Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and Organizations
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Information Systems |
| ✅ Wordcount: 3365 words | ✅ Published: 23 Sep 2019 |
Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and Organizations
ABSTRACT
This research paper explains the Risk Management Framework (RMF) and provides the recommendations on implementing the RMF on information systems and organizations. The Risk Management Framework provides six structured and flexible steps, i.e., information security categorization; control selection, implementation, and assessment; system and common control authorizations; and continuous monitoring for controlling security and privacy risks. The RMF also contains tasks to help the organization implement the framework at suitable risk management levels. The RMF additionally promotes near real-time risk management and ongoing information systems and general control authorization through the executions of continuous monitoring procedures, it also offers the higher management and the executives with the required information to make efficient and cost-efficient decisions about the systems supporting the organization’s business function and also incorporate the security and privacy in their development life cycle.
- INTRODUCTION
Necessity to manage the security and privacy risks
To achieve the missions and business goals most of the organizations depend on their information systems. For these missions to be successful, it is important to protect the confidentiality, integrity, availability of information processed, stored, and transmitted by those systems and the privacy of individuals. There are various types of threat to the information systems; it could be natural disaster, system failure or human error and malicious attacks which are well organized. If these attack are successful, then the impact of the attacks on the information system could be catastrophic bringing the organization to halt. Hence it is imperative for the organizations to be alert and also senior officials, managers should be aware of their responsibilities and organization’s important assets and protect them from attacks and also manage the risks.
Along with the protecting organization assets and managing risks, it’s imperative to protect and manage the risk to all the individuals the personally Identifiable information. The information security and privacy programs carried out by organizations have supporting objectives for the management of the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PII. Although most of the privacy risks results from unauthorized access to the PII but there could also be authorized activity which could add risk to the PII handled processes like creation, usage, maintenance, storage, disclosure and disposal of PII information could compromise the PII.
As the organizations these days depends a lot on third party or external providers for systems services and products , they need to be cautious about the Supply chain risk too, If an attack is successful on the Supply chain management , it would be very difficult for the organization to trace . Hence it is of utmost importance that the supply chain risk management should be in harmony with the organization’s own privacy and risk management, this publication combines both supply chain management risk and risk management framework and promotes the comprehensive approach to manage both security and privacy risk.
The Risk Management Framework focus attention on risk management by implementing the security and privacy procedures into the information systems throughout the software development cycle by supervising the security and privacy procedures progress on an ongoing basis and also by keeping the seniors executives updated with the information about the security and privacy for them to take appropriate decisions regarding acceptance of risks of various types arising from the information system.
The Risk management framework can be used by organizations developing information systems, individuals or organizations responsible for assessing the privacy and security and for monitoring information systems.
1.1 BACKGROUND
The Risk Mangement Framework is developed by NIST with its partner Department of Defense , the office of the Director of National Intelligence and the Committee on National Security Systems to enhance the information security. The RMF gives a dynamic and adaptable way to deal with successfully manage security and privacy risks in various situations with troublesome and modern threats, developing missions and business functions, and changing framework and organizational vulnerabilities. The framework is policy and technology impartial, which encourages continuous upgrades to IT resources.
1.2 RISK MANAGEMENT – ORGANIZATION LEVEL
Managing Information systems related security and privacy across the organization involves a great amount of coordination among all the levels of officials, higher officials provide the plans strategies and goals, mid-level officials plan, execute and manage projects. Risk management is a comprehensive activity and influences every aspects of the organization.
