Contemporary Issues in Management at Walmart
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Management |
| ✅ Wordcount: 3705 words | ✅ Published: 23 Sep 2019 |
Chosen company: Walmart
Introduction
Numerous publications have been made in recent years regarding Walmart and its unfair corporate policies – ranging from child labour, unethical supply chains, and gender inequality. (Osterndorf, 2015). However, Walmart remains the biggest retail chain in the world with the largest retail revenue of “482.1 billion”. (Papadopoulos, 2017). There are possibly two main questions that could be derived from speculating their prosperity in the world of business and then all the negative publicity;
– Are social norms in fact valued in the world of business?
– Or do corporate policies exceed social norms/values such as CSR? Is it a social construct and only in implementation for the sake of profit margins? Do consumers actually care, or are they conforming to a societal standpoint?
The intent behind selecting Walmart for this assignment is based upon their corporate policies and how these policies have affected their business, whether it be negative press or loss of revenue. The three issue areas that will be addressed throughout the assignment are as follows;
- Usage of foreign labour, to have included working children. To what extent is this right or wrong? Are Walmart wrong for hiring foreign workers in the hopes of gaining economies of scale or is the media following suit to discredit the company?
- Gender inequality – modern-day discrimination in relation to women receiving less pay. Are there any other factors or variables affecting this pay inequality or are Walmart in actual fact underpaying their female workers? (Holman, 2017)
- Unethical Supply Chain – exploiting enslaved and migrant labourers in certain segments of their supply chain. Is Walmart exploiting modern day slavery? (Chen, 2015)
Now the assignment will address the three proposed issues Walmart faces and/or has faced. The issues will be analysed in detail with given recommendations that the company could possibly implement in their future endeavours.
Issue 1 – Use of foreign labour
We begin by addressing Walmart and its use of foreign labour. Walmart has continuously outsourced many parts of its supply chain internationally to gain economies of scale, which includes young working children. NBC television first exposed Walmart in 2005 of using foreign labour, including underage children working extremely long hours and in abysmal conditions. (Gereffi and Christian, 2009). Many large retail conglomerates, including Walmart, have had “allegations of labor exploitation”. (Smestad, 2009). However, with the various allegations and publications made against Walmart on its exploitation of foreign labour, the organisation continues to generate heavy profits with operation longevity and prosperity.
With all the continuous allegations made against Walmart, the company remains to respond back to media outlets and its stakeholders withdrawing these accusations, with for instance; “we have made a commitment to our associates, customers, and suppliers that when false allegations are made about Wal-Mart, we will actively correct the record.” (HRM Guide, 2013) Although, with Walmart and its increasing efforts to reverse these accusations, media outlets continue to belittle the company’s reputation with on-going publications. In 2016, Walmart did suffer from very bad sales performance of a “0.7% decline in revenue”, mainly due to fierce competition with Amazon. (Whipp, 2016). However, this could potentially be interpreted with consumers being more aware of Walmart’s corporate policies, i.e. foreign labour and thereby selecting its competition.
There are several scholar studies with an indication of defending the use of foreign labour, as well as sweatshops that many large conglomerates, such as Walmart utilise. In 2005, Richard Rothstein published a scholarly article defending the use of sweatshops. He states that our perception of the use of foreign labour is simply skewed and distorted by the entitlements our western society receives. However, these sweatshops and overseas factories are providing a set wage for these individuals. (Rothstein, 2005). Although, this statement is factual and that it provides employment and a set wage for these workers in underdeveloped countries. However, the wage even by these country standards is far too low. The image below depicts the wages in accordance to specific countries that companies like Walmart outsource their operations;
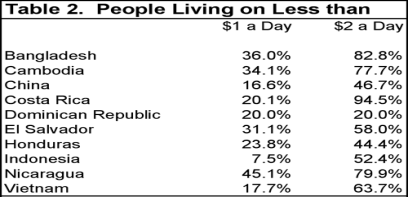
(Worstall, 2017)
Though, these wages may astound some individuals. However, it provides workers within these countries a stable income. Although, if companies were to provide a minimum wage implemented within most western cultures/societies, these workers may afford to accumulate enough funds to quit these jobs, and work elsewhere. Thereby, large conglomerates, such as Walmart refuse to do this as it would increase their labour costs and finding new employees.
