside B, prioniside, barlerinoside, verbascoside, shanzhiside methyl ester
- Saponins- lupulinoside, luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucoside
- Flavonoids – apigenin 7-O-glucoside, 6-hydroxyflavones
- Phenolic acid – melilotic acid, syringic acid, vanillic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid
It also sowed the presence of triterpenoids and steroids such as lupeol and B-sitosterol. Bark consist of 16% tannins and ellagic acid
Standards
Foreign matter Not more than 2%
Total ash Not more than 7%
Acid-insoluble ash Not more than 1%
Alcohol-soluble extractive Not less than 4%
Water-soluble extractive Not less than 10%
Uses
Charaka recommended leaf paste as an ingredient of hot poultices and steam bath in the treatment of stiffness of limbs, enlargement of scrotum, sciatica and erysipelas.
Sushruta prescribed flowers internally in migraine, internal abscesses, oedema, haemoptysis. urethral discharges, seminal disorders and also to reduce obesity.
The herb’s extract in oil was prescribed for massage in arthritis and gout
Traditionally the plant parts has recommended in different health aliments
Leaves: leaf juice in diarrhoea,
The leaves of Barleria prionitis can be crushed and applied on wounds, boils and in joints for relief. It also reduces swelling.
Crushed leaves can also be applied on the scalp to fight fungal growth and promote hair growth
Leaves and flowering tops are recommended as diuretics and in urinary infection
Fruit : Fruit as bitter, acrid, anthelmintic, haemolytic; also prescribed in gingivitis as expectorant.
Seed : Seed powder were used as emetic and expectorant.
Bark: Bark as astringent, useful in diarrhea and blennorrhoea. It is also used against whooping cough and expectorant.
Roots: Roots are utilized in bleeding gums, loose teeth, dental cavities and sensitive teeth. Decoction of Barleria prionitis root for treatment of viral fevers.
The Ayurvedic pharmacopoeia of India recommended it in goiter and psychological disorder.
The whole plant is antiseptic, diuretic and applied ovver boils and glandular swelling.
Pharmacological uses
- It exhibited following pharmacological effects as
- Antimicrobial activity over a wide pathological microorganism.
- Iridoid glycoside shown to have potent antiviral property
- Whole plant extracts posses anthelmintic activity in in vitro studies.
- The Iridoid glycoside present in roots shown reduced spermatogenesis in male albino rats
- The areal parts of plant shown to posses strong antioxidant hepatoprotective, antidiabetic and cytoprotective ability in experimental animals
- The plant also exhibited strong anti-inflammatory, anti-arthritic, analgesic and diuretic property
Marketed formulation
Vicco vajradanti tooth powder
Sahacharadi Taila – Gururaja Ayurvedic Pharma (Visveshwara Nagar, Mysuru, Karnataka)
Centratherum anthelminticum/ kalijiri
Synonyms: Ayurvedic names:Aranya jiraka, vanjiraka, arjiri, somaraaji
English names: Purple Flea-bane, Achemes
Unani name: Kamoon barri, siddha/ tamil: kaattu seerakam
Biological source: it consists of dried fruit/ seeds of centratherum anthelminticum Kuntze. (Vernonia anthelmintica Wild.) family: asteraceae
 Geographic source:
Geographic source:
Discription
It is widely used as a preparation in the Ayurvedic system of medicine preparations and is distributed widely in India, even to the heights of 5500 ft. Certain other plants such as Nigella sativa and Bunium persicum Boiss are also known as kalajiri or black cumin in India, but even than these three species are still called black cumin or kalajiri.
It is a roubust branched glandular-pubiscent annual plant reaches up to the highet of 2-3 ft.
Leaves: 3-8 in. membranous, lanceolate or ovate-lanceolate, coarsely serrate.
Flower: purplish tips with linear involucral bract of ½ to ¼ inch diameter.
Ayurvedic description
Rasa- katu; tikta
Guna: Laghu, tikshna,
Veerya- ushna
Vipak- katu
Chemistry:
Sterols, avenasterol and vernosterol, a bitter principle, essential oil, resins and fixed oil consisting of myristic, palmitic, stearic, oleic, linoleic and vernolic acids
The two novel compounds a flavone glycoside and 8,5′-dimethoxy 3′,4′- methylenedioxy 3,7-dihydroxy flavones has been isolated. It also shown the presence of pentacyclic hederagenin triterpenoids such as hederagenin (3-O-[β-Dglucopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl]-28-O-[β-D-glucuronopyranosyl-(1→4)-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→3)-β-Dglucopyranosyl]-hederagenin).
 It also showed the presence of stigasterols and sitosterols. Additionally seed oil shown the presence of unsaturated and saturated fatty acids and little amount of proteins.