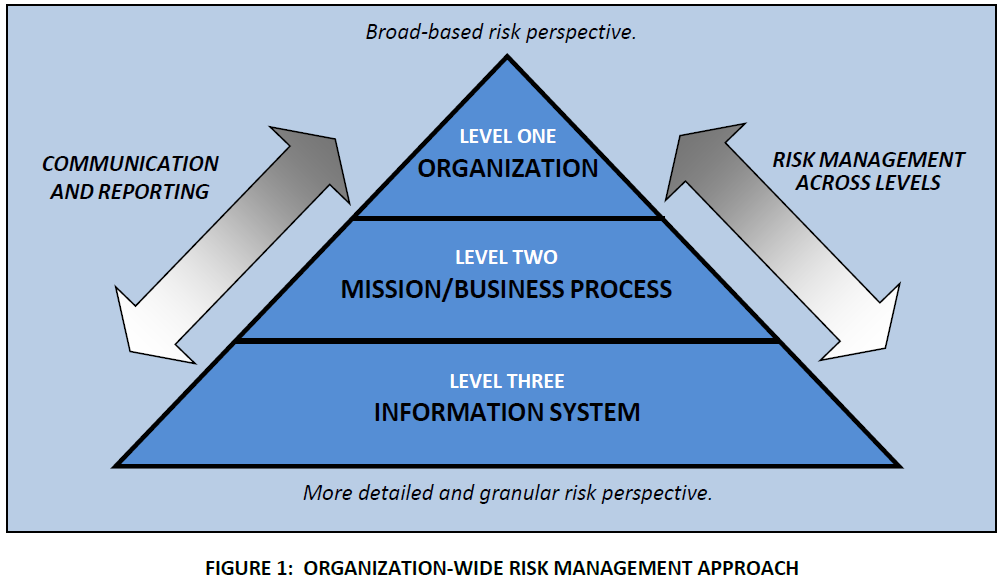
The organization-wide risk management approach depicts multi-level approach to the risk management across the three different levels. The communication and reporting of relevant information is bi-directional to make sure the risk is taken care throughout the organization.
The activities taking place in Level 1 and 2 are very crucial for an organization to implement the Risk management framework. Decisions regarding managing risks cannot be done independently .These decisions are often based on:
- organization’s Mission and Business Objectives
- Innovative initiatives for systems process and services
- Large Enterprise architecture for managing and reducing complexity by consolidation, optimization, and standardization
And, the activities for implementing the RMF includes:
- Assigning roles and responsibilities for risk management processes
- Laying a risk management strategy and organizational risk tolerance
- Identifying the Business processes and functions which needs the support of information systems
- Identifying the stakeholder who are interested in the information systems.
- Prioritizing the organization’s assets and security and privacy requirements.
- Analyzing potential threats to the organization.
- Understand the effect of the threats on the individual
- Determining authorization boundaries for common controls and information systems
- Developing the security and privacy architecture plan which includes intern controls compatible with the information systems
- Identifying, aligning and deconflicting the security and privacy requirements
In contrast to the previous levels, Level 3 address the risk from an information systems perspective and is supported by the risk decisions decided in the level 1 and level 2
2 RISK MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK STEPS AND STRUCTURE
There are seven steps in the framework, the first step which is the preparation step is to make sure that the organization are set to execute the remaining six important steps
PREPARE: to carry out the risk management framework from organization & system level based upon the priorities for managing security and risks.
CATEGORIZE: entire system and the information it processes, stores and transfers based on impact of loss.
SELECT : identify the set of controls for the systems and modify it as much as required to minimize the risk to an acceptable level based on the assessment.
IMPLEMENT: the controls and explain the way these control are related to the systems and its environment of operation.
ASSESS: check the controls which are implemented if they serve the purposes for which they have been implemented and whether they align with security and policy requirement
AUTHORIZE : the controls are authorized based on the intention that the risk to assets, organization is acceptable.
MONITOR : all the systems and the related controls to in a continuous manner to examine the effectiveness of control, documenting changes done to the systems and the environment , carrying out risk assessment and impact analyses and filing the security and privacy posture of systems.