So, what could Walmart possibly do?
We look at two strategies and /or theoretical frameworks utilised within the industry which Walmart can likely add to their business model in the hopes of eradicating or slowing down the issue of foreign labour.
The first way on how Walmart could potentially improve their policies of foreign labour is by implementing a social responsibility initiative; ISO26000. The image below depicts what the framework represents and how Walmart could employ specific segments;
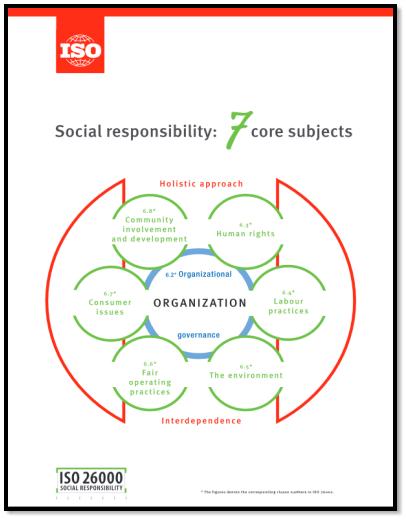
(ISO, 2010)
ISO26000 is an initiative that creates a harmonious awareness of generating a coalition to encourage the concept of “social responsibility”. Walmart can consider many viewpoints, including, societal, economic, environmental and organisational factors when deciding to employ this strategy. If Walmart is to practice and implement the ISO26000 initiative and considering “human rights” and “labour practices”, they are able to achieve sustainable development, as well as good reputation and competitive advantage within the eye of the public of improving its overall business perception. (Herciu, 2016). With the use of IS026000 across the global business, Walmart can certainly take advantage of health and safety within the workplace and human development within these underdeveloped countries.
In contrast, Walmart could also implement a “Convergence of Interests” initiative first proposed in 2002 by Michael E. Porter and Mark R. Kramer. Its aim is to have an impact in terms of both commercial and societal prosperity, simultaneously. The image below illustrates the framework;
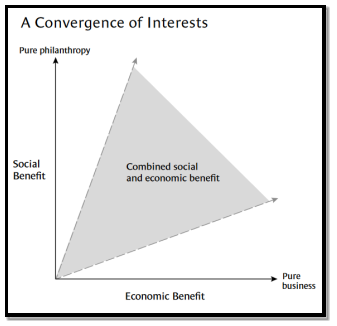
(Porter and Kramer, 2002)
It seems that Walmart with its current business processes is outside the bracket of “combined social and economic benefit” and focussing entirely on pure business. However, with the utilisation of the above framework, Walmart can improve lives and can participate in “human capital development”. For instance, Walmart can offer workers within the underdeveloped countries health products, medicine, and nutritional food in the working factories. Not only that, but the company can also offer better training and development. Thereby, they would achieve both social (satisfied workers) and economic benefit (efficient workload with more profitability). (Reed, 2011).
Issue 2 – Gender inequality
Diverting away from Walmart’s first issue of the use of foreign labour, we can now discuss “gender inequality”, specifically, underpaying female workers.
Gender studies have been an ongoing phenomenon for several years, and it continues until this day. Celica L. Ridgeway argues that “sex segregation” remains to persist within the workplace, in the case of dividing men and women and that most men work with other men and most women are working amongst other women. However, there has been a reduction of sex segregation within the workplace since the early 90s. Although, approximately 40% of women within the United States would need to “change occupations” in the hopes of eradicating this issue. (Ridgeway, 2011). Though, many recent studies have found gender inequality to be not just a “female issue”, but rather it is going both directions.
It has been argued that men from a very young age have been programmed to “think and behave like a man”, having to go through physical bullying, teasing and psychological torture to demonstrate “physical and emotional strength”. (Gov.au, 2018). Thereby, men may perform better within the workplace in the hopes of seeking validation.
