Patient Medical Record Dispatch System
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Information Systems |
| ✅ Wordcount: 2149 words | ✅ Published: 23 Sep 2019 |
Project Charter: Patient Medical Record Dispatch System
Patient Medical Record Dispatch
Electronic patient medical record dispatch provides an efficient and streamlined data collection process. The system produces an accurate, complete, and legible electronic patient data, thereby reducing liability as well as improving the quality of patient care and reimbursement. Patient medical record dispatch intends to use the system for both internal and business purposes including the delivery of patient care services.
Our study contributes several key findings to the literature on the outcomes of providing patients access to medical records. Most of the patients were uniformly positive about the idea of having facilitated access to their records. Providing patients access to their medical records may facilitate a more collaborative relationship between provider and patient
The patient medical record, seen as a life-time’s accumulating of health care information, presents fascinating issues in database arrangement. The essential may be a database where structure is to some degree controlled by customers at terminals. The objective of this project is to develop a software module to make the medical record dispatching easier.
Problem Statement
Paper based records has many disadvantages. The records also needs to be protected from natural calamities. Paper Based records may not be readable and hence may result in health mistakes. The digitization of health-care records eases the search of the terms. The healthcare organizations today need to make sure that medical information, such as doctor’s notes and lab reports, can be accessed immediately from anywhere and anytime when required.
Hospitals now not only must care for and educate patients but also confirm that they are using their electronic medical record. It’s something hospitals haven’t used, and it’s a very great change and is very much useful for the patients and also the doctors.
Project Description
In a hospital, doctors order many medical tests for patients. The order goes to the testing lab and the results of a test is sent back to doctors. This a highly manual-intensive. The entire reporting activity can be automated. The purpose of this project is to develop a software module to automate the request and report process. The digitalization of this process is specifically done among the doctor, patient and the testing lab. This automation is done in such a way that the doctor sends the prescribed tests for a particular patient to the testing lab. The testing lab will perform the tests and instead of giving the reports manually, they upload them into the system which can be viewed by both the doctor and the patient. Patients, doctors and lab technicians are given an id and password to access the system.
The authorization of the users is checked by validating their information. To provide an extra layer of security the passwords are stored in encrypted format in the database. Providing patients access to their medical records may facilitate a more collaborative relationship between provider and patient. Existing literature suggests that patient-accessible records can improve patient–provider communication, self-management, and patient satisfaction.
Scope
• Assist the physician or doctor in providing the best possible care to the patient.
• Offer legal protection to those who provide care to the patient.
• Provide statistical information that is helpful to researchers.
• Vital for financial reimbursement.
• The system should provide easy retrieval, organized storage.
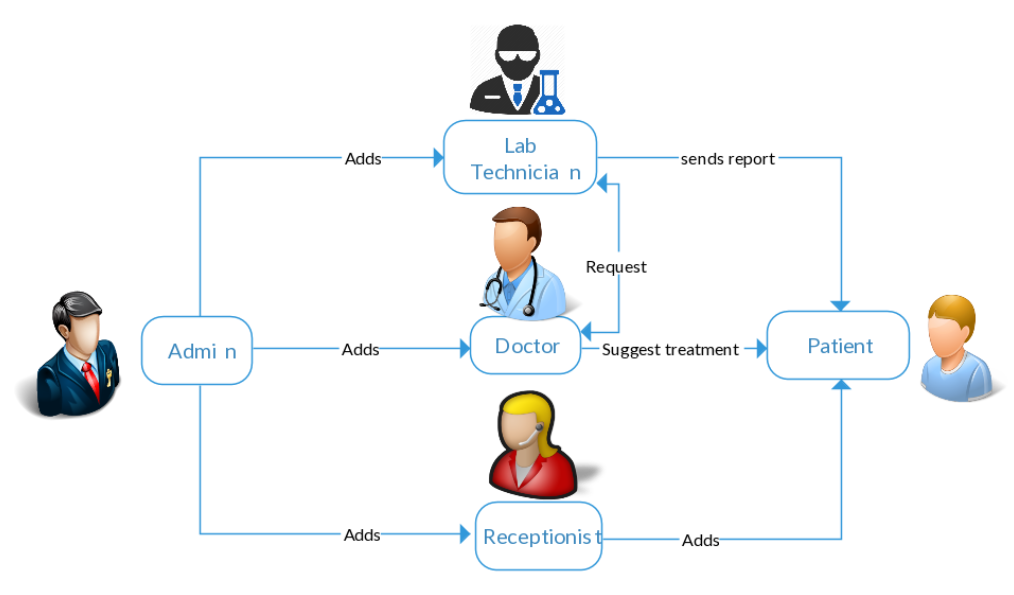
• Implement the following functionalities and flow of data as listed in the diagram.