It also showed the presence of stigasterols and sitosterols. Additionally seed oil shown the presence of unsaturated and saturated fatty acids and little amount of proteins.

Flavone glycoside – 8,5′-dimethoxy 3′,4′- methylenedioxy 3,7-dihydroxy flavones
The centratherin and germacranolide are present in seeds and leaves.
Standards
Foreign matter Not more than 2.0 per cent,
Total Ash Not more than 7.5 per cent,
Acid-insoluble ash Not more than 4.5 per cent,
Alcohol-soluble extractive Not less than 20 per cent,
Water-soluble extractive Not less than 14 per cent,
Uses:
Pharmacological uses:
- Seed alcohol extracts has analgesic, antipyretic and diuretic activity
- Moderately polar extracts of seed exhibited antifilarial property against S. cervi and S. digitata.
- Seeds extracts found as effective antihelmintic agent in vitro and in vivo studies
- Plant shown to posses antihyperglycemic activity due to polyphenolic content.
- Plant reported to posses antimicrobial property.
- Clinical studies validates the ised of the drug in skin diseases.
- The drug exhibited smooth mscle relaxant and hypotensive activity in animals
Traditional uses
- Kapha vat shamak; sathahar, badana sthapan, krimighan. Kustaghan, dipan, vaman karak, rakt sodhak, jwaraghana
- Traditionally medicine used for fever, cough and as general tonic.
- It is also used for anthelmintic, diuretic, digestive and febrifugal property.
- It also known to be effective in kidney disorder.
- Seeds are used as anthemintic, tonic, stomachic and diuretic.
Dose: 1-3 gm of seeds and 25-30 ml of infusion
Marketed formulation
Gastrex tablet– Ban lab (P) Ltd India (Kalawad Road, Rajkot, Gujarat)
Kani capsules – Vignesh pharma ( Yousufguda, Hyderabad, A.P.)
Madhumardan Tablets – Jain Ayurved pharmacy (Siddiamber Bazar, Hyderabad)
Indian bay leaf/ tamal patra
History There are different beliefs associated with the bay leaf. Some people belonging to the Elizabethan era believed that pinning bay leaves to one’s pillow on the eve of Saint Valentine’s Day can help them see their future spouse in their dreams.
Synonyms- Punnai ilai (Tamil), Karuvaela (Malayalam), Masala Aku (Telugu), Tamal patra (Marathi), Tej pata (Bengali), Tamal patr (Gujarati), Tejpatra (Oriya), Tejpata, Tezpatta (Punjabi), Tez pat (Urdu) Tej patta (Hindi), Bay Leaf (English) Biological source-
It consist of dried leafs of plant Cinnamomum tamala belonging to family Louraceae.
 Cultivation and collection
Cultivation and collection
It is a small to moderately sized ever green tree. Plants are raised from seeds sown in nursery beds in March-April. Seedlings are transplanted to the field in rows of 2 m apart with a spacing of 3 – 3.5 m between plants. Leaves are collected in dry weather every year from vigourous plants, dried in the sun and tied up into bundles for marketing. Flowers are tiny, greenish yellow, insignificant. The plant produces flowers in last week of March or first week of April commonly pollinated by insects such as honey bees. After pollination it converts to drupe fruit and takes at least one year for maturity. Today, Indian bay-leaves are a spice used almost exclusively in the kitchens of Northern India, especially in the famous Moghul cuisine that was developed at the Imperial courts in Delhi and Agra.
Plant description
It is a perennial or small evergreen tree, attaining 8 – 12 meters height and a girth of 150
cm.
- Stem rough with gray – brown, soft wrinkled bark which produces mucilage.
 The leaves are large, 12 – 20 cm long and 5 – 8 cm broad, ovate – lanceolate, thick leathery, acuminate, coriaceous, glabrous, shining green above and glaucous beneath, opposite, sub- opposite or alternate and short stalked; the midrib dividing some distance above the base into 3 longitudinal nerves, joined by distinct reticulate veins. Petiole slender, 0.8 – 1.8 cm long.
The leaves are large, 12 – 20 cm long and 5 – 8 cm broad, ovate – lanceolate, thick leathery, acuminate, coriaceous, glabrous, shining green above and glaucous beneath, opposite, sub- opposite or alternate and short stalked; the midrib dividing some distance above the base into 3 longitudinal nerves, joined by distinct reticulate veins. Petiole slender, 0.8 – 1.8 cm long.- It has bisexual flowers, but on the same plant (monoecious). Flowers whitish, numerous, small, in axillary cymes and terminal pubescent panicles, pedicels are as long as calyx.
- The fruit is an ellipsoidal drupe. Ripe fruits are dark purple in color and contain single seed.
Ayurvedic properties
Rasa : Madhura, Katu
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