The issue of the gender pay gap at Walmart began around 2001 when the company had a lawsuit filed against them by their female workers of pay disparity. “For example, in a class action lawsuit against Walmart, female workers claimed they were receiving fewer promotions than men.” (Stamarski and Son Hing, 2015). However, another study demonstrates that women workers within Walmart are receiving less pay due to working in “lower paying hourly jobs”, however, women within the same jobs but working “salary” or full-time roles are receiving higher pay. (Drogin, 2003).
The image below depicts women working the exact same roles within Walmart. However, the higher paid are working salaried roles, but female workers with less pay are working hourly roles – thereby, receiving considerably less pay.
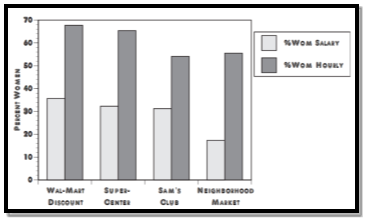
(Drogin, 2003)
In speculation and interpretation, this suggests that Walmart are in fact not discriminating against women in terms of pay. There are variables, as described above, which is causing the pay gap. However, many women across the country have continued to file discriminatory court cases against Walmart, with using “gender” as requisite for their continuation of the “pay gap” agenda.
Despite the negative publicity against Walmart in relation to gender inequality, the company has been working on several initiatives in the hopes of improving their image amongst its several stakeholders. They have spent 18 months, beginning in early 2017, renovating their career website to make it more gender neutral. “The site itself now features more images of women and people of colour”. (Jones and Donnelly, 2017). More than 4000 Walmart job postings were analysed for language and it was found that more than 50% of “job descriptions” were targeted at men.
However, Walmart has since been working on and have continuously been rectifying the issue with more women than before in management positions. Although, the number of men in management/executive positions within Walmart remains to exceed in comparison to women in similar positions. In 2015, 57% Walmart’s management cohort were men and that figure remains very similar until this day. The image below illustrates the statistics of female workers within Walmart;
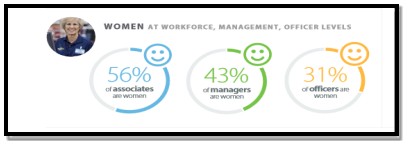
(Walmart, 2016)
So, how can Walmart strategise to demolish its gender inequality?
Although Walmart has been doing their best to eradicate gender inequality and several accusations made against them, they are able to implement several on-going approaches which many real industry organisations utilise.
In 2018, McKinsey & Company have conducted data analysis and reporting of “gender diversity” and “women in the workplace”. They have addressed several issues that women face within the workplace, ranging from pay gaps, lack of support from management, sexual harassment, advancements and promotions, and hierarchies. (McKinsey&Company, 2018). They have also proposed various strategies that organisations, such as big conglomerates as Walmart could employ. The following are two appointing strategies which Walmart are able to go ahead with, in demolishing the issue;
- Making sure that the recruitment, hiring, and promotions are a fair process. Walmart should accept applications without the use of “names” or “gender” as a prerequisite. This way the central focus of the hiring process would be based on competence, skills, and experience. It has been said that many organisations do not interview job candidates by using a “diverse group of employees” and this is something can be implemented at Walmart to encourage diversity amongst men and women. (McKinsey&Company, 2018).
- Another strategy that can be employed within Walmart is ensuring that senior leaders and/or managers are fully aware of gender diversity. According to McKinsey&Company, many organisations are not making management or senior level employees aware of gender equality and diversity and/or possible ways it could be improved. (McKinsey&Company, 2018). Thereby, what Walmart can do is have regular and major presentations on gender equality and diversity across its different stores and locations. This would help the company and many of its employees to become fully aware of the matter.
Issue 3 – Unethical supply chain
The final issue to be addressed is Walmart’s participation in unethical supply chains, more specifically exploiting enslaved and migrant workers for their seafood products, more specifically, shrimp and tuna.