Project Goals and Objectives
The goals of this project are:
• Decrease transcription turnaround time and reduce transcription cost.
• Decrease waiting room time for patients.
• Improve the quality of patient care.
• Increase the quantity/quality of patient education materials given to the patient.
Assumptions
• Admin is the only one who has an access to create and view new receptionists, doctors and lab technicians in this system.
• Patients can view his lab reports given by the lab technician and the treatment given to him by the doctor.
• If a patient needs to take some tests then the doctor sends a request to the lab technician to perform the tests like Blood test, ECG, MRI, X-ray.
• Lab technician can view new lab tests to be done to the patient suggested by doctor and then he uploads those reports and submit them both to the doctor and patient once the tests are complete.
• Receptionist suggests all the available doctors based on his problem.
Constraints
• All work is able to be completed prior to May1, 2020. The development team must begin and complete all work listed in milestone deliverables within specified dates without variation.
• Resources must be available to execute assigned tasks as defined in the project plan/schedule.
Success Criteria
• Developing the doctor, patient and lab technician module within the assigned time and toolset.
• Implementation of object oriented API for the interaction of doctor and technician and support secure report transfer.
• Developing services that provide safe storage as well as retrieval of secured data.
Performance Indicators
|
Goal |
Action Plan |
Performance Indicator
|
|
Decrease the number of pharmacy phone calls regarding prescriptions. |
Use the e-prescribing feature in PMRDS to eliminate paper prescriptions. |
In six months, there should be 40% decrease in pharmacy phone calls. |
|
Reduction in the transcription cost. |
Use of PMRDS eliminates the need of transcription service. |
In 6 months, the transcription cost will decrease by 45% |
Cost & Budget
|
Stage |
Budget |
Effort(months) |
|
Define |
$20,000.00 |
2 |
|
Develop |
$70,000.00 |
7 |
|
Deploy |
$20,000.00 |
2 |
|
Evaluate |
$10.000.00 |
1 |
|
Total |
$120,000.00 |
12 |
Risk Management
|
Description |
Likelihood |
Risk Mitigation |
Impact |
Contingency |
|
Sponsor withdraws from the project. |
1 |
The team will maintain communication and a positive rapport with the sponsor to minimize the likelihood of conflict-based withdrawal. |
10 |
In the event the sponsor is unable to continue with the project, the team will attempt to identify a substitute, such as a faculty member with an interest in game development.
|
|
Team member withdraws from the project.
|
3 |
The team will uphold a set of behavior guidelines to avoid conflict related attrition. Other sources of attrition are assumed to be unlikely.
|
7 |
If one or two members withdraw, the team will adjust the schedule and requirements. The project is unlikely to succeed if more than two members withdraw.
|
|
Major requirements change during later iterations. |
3 |
The iterative process defers effort investment in requirements prior to implementation |
5 |
The requirements change management procedures will allow the team to evaluate the most appropriate course of action. |
|
Realized level of significantly exceeds estimates for an iteration.
