Issues Caused by the Great Pacific Garbage Patch
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Environmental Studies |
| ✅ Wordcount: 1661 words | ✅ Published: 23 Sep 2019 |
GPGP
Great Pacific Garbage Patch
The biggest threat to the Ocean today
Table of Contents
|
Item |
Description |
Page |
|
|
Introduction |
3 |
|
|
What is the great pacific garbage patch? |
3 |
|
|
How much plastic floats in the great pacific patch? |
4 |
|
|
The four plastic categorization types found in the Pacific Garbage Patch |
4 |
|
|
The 10 top items collected |
5 |
|
|
How long till the plastic and some other substances are gone? |
5 |
|
|
Impact on wildlife |
5 |
|
|
Impact on Human life |
6 |
|
|
Impact on Economy |
6 |
|
|
Impact on Climate |
7 |
|
|
Solutions |
7 |
|
|
Conclusion |
9 |
|
|
References |
10 |
Introduction
The discovery of plastics was revolutionary for all mankind due to its many benefits in the material and what it was able to produce. The use of plastic has been cumulative dramatically worldwide since the mid-1970s. In July 2016, Industrial ecologist Dr. Roland Geyer reported to the Journal Science Advances that of all plastics fabricated at 8.3 billion tones, 80% of this total sum is presently waste in the ocean. High rates of plastic waste is due to the fact that most of these wastes are used only once. The guardian reported that, “480 billion plastic bottles were sold globally. By 2016 a production of bottles was as high as a million per minute and 110 billion of those were made by drinks giant Coca Cola”. National geographic reports that, “Each year, an estimated 18 billion pounds of plastic waste enters the world’s ocean from coastal regions. That’s about equivalent to five grocery bags of plastic trash piled up on every foot of coastline on the planet”.
All different types of plastic is accumulated on enormous areas in specific locations. One of these locations is known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. It’s a huge patch of waste sitting on the surface of the ocean that covers hundreds of kilometers across the North Pacific that was discovered in 1997 by Captain Charles. In spotting the Great Pacific Gyre, Moore recalled. “I was confronted, as far as the eye could see, with the sight of plastic. It seemed unbelievable, but I never found a clear spot. In the week it took to cross the subtropical high, no matter what time of day I looked, plastic debris was floating everywhere”. (sciencehistory.org)
What is the Garbage Island?
The garbage island known also by the Great Pacific Garbage patch is the largest of five patches of visible sea debris in the world. A study in Scientific Reports said “the mass known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch is about 1.6 million square kilometers”, approximately one and half the size of Ontario or three time the size of France. It is found midway among California and Hawaii. Most of the debris is insignificant plastic resting on the water that are not instantly visible. However, large amounts of these wastes are made up of nanoparticles, commonly named marine environment experts as, “plastic soup“.
How much plastic floats in the great pacific patch?
The volume of trash is in an alarming number, according to Ocean cleanup site, the weight of the plastic pieces that is resting on the great pacific patch is about eighty thousand tones and approximately 1.8 trillion plastic pieces that is equal to every single person in the world covered by two hundred fifty piece of rubbish.
The four categorization types found in GPGP
For many years environmental scientists and researchers study anything having to do with the GPGP and the most important thing they studied is to identify the types of waste, which they divided into groups and each group including certain types of plastic. According to the Ocean Cleanup there are:
- Solid sheet.
- Fishing nets.
- Disks.
- Fragments.
Top 10 items collected
A brief overview of the main items collected in the GPGP:
|
Items |
Number of items |
Description |
|
|
9,500,000 |
Plastic beverages bottles |
|
|
14,700,000 |
Food wrappers |
|
|
1,091,107 |
Plastic bottle caps |
|
|
10,100,000 |
Tableware |
|
|
7,800,000 |
Plastic grocery bags |
|
|
746,211 |
Other plastic bags (takeout) |
|
|
13,500,000 |
Plastic caps and lids |
|
|
640,000 |
Abandoned fishing equipment |
|
|
52,900,000 |
Cigarettes and filters |
|
|
580,570 |
Foam takeout containers |
How long until this plastic breaks down?
Source: http://www.oceanhealthindex.org/methodology/components/trash-pollution
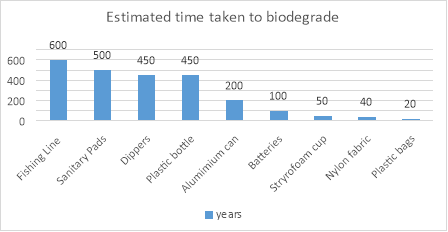
https://www.ecowatch.com/beach-litter-plastics-ocean-conservancy-2581760475.html
Impact on wildlife
It is very sad that we know that the plastic has become a widespread substance in the ocean. This huge amount of plastic materials, some of them partially break down into very small particles that cannot be seen by the naked eye. This phenomenon makes it very difficult for aquatic animals to differentiate between plastic material and food due to the color, size and shape of the substance. Unfortunately this confusion threatens the existence of these animals or causing them a huge destruction upon their behavior and activity. World Animal Protection Canada highlighted that,
“In 2014, an estimated 15 to 51 trillion microplastic particles were floating in the world’s oceans, weighing between 93,000 and 236,000 tones. Marine animals often eat microplastics because of their small size. Plastic contains toxic chemicals, which can increase the chance of disease and affect reproduction. After ingesting microplastics, seals, and other animals can suffer for months or even years before they die”.