Thai Union Group (TU) are the largest global producer of fish products and it also partakes in distribution and exportation to countries such as the US. Its major customer is Walmart, amongst others, many of their products can be found on their shelves. TU was found to be abusing and exploiting many of its workers at sea and land. The workers/teams are verbally and physically abused to work faster and are also subjected to being in deprivation of “adequate food and clean drinking water”.Many seafood workers, operating under these cruel conditions have been a subject of death. (Greenpeace, 2016). However, Walmart and many other large conglomerates have continued to use the supplier for years for profitability purposes, i.e. buying tuna and shrimp at a low price to sell at a higher price.
Many US retailers, including Walmart, were first exposed in 2015 for being part of a supply chain that utilised “systematic human trafficking” and modern-day slavery. Shrimp and tuna, the most popular seafood in the US are sourced from Thailand through supply chains that include “migrant workers who regularly work in shrimp sheds. Parents and kids were found inside dirty warehouses that smelled of sewage, and often worked 16-hour shifts with little pay.” (Chew, 2015). The company is generating profits discursively from workers who are highly monitored during their shifts and are forced to work long hours peeling fish. Although, Walmart does not hire these workers directly, however with a supply chain and supplier integration they become a huge part of the system. Thereby, encouraging this unacceptable type of behaviour.
Walmart has faced several backlashes from its stakeholders and media for their unethical sourcing systems within their supply chain, including bad reputation and pressured into letting go of their key suppliers. However, with the pressure the company has faced from its stakeholders, Walmart has responded back with the creation of “ethical sustainable sourcing” guidelines and that all their suppliers must abide by their regulations stated within these guidelines. (Chen, 2015). Since, the backlash, Walmart implements monitorisation and audits in place to evaluate supplier integrity and obedience. However, even with the audits in utilisation, Walmart remains to not make any guarantees that suppliers are fully compliant to their auditing policies and this is mainly due to the sheer size and scope of the organisation. (Walmart, 2018).
Besides Walmart’s auditing policing utilisation, what other strategies could the company implement to achieve more of a sustainable sourcing and supply chain?
There are several concepts of sustainable supply chain management, ranging from TQM (total quality management) and JIT (just in time). However, these concepts look at the performance values of supply processes and neglect the social issues that may come along within the supply chain. (PAGELL and WU, 2009). Walmart not only need to go beyond these measures, but also assess the social agendas and performance within their supply chain.
The proposed model that Walmart can utilise to achieve full supply chain prosperity, including the improvement of not only social factors but also environmental and economic. The image below depicts the framework;
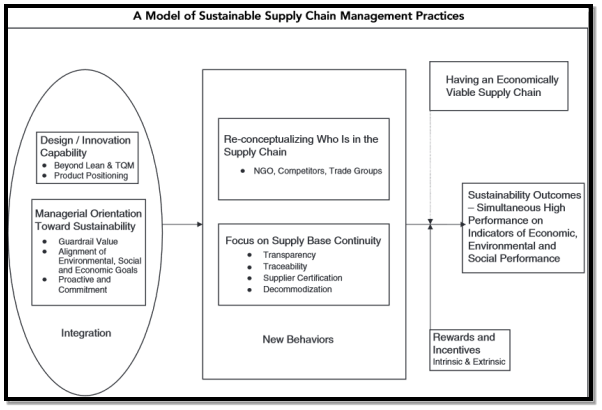
(PAGELL and WU, 2009)
Walmart can apply the above framework across its entire business model, with given proper training to supply chain managers in relation to the responsibility of social and environmental concerns. (PAGELL and WU, 2009).