|
5 |
Rapid prototyping and feasibility reviews at the beginning of each iteration will minimize investment in features which are too costly. |
5 |
The schedule change management procedures will allow the team to adjust the schedule as necessary. The methodology also allows for additional team members to be assigned construction duties for complex iterations. |
|
Realized level of effort significantly exceeds estimates for the project.
|
7 |
During the initial planning process, the team will attempt to refine the effort estimates based on actual development progress.
|
3 |
The iterative process with continuous integration is proposed primarily to address this risk. Beyond the first iteration, a functional system that satisfies a subset of the requirements will exist. If one or more iterations must be cancelled, this system will be deliverable. |
Resources
• Analyst- Performs accessibility audits, assessments, application and service testing and analysis of accessibility capabilities; design and recommend remediation tasks.
• Architect- Provides expertise regarding compliance with technology standards, campus ICT strategy, interoperability and reusability objectives across multiple technology platforms supported by campus ICT.
• Designer- Constructs and documents solutions for each specific domain, service and application. May also serve as an implementer.
• Implementer- Tests implements and manages application and service specific accessibility and compliance remediation tasks.
• Project Manager- Manages overall project, including resources, scope, cost, schedule, constraints, stakeholder expectations and communications activities in coordination with team leads and ICT accessibility coordinator.
• Subject Matter Expert- Provides application and service specific expertise, consulting, and vendor coordination.
• Team/Tech Lead- Leads one or more teams, performing tasks including implementation and management of application and service specific accessibility and compliance remediation activities.
• Verification & Validation- Creates plans, quality assurance and solution validation tasks for one or more application and service specific accessibility and compliance remediation activities and scope of work.
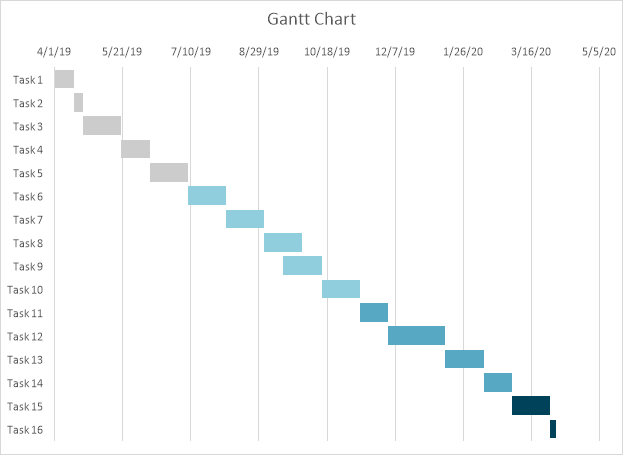
Milestones and Work breakdown Structure (WBS)
|
TASK NAME |
START DATE |
DUE DATE |
DURATION |
DESCRIPTION |
MILESTONE |
|
Task 1 |
4/1/19 |
4/15/19 |
14 |
Project Planning. |
Release 1 |
|
Task 2 |
4/15/19 |
4/22/19 |
7 |
Technical Configuration and Work space set up. |
Release 1 |
|
Task 3 |
4/22/19 |
5/20/19 |
28 |
Database design and analysis for admin, doctor and patient modules. |
Release 1 |
|
Task 4 |
5/20/19 |
6/10/19 |
21 |
Home screen and admin login development. |
Release 1 |
|
Task 5 |
6/10/19 |
7/8/19 |
28 |
Doctor registration screen: UI and services development. |
Release 1 |
|
Task 6 |
7/8/19 |
8/5/19 |
28 |
Patient problems and treatment screen. |
Release 2 |
|
Task 7 |
8/5/19 |
9/2/19 |
28 |
Doctor and patient integrated functionalities. |
Release 2 |
|
Task 8 |
9/2/19 |
9/30/19 |
28 |
Integration, regression testing and bug fixes for doctor an patient modules. |
Release 2 |
|
Task 9 |
9/16/19 |
10/14/19 |
28 |
Patient report screen. |
Release 3 |
|
Task 10 |
10/14/19 |
11/11/19 |
28 |
Receptionist registration screen. |
Release 3 |
|
Task 11 |
11/11/19 |
12/2/19 |
21 |
Lab technician registration screen. |
Release 3 |
|
Task 12 |
12/2/19 |
1/13/20 |
42 |
Lab tests: UI and services development. |
Release 3 |
|
Task 13 |
1/13/20 |
2/10/20 |
28 |
Lab technician to doctor report transfer module. |
Release 4 |
|
Task 14 |
2/10/20 |
3/2/20 |
21 |
Integrated functionality development for all modules. |
Release 4 |
|
Task 15 |
3/2/20 |
3/30/20 |
28 |
Regression testing and bug fixes for all modules as part of final deliverable. |
Release 4 |
|
Task 16 |
3/30/20 |
4/3/20 |
4 |
Project Closeout. |
Release 4 |
Schedule
Deliverables
• Fully functioning PMRDS system that is visually pleasing.
