Play Activity on Fine Motor Skill Development for Children
| ✅ Paper Type: Free Essay | ✅ Subject: Childcare |
| ✅ Wordcount: 2892 words | ✅ Published: 18 May 2020 |
INTRODUCTION
Every child deserves the opportunity to develop their unique potential, as a children educator, it is important we provide them the opportunity to explore and develop through play. Play sets the foundation for the development of social, cognitive and emotional knowledge and skills. Through play, children learn to make connections with their peers, and to share, negotiate, work as a team and resolve conflicts, as well as learn self-advocacy skills. Children also learn leadership skills through play. Play is a natural tool that children use to build creativity, for example through acting fantasy heroes. Play creates strong learning opportunities across all areas of child development through play children develop various skills including fine motor, gross motor, cognitive, social and emotional skill.
For the purpose of this assignment, I will devise a play activity on fine motor skill development for children. Fine motor skills involve in smaller movements that occur in the wrists, hands, and fingers. it is an essential to carryout everyday self-care and it encourage independence, for examples fastening zipper, opening a lid, pencil skills including grip and colouring as well as cutting.
Play Activity- Peg Painting
Peg painting is a fun activity for kids; it is great for building strength of fine motor muscle and increase coordination. It also encourages the pinching action between the thumb and fingers which helps in the development of good finger grip.
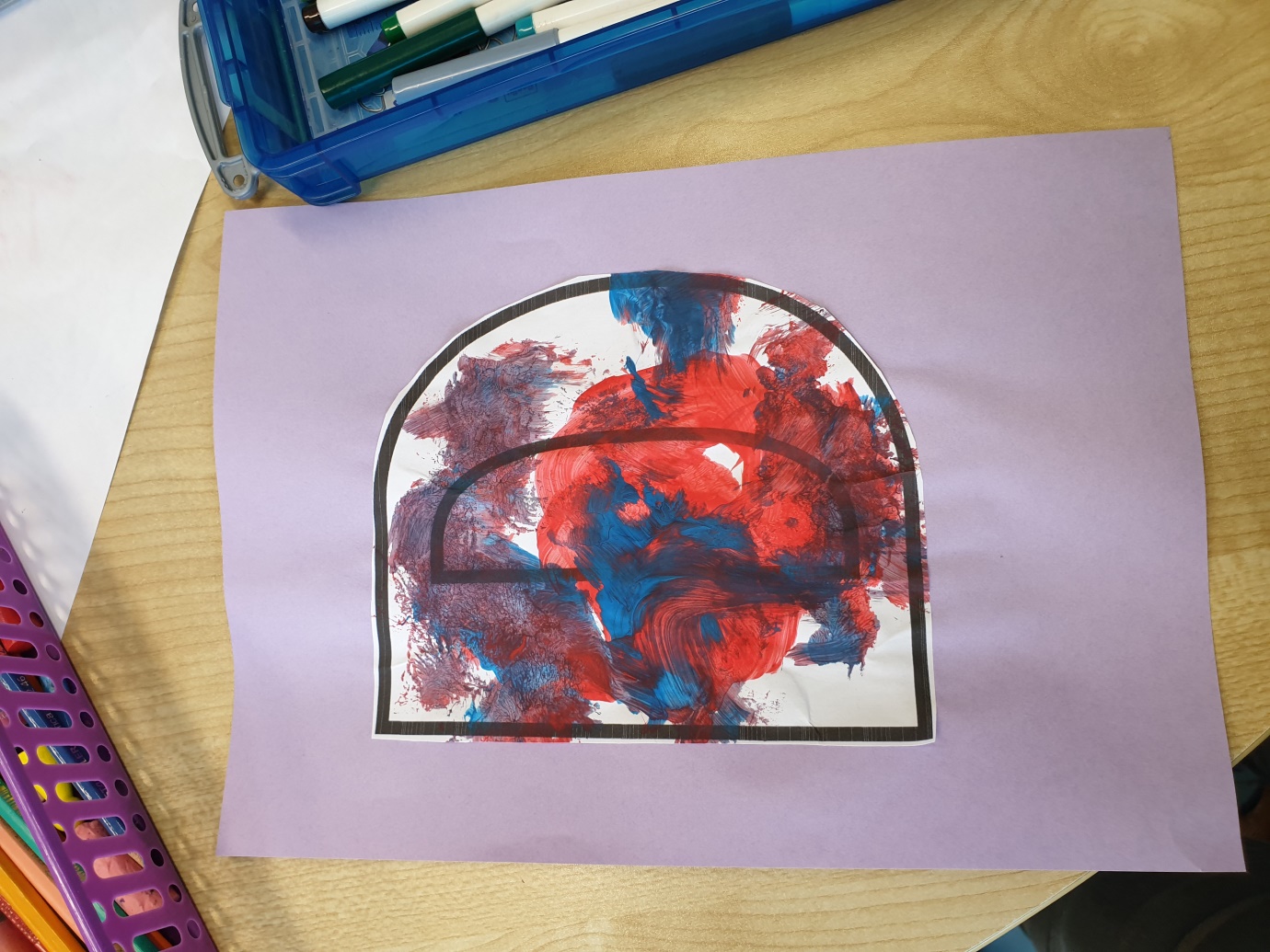
Materials needed– Different letter print/plain paper, makers, paint, some cotton wool, pegs, paint brushes and paint tray. Four children participated in the play activity and the first letter of their names was given to them to paint, using the peg and cotton wool to help with their fine motor skill, after which it was cut out and placed on a plain sheet. See Appendix 1
Learning Development
Eye and hand coordination
Fine motor development
Experimenting and exploring ideas
Letter recognition
Create the ability to master colours
VALUE OF PLAY IN YOUNG CHILDREN’S LIVES
The value of play in the lives of young children cannot be underestimated. During play children develop skills, habits and attitudes that will stay with them throughout their lives. As they play they learn to work together as a team, they learn to cope with frustration, to care about others, to share what they have with others, they practice imagination and fantasies and also to express their emotions. Though play is