Impact on Human life
One of the most polluting and destructive element of aquatic animals and the greatest danger to human life is that these plastics are decomposed for hundreds of years and may sometimes exceed one thousand years until they decompose. As a result of this slow decomposition, these elements are a source of toxins from aquatic animals. This transformation in nature has become the source of the nutrients for these aquatic animals, they in turn contribute to the transference of these toxins to humans through a process called bioaccumulation This process is the absorption of chemicals found in these plastics in the body of the fish and in case Human consumption of these fish. Of course, the chemicals found in the body of the fish are transmitted to humans. This process in the transfer of chemicals from fish to humans is a threat to the lives of humanity.
Impact on Economy
Sea disorder can cause a series of economic effects that both rise the costs related with sea and coastal activities, and decrease the economic benefits derived from them
- Effect in quality of life.
- Effect biodiversity.
- Effect on the quality of food.
- Effect on water and waste purification.
- Effect on tourism.
- Increase on the costs of cleanup of beaches.
- Effect on the economic revenue.
- Effects the health of humans, which exhausted welfare costs for modern-states who must provide health care to their citizens.
- Effect on the recreation or landscape aesthetics.
Impact on climate
• Recycling 1 million tons of plastic equals to 1 million cars off the road in terms of Carbon Dioxide emission. The latest studies shows the concentration of (CO2) in our atmosphere, as of 2018, is the highest it has been in 3 million years.
• According to a new study by a group of researchers from University of Hawaii indicates that plastics produce great greenhouse gases as they degrade. In addition, the study revealing that plastic, when exposed to the elements, releases methane and ethylene – two great greenhouse gases that can worsen climate change.
Solution
To stop ocean contamination and pollution, environmental experts recommend:
- Global policy reforms must be implemented by the United Nations, which sets out the necessary measures that the countries of the world must take control of production and use of plastic and to impose severe penalties on countries that violate these policies.
- All nations must set a waste-prevention strategy to reduce plastic waste individuals, or industries and non-industrial institutions.
- Stimulate countries to educate their communities about how to use plastics and sanitary procedures to destroy them through a proper recycling.
- Governments set “new” tools to help students learn about plastic pollution and encourage them to contribute to preserving the cleanliness and safety of the environment for generations to come.
- Countries should also take initiative by creating motivating policies and procedures that will help corporations do their part to end plastic pollution by stop or reducing the production or use of plastics.
- Encourage associations and non-profit organizations to play an active role in educating communities and guiding them on the dangers of plastics to the environment and humans.
- Implement new innovative technology to help reducing the amount of litter reaching the oceans. Example: types of ocean filters, similar to pool filters that trap plastic waster to be disposed of.
- Encouraging the state and non-profit organizations to work voluntarily to clean up places where plastic and non-plastic waste accumulates in the environment, human or animal, such as watercourses, rivers, seas and oceans.
- Increase awareness by establishing national and international conferences involving scientists, experts and specialists in the field of environment. These events should include all the leaders of the government, private and non-profit sectors. These conferences address the seriousness of the wastes that are deposited in the seas and oceans, which pose a great danger to animals and humans.
Conclusion
The GPGP is a Universal problem increasing each moment as long as plastic is still produced and disposed of into the ocean. Along with the other Garbage Patches worldwide, our globe is facing a crisis of mass proportions to our wild life, ecosystems, and natural food chains for humans, economies and climate. If all nations do not cooperate to eliminate these garbage patches, flora and fauna could be greatly impacted therefore threatening human survival on planet earth indefinitely.
References
- https://www.theoceancleanup.com/fileadmin/media-archive/Documents/Lebreton2018_SciRep.pdf
- https://response.restoration.noaa.gov/about/media/how-much-would-it-cost-clean-pacific-garbage-patches.html
- https://blog.csiro.au/the-oceans-are-full-of-our-plastic-heres-what-we-can-do-about-it/
- https://www.asyousow.org/our-work/waste/ocean-plastics?gclid=Cj0KCQiA68bhBRCKARIsABYUGiekm_LlnVj0XYu39JKBiXsB7X8kwrYDX29ytOQboE7td0bwxGBy3qwaAvHSEALw_wcB
- https://www.enviropod.com/?gclid=Cj0KCQiA68bhBRCKARIsABYUGifcXhLQCCq3zR8VLjaZ4H7yclXnyKVd9UBEnQ8QG29iI3IQ0x4LDCAaAlKeEALw_wcB
- https://www.surfrider.org/coastal-blog/entry/new-study-shows-plastic-as-source-of-greenhouse-gases-potentially-contribut
- https://www.worldanimalprotection.ca/news/how-plastic-pollution-affecting-seals-and-other-marine-life
- http://www.oceanhealthindex.org/methodology/components/trash-pollution
- https://www.ecowatch.com/beach-litter-plastics-ocean-conservancy-2581760475.html
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