Sharing awareness is the first step in eradicating the issue. If parts of Walmart are aware of unethical sourcing issues, and the other half are not, it creates an unfortunate imbalance. Thereby, the first step is to implement and embed this framework across levels of management. However, if management is not aware of the issues then no one is likely to follow suit of the sustainability orientation. If Walmart requires this initiative to work, then getting community involvement is essential – addressing the issue with the community and then working on an outcome in a strategic coalition. However, the most important factor that Walmart needs to address is supplier integrity. A full in-depth supply analysis should be conducted prior to selecting suppliers, and supplier certifications that include social and environmental criterion. For the continuation of this initiative of sustainable supply chains and sourcing, Walmart should make it mandatory with the implementation of reward systems, such as; healthcare, company cars, extra holidays, recognition and appreciation within the company etc.
Although, this framework can be very useful in the real working world. However, what it possibly lacks is the component of human behaviour and how that could potentially be tackled. Not all humans behave the same, and thereby some managers may not follow it as well, or if at all, as other managers across the organisation. Therefore, the utilisation of the above framework in the hopes of eliminating unethical sourcing across Walmart’s may be paradoxical.
Conclusion
Walmart is a big, global conglomerate and the three main established issues of the use of foreign labour, gender inequality and unethical supply and sourcing is mostly the tip of the iceberg. A global organisation comes with global issues and is more prone to negative targeting by media outlets. However, Walmart being aware of their issues is what makes it somewhat plausible, but not implausible – what makes it plausible is them partaking to rectify these issues. Although, these issues remain not to affect the business that significantly, considering that Walmart remains to generate extreme revenue. Thereby, it could be argued that CSR or similar initiatives encouraged by society are simply socially constructed and that majority of the population that shops at Walmart most likely are attentive to the on-going issues, however, are more attentive to their purchases. No company, even Walmart, can ever be perfect and will certainly have its issues in the future. However, an organisation that addresses its issues right away with the implementation of correct strategies is what differentiates them from companies that do not.
Key recommendations
To maintain strategies proposed within the report, Walmart should do the following;
- Many theoretical frameworks have been mentioned for all the issues the company has faced. Frameworks are very often updated with better strategies for companies to fully benefit from, and Walmart should invest its time in ensuring that they also renovate their business model as the frameworks incrementally also go through change.
For instance, the ISO organisation constantly makes changes to its models and the ISO26000 mentioned in the first issue is likely to change over the subsequent years and thereby Walmart should change with it to fully benefit from it and to avoid similar issues.
- Although Walmart’s supply chain management process is evidentially innovative with high involvement of inbound and outbound logistics and its systematic use of its inventory management, the company undoubtedly gets all its products stacked on shelves ready for sales. The company is also working on their sustainability with incremental changes in different segments of its supply chain. However, most of the products it sells are of a low, budget quality which reflects badly on the brand. A strategy that they could utilise is getting suppliers who are able to sell products with better and robust quality – and Walmart’s revenue would not be affected if they are to utilise their bargaining power and brand name proficiently.
References
- Chen, M. (2015) Here Are All the Reasons Walmart’s Business Is Not Sustainable [online]. Available from: https://www.thenation.com/article/here-are-all-reasons-walmarts-business-not-sustainable/ [Accessed 7 November 2018]
- Chew, J. (2015) Report Alleges Walmart and Whole Foods Are Selling Shrimp Peeled by Slaves [online]. Available from: http://fortune.com/2015/12/14/thailand-slaves-shrimp/ [Accessed 17 November 2018]
- Drogin, R. (2003) STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF GENDER PATTERNS IN WAL-MART WORKFORCE., 1 (1): 11
- Gereffi, G. and Christian, M. (2009) The Impacts of Wal-Mart: The Rise and Consequences of the World’s Dominant Retailer. Annual Review of Sociology, 35 (1): 581.
- Gov.au (2018) Gender inequality affects men too [online]. Available from: https://www.vic.gov.au/women/gender-equality/a-victorian-gender-equality-strategy/case-for-change/gender-inequality-affects-men-too.html [Accessed 16 November 2018]
- Greenpeace (2016) Walmart’s Unsustainable and Unethical Canned Tuna Procurement. 1st ed [online]. Greenpeace. Available from: http://www.greenpeace.org/usa/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Walmart-Thai-Union-Canned-Tuna-Briefing.pdf?f3025c [Accessed 17 November 2018]
- Herciu, M. (2016) ISO 26000 – An Integrative Approach of Corporate Social Responsibility. Studies in Business and Economics, 11 (1): 73-79.