The steps after prepare can be carried out in nonsequential manner. After organization plans the tasks for the prepare step, if they execute risk management framework for first time for a system or set of controls, then organization mostly carry out the remaining steps in sequential manner, Although there could be situations in while carrying out the risk management assessment where the organization would have to deviate from the sequence and carry out other steps based on the type of system and the risk decisions
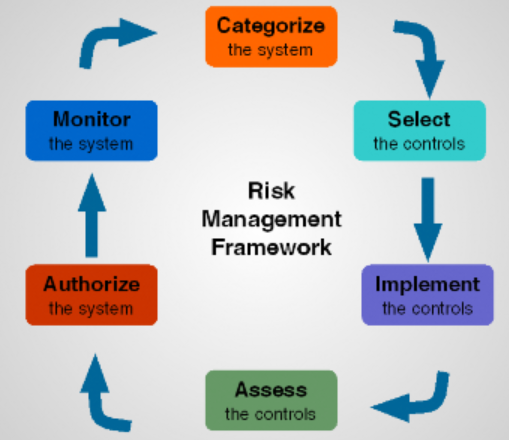
FIGURE 2 : Risk Management Framework
Each sequence has a purpose statement, set of outcomes and tasks to achieve the outcomes. The outcomes could be achieved by various risk management levels, meaning few outcomes could be common for the entire organization, and some outcome could be system-focused or business objective focused.
Each tasks within the sequence has a possible set of inputs required to carry out the task and expected outcome produced from the task carried out. Also, each tasks explains the various risk management roles and roles adhered to the task and phase of SDLC where the task is carried out. Also, the discussion segment in the sequence provides information about the task for better understanding and effective task implementation.Finally, after winding the RMF, a set of references provided wherever applicable to provide the related system security tasks.
2.1 INFORMATION SECURITY AND PRIVACY IN THE RMF
Implementation of the risk management frameworks needs collaboration between the information security program and privacy programs, though the objectives of both the program could be different, the objectives are often overlapping and complimentary. Information security programs are chalked to protect the data and systems from unauthorized access, use, deletion, disruption or destruction in order to preserve the CIA triad. The goal of the privacy programs is to ensure the compliance with relevant privacy requirement for managing the risks to each person related to creation, collection, processing, storage and disclosure of PII. Organization must consider that the objectives of both the programs are met in every sequence while preparing to carry out sequences of the RMF.
2.2 SYSTEM AND SYSTEM ELEMENTS
Organizations executing the RMF take a wide perspective on the life cycle of information system development to give a logical relationship and linkage to architectural and engineering ideas that permit security and protection risk to be sorted for the duration of the life cycle and at the correct level of detail to help guarantee that such capabilities are accomplished. [ISO 15288] gives an engineering perspective of information system and the elements with which the systems communicate in its condition of activity. [ISO 15288] characterizes a system as a set of interconnecting elements that are sorted out to accomplish at least more than one expressed purpose. Like the information resources that involve an information system incorporates data and different assets (e.g., workforce, hardware, assets, technology), system elements incorporate technology or machine components, human components, and physical or natural components.
2.3 AUTHORIZATION BOUNDARIES
The authorization boundaries define the scope of the protection of an information system. The authorization boundaries are drawn for people, processes and information technologies that are part of the systems supporting the organization objectives. Too large boundaries increase the complexity of the risk management framework, whereas too confined boundaries additionally requires many systems to be monitored individually and might be expensive to the organization.
The authorization boundaries are part of Prepare sequence and belong to the task system level. The organizations are free to define their own boundaries based on various factors like similar mission and objectives, have common operating characteristics and similar security privacy requirements, systems containing similar kind of information. The scope of the boundaries is checked and changed when necessary.
2.4 REQUIREMENTS AND CONTROLS
It is essential to understand the concept of security and privacy requirements and the relationship between requirements and controls. The term requirement may have a different meaning in different context; for example, in the federal security and privacy policies, requirement could be to information security and privacy obligation imposed on the organization. The term requirements, as utilized in this guideline, incorporates both legal and policy requirements. These requirements help decide the required attributes of the system-enveloping security, privacy, and assurance.
Controls can be seen as portrayals of the safeguards and assurance abilities apt for accomplishing the specific security and privacy objectives of the organization. Controls are implemented to address the system requirements. Controls could be technical, administrative and physical.
