Large Scale Milk Power Production
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Organisations |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1824 words | ✅ Published: 02 Aug 2018 |
Introduction
Milk powder production is a very simple process. But now it become on a large scale. It involves the gentle removal of water at the lowest possible cost under hard health conditions. But while this process we want to retain all the desirable natural properties of the milk such as color, flavor, solubility, nutritional value.
There are two types of milk.
- Whole milk (full cream)- typically about 87% water
- Skim milk-about 91% water
During milk powder production, this water is removed by boiling the milk under reduced pressure and low temperature. This special process is known as evaporation. The result is concentrated milk. Then it sprayed in a fine mist into hot air to remove further moisture and then give a powder.
Approximately 13 kg of whole milk powder (WMP) or 9 kg of skim milk powder (SMP) can be made from 100 L of whole milk.
Demand
Demand of powdered milk is being increased according to the rate of the population growth of Sri Lanka. The calculated requirement of milk powder in 2015 is 91156730.43kg, shown in table 1.
Table 1 – Estimated Requirement of milk powder 2010-2015
|
Year |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
|
Population (million) |
20.653 |
20.869 |
20.328 |
20.483 |
20.646 |
20.812 |
|
Recommended Dietary Allowance (ml/.person/day) |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
Requirement of Milk (million liters) |
753.834 |
761.719 |
741.972 |
747.630 |
753.611 |
759.639 |
|
Requirement of Milk Powder (million kg) |
90.460 |
91.406 |
89.037 |
89.716 |
90.433 |
91.157 |
World Bank. Population. Retrieved from http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL
World Bank. Population growth (annual %). Retrieved from http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.GROW
Ministry of Livestock and Rural Community Department. (2010). Diary Development Project. Retrieved from http://www.livestock.gov.lk/site/images/stories/dairy_deve.project_rev_150_last.pdf
Supply
Total supply of milk powder is fulfilled by local productions and imports. As local production of milk powder in the first half of 2014 has increased 65% than 2013, the amount of imported milk powder decreases 10% to 32,500 metric tons in the first half of 2014.
Central Bank of Sri Lanka. (2013). Annual Report. (ISBN 978-955-575-288-6). Retrieved from http://www.cbsl.gov.lk/
Figure 1 – Production and Imports of milk powder 1998-2010
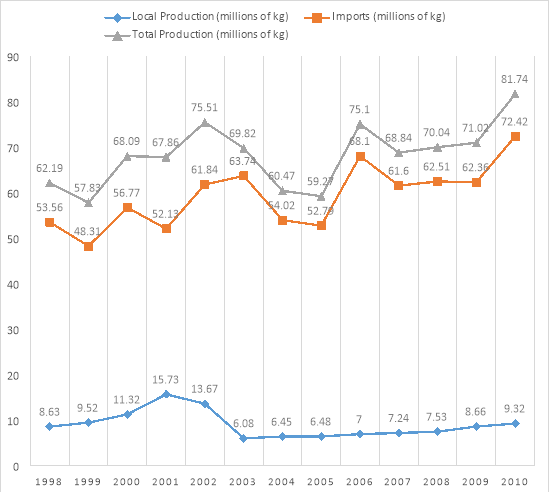
Agriculture and Environmental Statistics Division. Milk Production. Retrieved from http://www.statistics.gov.lk/agriculture/Livestock/MilkProduction.html
Total supply of milk powder can be calculated by using milk powder consumption and population. Local production of milk powder is estimated by using annual imports and total production. Estimated total production of milk powder will be increased by about 1.8% to 86.97 million kilograms by the 2015. Imports were reduced due to investigation of DCD and melamine in imported milk powder from New Zealand and duty taxes. Local productions are being improving about 65% during 2013 and 2014 and estimated local production of 2015 is 25.22 million kilograms, shown in table 2.
Table 2 – Estimated Milk Production 2013-2015
|
Year |
Unit |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
|
Milk Powder Consumption |
average month per person |
341.36g |
344.77g |
348.22g |
|
Total Production |
Million.kg |
83.91 |
85.42 |
86.97 |
|
Imports |
Million.kg |
71.5 |
65 |
61.75 |
|
Local Production |
Million.kg |
12.41 |
20.42 |
25.22 |
Department of Census and Statistics. (2012/13). Household Income and Expenditure Survey. (ISBN978-955-577-856-5). Retrieved from www.statistics.gov.lk
Figure 2 – Forecasting of Production and Imports of milk powder 2015

Forecast
About 91.16 million kilograms of milk powder will be required to satisfy the demand of 2015, but 86.97 million kilograms of milk powder will be supplied by present industries and imports. The estimated gap of 4.19 million kilograms of milk powder should be produced by Sri Lankan fresh milk supply.