• Provision the Test and Prod infrastructure environments.
• Benchmarks of performance testing.
• The system should meet the acceptance criteria and Negotiation Contract terms.
• Support documents which includes troubleshooting steps for key issues.
• ‘How to doc’ document which will help the end-user in navigation and understanding the functionality of each module.
Project Charter Approval
|
Approver Name |
Title |
Signature |
Date |
|
John Payonk |
Vice President |
|
|
|
Dean Stasio |
Associate Vice President |
|
|
|
Keith Cyktor |
Director |
|
|
References
- Minseon Park, Using Patient Medical Records for Medical Research, Korean J Fam Med (2013 May; 34(3): 159).
- Ben Sutherly, Hospitals must help patients access digital records — or else, The Columbus Dispatch (Sunday August 17, 2014 6:39 AM)
- Tom Murphy & Brandon Bailey, Health-care records are easy targets for hackers, Associated Press (Sunday February 15, 2015 9:19 AM)
- Traber Davis Giardina, Shailaja Menon, Danielle E Parrish, Dean F Sittig and Hardeep Singh, Patient access to medical records and healthcare outcomes: a systematic review, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/amiajnl-2013-002239 737-741 first published online: 1 July 2014
- MARK A. EARNEST, MD, PHD, STEPHEN E. ROSS, MD, LORETTA WITTEVRONGEL, BA, LAURIE A. MOORE, MPH, CHEN-TAN LIN, MD, Use of a Patient-Accessible Electronic Medical Record in a Practice for Congestive Heart Failure: Patient and Physician Experiences, 2004 Sep-Oct;11(5):410-7. Epub 2004 Jun 7.
- CLEMENT J. MCDONALD, MD, RAYMOND MURRAY, MD, DAVID JERIS, MS, BHARAT BHARGAVA, PHD, JAY SEEGER, BS, AND LONNIE BLEVINS, BS, A Computer-Based Record and Clinical Monitoring System For Ambulatory Care, Am J Public Health(1977 March; 67(3): 240–245).
- Moira Stewart, PhD, Amardeep Thind, MD, PhD, Amanda L. Terry, PhD, Vijaya Chevendra, BEd, MSc, and J. Neil Marshall, MB, BCh, Implementing and Maintaining a Researchable Database from Electronic Medical Records: A Perspective from an Academic Family Medicine Department, Healthc Policy(2009 Nov; 5(2): 26–39).
- [Kim Murphy-Abdouch, MPH, RHIA, FACHE, Patient Access to Personal Health Information: Regulation vs. Reality, Online Research Journal, Perspectives in Health Management, Jan 4, 2015.
- RANDOLPH C. BARROWS, JR., MD, PAUL D. CLAYTON, PHD, Privacy, Confidentiality: and Electronic Medical Records, Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association Volume 3 Number 2 Mar / Apr 1996.
- Jinhyung Lee, Yong-Fang Kuo and James S Goodwin, The effect of electronic medical record adoption on outcomes in US hospitals, BMC Health Services Research 1, February, 2013, 13:39
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