2.5 SECURITY AND PRIVACY POSTURE
The main motive of risk management framework is to protect the organization, its information systems, and individuals throughout the development cycle and keep the senior officials updated with the information required to make right risk-based decision the operations, controls or systems. One of the main aspects to make risk-based decision for the organization is to make sure that authorized officials understand the security and privacy posture of information systems and the common controls applicable to those systems. The privacy and security posture displays the state of information systems and resources like funds, technology within organization based on information assurance resources like policies and people. The privacy and security posture is monitored on an ongoing basis by checking the system-specific, hybrid and common controls.
This checks makes sure that the controls selected by the organization is implement correctly, working as desired and satisfying the security and privacy requirements with respect to law, orders, policies, standards, directives or mission/business objectives.
2.6 SUPPLY CHAIN RISK MANAGEMENT
organizations are greatly dependent on products, services, and systems supplied by outside suppliers to fulfill missions and business functions. organizations are capable and responsible for the risk acquired when utilizing third party products or services. Organizations with outside suppliers can be set up in an assortment of ways, for instance, through joint ventures, business partnerships, different kinds of formal agreements (e.g., contracts, interagency agreements, lines of business plans, licensing agreements), or outsourcing arrangements. This dependence on third party increases the amount of risk of an organization.
To tackle these risks, the organizations develop SCRM policy. This policy is important to carry out the SCRM activities.The policy meets the goals and missions of organization’s strategic plan and business function and both internal and external customer requirements.
The RMF can be used to manage the supply chain risks appropriately. Additionally, it can also guide information security privacy and risks management tasks for all the elements in supply chain
.
3.THE PROCESS: EXECUTING THE RMF TASKS
The RMF comprises of sequences and associated tasks and the individuals or groups; it is important to describe the tasks within in each sequence and also about the roles and outcomes of the tasks needs to be explained.
The RMF tasks are carried out simultaneously with the SDLC process in the organization to ensure that the organization is able to integrate the process concerning privacy risks and security with the SDLC process. Also, the expected outputs of the RMF tasks could be often achieved by the SDLC process in place and need not be developed separately for RMF.
3.1 PREPARE
The Prepare step is necessary to execute the required activities at the organization, mission and business functions and information system levels of the organization to prepare the organization to supervise the its security and privacy risk using the RMF.
The Tasks under the Prepare step are categorized into two levels; Organization Level, System Level.
Prepare steps – Organization Level and System Level
Each tasks in Prepare step comprises of section Task, Potential Inputs, Expected Output, Primary responsibility, Supporting Roles, Discussion and references.
TASK : This section defines the kind of task or activity.
The tasks involved in the organization level are:
1)Identification of the risk management roles , 2)Plan risk management strategy providing the organization’s risk tolerance levels, 3)Carry out or update the existing risk assessment throughout the organization, 4)Establishment of organizationally-customized control baselines and cybersecurity framework, 5)Identification and inheritance of existing of common controls in the organization, 6)Prioritization of organizational systems and 7) Implementation if continuous monitoring strategy throughout the organization.
The tasks involved in the System Level are:
1)Identification of organization’s mission and business objectives that the systems are to support 2) Identification of Stakeholders of those systems 3) Identification of Stakeholder assets and prioritizing them 4) Determination of authorization boundaries 5) Identification of all the types of information processed transmitted or stored 6) Identification of all the stages of Information Lifecycle and understand all stage for the each information processed transmitted or stored 7) Definition and Prioritization of Security and privacy requirements 8) Determination of placement of the system within the enterprise architecture 9) Allocation of security and privacy requirements to the systems and 10) Registration of the systems to maintain accountability and coordination.
POTENTIAL INPUTS: Inputs could be any resource or requirements which is needed to carry out the tasks. Based on the tasks the potential inputs are identified. Few of the inputs are security and privacy policies and procedures, Mission statement, Organization’s assumption, Risk management strategy, and current threat information.
EXPECTED OUTPUTS: Outputs are the purpose of the task. The result of the task is provided here few examples are Organization-level risk assessment results, Documented Risk Management Framework role assignments and Organization-level risk assessment results.