 Figure 3 – Annual Milk Production
Figure 3 – Annual Milk Production
Agriculture and Environmental Statistics Division. Milk Production. Retrieved from http://www.statistics.gov.lk/agriculture/Livestock/MilkProduction.html
Estimated fresh milk production of year 2015 will be 309.28 million litres, shown in figure 3. If all fresh milk converted into milk powder, 37.11 million kilograms of milk powder will be produced.
Table 3 – Estimated Production of Milk Powder from Sri Lankan Milk Supply 2015
|
Estimated Demand |
91.16 million kg |
|
Estimated Imports |
61.75 million kg |
|
Required Local Production |
29.41 million kg |
|
Estimated Fresh Milk Production |
309.28 mllion l |
|
Feasible Milk Powder Production |
37.11 million kg |
The fresh milk supply of Sri Lanka is well enough for fulfil required local milk powder production of 29.75 million kilograms of 2015. Therefore milk powder production is a feasible industry for Sri Lanka.
PROCESS
There are five main unit operations.
- Separation
- Preheating
- Evaporation
- Spray Drying
- Packaging and Storage
SEPARATION
This is the first step of milk powder production. Milk powder manufacturing is starts with taking the raw milk to dairy factory. Then pasteurize them. There is a machine called centrifugal cream separator. It use to separate raw milk into skim milk and whole milk.
When whole milk powder is to be manufactured, a portion of this whole milk powder is added back to the skim milk. The reason is to produce milk with standardized fat content. Typically milk powder should have 26-30% of fat content. Surplus cream is used to make butter.
PREHEATING
The next step in the milk powder process is preheating. In this process standardized milk is heated to temperatures between 75 C and 120 C. this temperature is held for a specified time from few seconds to several minutes. Like 72C foe 15s.
Preheating causes:
- controlled denaturation of the whey proteins in the milk
- It destroys bacteria, inactivates enzymes
- Generates natural antioxidants
- Imparts heat stability.
- The exact heating/holding conditions depends on the type of product and its intended end-use.
- High preheats in whole milk powder are associated with improved keeping quality. But it reduce solubility.
Three types of Preheating:
- Indirect (via heat exchangers)
These indirect heaters are generally used waste heat from other parts of the process as an energy saving measure.
- Direct (via steam injection or infusion into the product)
- Mixture of the two.
EVAPORATION
In this step the preheated milk is concentrated in stages.
After evaporation we can produce:
- 9% of skim milk
- 13% of whole milk
This is achieved by boiling the milk under a vacuum. The temperature is below 72C in a falling film on the inside of vertical tubes. And water is removed as vapour.
This vapour, which may be thermally or mechanically compressed, is next used to heat the milk which in the next effect of the evaporator. It may be operated at a lower pressure and temperature than the preceding effect.
Modern plants may have more effects for maximum energy efficiency. More than 85% of the water in the milk is removed in the evaporator.
Evaporators are extremely noisy. Reason is the large quantity of water vapour travelling at very high speeds inside its tubes.
SPRAY DRYING
Spray drying is the step of atomizing the milk concentrate from the evaporator next into fine droplets. This is done inside a large chamber. There is a flow of hot air in the chamber. The temperature of this air is up to 200C. This flow of air is holed by using either a spinning disk atomizer or a series of high pressure nozzles.
The milk droplets are cooled by evaporation. And they never reach the temperature of the air. And these milk droplets never reach the temperature of air. The concentrate may be heated prior to atomization to reduce its viscosity and to increase the energy available for drying.
Much of the remaining water is evaporated in the drying chamber. It leave fine powder of around 6% moisture content with a mean particle size (<0.1mm diameter).
PACKAGING AND STORAGE
Milk powders are immensely more stable than fresh milk.
But milk powder is protection from moisture, oxygen, light and heat. It is needed in order to maintain their quality and shelf life. Milk powders quickly take up moisture from air and leading to a rapid loss of quality and caking or lumping. The fat in whole milk powder can react with oxygen in the air to give a off flavor. It happens at especially high storage temperatures. (>30C)
Milk powder is packed into either plastic bags or bulk bins. Whole milk powders are often packed under nitrogen gas to protect the product from oxidation and also maintain their flavor and extend their keeping quality. The packaging is chosen to provide a barrier to moisture is air, oxygen and light.
Bags also consist of several layers to provide strength and the necessary barrier properties.
|
|
|
HEALTH AND SAFETY
PHYSICAL HAZARDS Physical hazards include exposure to same-level fall hazards due to slippery conditions, the use of machines and tools, and collisions with internal transport equipment (e.g. forklift trucks and containers). How do falls happen? Statistics show that the majority (66%) of falls happen on the same level resulting from slips and trips. The remaining 34% are falls from a height. Slips Slips happen where there is too little friction or traction between the footwear and the walking surface. Common causes of slips are:
Trips Trips happen when foot collides (strikes, hits) an object causing you to lose the balance and, eventually fall. Common causes of tripping are:
In addition to above mentioned reasons collision with transportation vehicles when lifting the packages into the truck also contribute to physical hazards to people working in the processing factory. BIOLOGICAL HAZARDS Exposure to biological and microbiological agents may be associated with inhalation and ingestion of dust and aerosols, particularly in milk powder operations. Dust from the ingredients used in dairy processing and high levels of humidity may cause skin irritation or other allergic reactions. The elaboration of above stated point is that in diary processing plants due to the presence of microbiological agents involved in the milk products can cause infections to employees working there. It can also be seen there that emissions of dust particles from the burning of aerosols used for obtaining energy can also cause respiratory diseases Inhaling of particulates from the milk powder production can also cause respiratory diseases in employees. The present study provides new evidence that workers exposed to milk powder by inhalation are at an increased risk of nasal symptoms, wheezing and breathlessness, and exhibit reduced Spiro metric lung function, even at relatively low air concentrations of milk dust. CHEMICAL HAZARDS Exposure to chemicals (including gases and vapors) typically involves chemical-handling activities related to cleaning operations and disinfection of process areas, in addition to the maintenance of heating (thermal oils). In milk processing factories certain chemicals are used for sanitizing, detergents for cleaning of storage tanks as well as emission of certain gases (CO2, CO, NOX, SO2) in the process of combustion can cause smog which in turn is carcinogenic. As well as emission of CFC’s and NH3 into the air as a result of leakage and stripping of chilling machines when out of use. EXPOSURE TO HEAT, RADIATION AND COLD In the production of milk powder employees are frequently exposed to heat due to heating up of machines and near the evaporation unit. Cold can be experienced by employees in the cooling room for the storage of the milk. In the pasteurization process small amount of gamma rays are used which is dangerous to employees since frequent radiation for small time frequently can also be dangerous as being exposed for a long time. REFERENCES
|
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal



























 c
c