- Holman, J. (2017) Wal-Mart Female Employees Try Again for Sex-Bias Class Action [online]. Available from: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2017-11-07/wal-mart-female-employees-try-again-for-sex-bias-class-action [Accessed 7 November 2018]
- HRM Guide (2013) Wal-Mart Hits Back [online]. Available from: http://www.hrmguide.com/relations/wal-mart.htm [Accessed 8 November 2018]
- McKinsey&Company (2018) Women in the Workplace 2018. 1st ed [online]. McKinsey&Company. Available from: https://movimentomulher360.com.br/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/Women_in_the_Workplace_2018-.pdf [Accessed 16 November 2018]
- ISO (2010) Social Responsibility: 7 core subjects. 1st ed [online]. ISO.org. Available from: https://www.iso.org/files/live/sites/isoorg/files/archive/pdf/en/sr_7_core_subjects.pdf [Accessed 12 November 2018]
- Jones, S. and Donnelly, G. (2017) http://fortune.com [online]. Available from: http://fortune.com/2017/04/04/walmart-jobs-gender-bias/ [Accessed 16 November 2018]
- Osterndorf, C. (2015) 10 reasons you should never, ever shop at Walmart [online]. Available from: https://www.dailydot.com/via/walmart-labor-unions-bad-company/ [Accessed 8 November 2018]
- PAGELL, M. and WU, Z. (2009) BUILDING A MORE COMPLETE THEORY OF SUSTAINABLE SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT USING CASE STUDIES OF 10 EXEMPLARS. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 45 (2): 37-56.
- Papadopoulos, A. (2017) Giants Of Retail: The World’s 25 Largest Retailers By Revenue, 2017 | CEOWORLD magazine [online]. Available from: https://ceoworld.biz/2017/01/24/giants-retail-worlds-25-largest-retailers-revenue-2017/ [Accessed 6 November 2018]
- Porter, M. and Kramer, M. (2002) The Competitive Advantage of Corporate Philanthropy. Harvard Business Review, 1 (1): 7
- Reed, R. (2011) Accenture Development Partnerships – ppt video online download [online]. Available from: https://slideplayer.com/slide/1621260/ [Accessed 13 November 2018]
- Ridgeway, C. (2011) Framed by gender. 1st ed. [Oxford]: Oxford University Press
- Rothstein, R. (2005) Defending Sweatshops: Too Much Logic, Too Little Evidence. Dissent, 52 (2): 41-47.
- Smestad, L. (2009) The Sweatshop, Child Labor, and Exploitation Issues in the Garment Industry. Fashion Practice, 1 (2): 147-162.
- Stamarski, C. and Son Hing, L. (2015) Gender inequalities in the workplace: the effects of organizational structures, processes, practices, and decision makers’ sexism. Frontiers in Psychology, 6: 5.
- Walmart (2016) THE CULTURE AND HUMANITY OF OUR ASSOCIATES MAKE US SPECIAL. 1st ed [online]. Walmart. Available from: http://cdn.corporate.walmart.com/8c/08/6bc1b69f4a94a423957d4c2162db/wm-cdireport2016-v27-reader-pages.pdf [Accessed 16 November 2018]
- Walmart (2018) Responsible Sourcing [online]. Available from: https://corporate.walmart.com/responsible-sourcing [Accessed 18 November 2018]
- Whipp, L. (2016) Walmart suffers worst sales performance in 35 years | Financial Times [online]. Available from: https://www.ft.com/content/cbcb3f9e-d640-11e5-8887-98e7feb46f27 [Accessed 8 November 2018]
- Worstall, T. (2017) There’s no need to change trade agreements to achieve this [online]. Available from: https://www.adamsmith.org/blog/theres-no-need-to-change-trade-agreements-to-achieve-this [Accessed 8 November 2018]
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