PRIMARY RESPONSIBILITY: This defines the group or the person responsible to carry out or supervise the tasks. Generally, these are the security officials of the organization, for example, Chief Information Officer, Head of Agency and Senior official for privacy.
SUPPORTING ROLES: Supporting roles are the individual who are involved in carrying out the task for providing additional information and support. Few examples are Risk executive, Accountable office for Risk management.
DISCUSSION: The section describes the tasks in detail and all the required activities needed to find achieve outcomes. This section is generally elaborated providing a thorough understanding of the task and the actions carried out to execute the task.
REFERENCES: This section provides the references used to carry out the tasks. Often Other frameworks are referred to help provide understanding and information about the task.
3.2 CATEGORIZE
The Categorize step is used to inform organization risk management process and tasks. This is done by analyzing impact on operations and assets, individuals and other organizations. Analysis is done in areas like confidentiality, integrity, and availability of systems. Analysis is also done on information processed, stored and sent.
TASKS: The RMF Categorization step has 3 tasks and expected outcomes.
The tasks involved in the categorization of tasks and outcomes are:
1) System description mentioning the characteristics of the system and documenting them.
2) Categorization and Documentation of the system based on security and information processed by the system.Documentation of security categorization in security, privacy, and SCRM plans. Analyzing enterprise architecture and checking consistency with security categorization along with commitment to protecting organizational mission and processes. 3) Reviewing and approval of security categorization results. Checking if categorization results are approved by senior leaders.
POTENTIAL INPUTS: System design requirements documentation and authorization of boundary information. Having system supply chain information and data maps. Risk management strategies and organization and system level risk assessment, Impact levels determined for each information type and for each security objective.
EXPECTED OUTPUTS: Document system description, each security objectives having its own impact levels, Security categorization for information impact levels, Approval of security categorization for system.
PRIMARY RESPONSIBILITY: System Owner, Information owner, Senior Agency Official for Privacy, Authorizing official.
SUPPORTING ROLES: Authorizing Official, Accountable officer for risk management, System security officer, system privacy officer, Chief Information Officer.
SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE PHASE: Concept/ requirements definition for new phases and Operations/Maintenance for existing phases.
REFERENCES: [IR 8179]; [CNSSI 1253]; [NIST CSF], [FIPS 199]; [SP 800-30]; [SP 800-39]
3.3 SELECT
The select step is to select, customize, and document various controls needed to shield information systems with risk to company operations and assets, people, the organization and the country.
TASKS: Here are a few tasks and expected outcomes for the RMF Select step.
1) Controls are selected to protect system from risk. 2) Controls are tailored to provide accurate and tailored baselines. 3) Controls are allocated to specific systems. 4) Controls and tailoring actions are properly noted down and privacy plan related documentation is also created. 5) A system level continuous monitoring strategy is developed and documented. 6) Security and privacy plans and reviewed and approved.
POTENTIAL INPUTS: Security categorization, risk management strategy, CyberSecurity framework profiles, initial control baselines, organizational security and privacy policies, system component inventory, Security categorization; system level risk assessment results, organizational policy on system registration; enterprise architecture, system element information, business impact and criticality analysis, organizational continuous monitoring strategy,
EXPECTED OUTPUTS: Controls selected for system and operation environment, tailored controls of system and operation environment, system elements, Planning security and privacy, Strategies for time-based triggers of the system, Privacy plans approved by authorizing official.
PRIMARY RESPONSIBILITY: System Owner, Information owner, Senior Agency Official for Privacy, authorizing official, Security Architect, Privacy architect, Common controls provider, Authorizing official designated representative.
SUPPORTING ROLES: Authorizing official, Privacy engineer, System privacy officer, System security officer, Mission or Business Owner; Senior Information Security Officer; Senior Agency, Official for Privacy; System Owner.
SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE PHASE: Concept/ requirements definition for new phases and Operations/Maintenance for existing phases.
REFERENCES: [SP 800-64]; [SP 800-160 v1] , [FIPS 199]; [FIPS 200]; [SP 800-18]; [SP 800-30]; [SP 800-53]
References
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