important for people of all ages, but it is particularly meaningful and important for young children. Actually play is their work, and they give a tremendous amount of energy and effort to it. Relating this to my work placement, the young children I presently work with love their play time, if for example I roll a ball to any of them, I will definitely be the one to quit the game because they derives so much energy from play, they want to do it over and over again ( Dr B M Caldwell 2019).
There are at least three ways in which play is important for young children: skill development, social development, and creativity development. Learning occurs in all areas of development as young children play and learn. I do observe skill development during my stay in the infant room of 18 to 30month old, as I watch them play with toys, moving from one toys to another, they develop various skills as they explore different toys, they also learn to coordinate movements of their hands with their eyes. According to a famous paediatrician, Dr Arnold Gesell, stated that ‘The mind of man is hand-made.’ This statement can be relate to playing with dolls, when they play with dolls, they practice the real life experience with the dolls. Play is significant for young children in the sense that as they play with toys while using their imagination to create something, they discover they is not always easy to put their imagination into reality but its requires a lot of hard work to achieve ones goal (Dr B M Caldwell 2019).
Play with other children is critical for the development of social skills. At first adults are their most important playmates, for example most babies/infants playmates is their parents but soon they become eager to interact with children of similar ages. And it is through such play that they learn how to get along with others, how to interact with their peer, learn to be courageous, develop self-esteem, try being bold and learn to be friendly. At this stage of development the help of early years education is vital to social development of the children, for example by help the shy children to get along and also encourage other children on sharing and team work.
Play is the initiation in which imagination and creativity can be cultivated and demonstrated. The child who pretends to be a doctor, a mother, a hairstylist, a firefighter, a shop keeper is demonstrating some knowledge of these roles and is working through his or her own imagination and real life context. And the child who pick up a doll to change it nappy, fed the doll and put to bed after, is also demonstrating care to the doll just from what she being seeing her parents do or watch from the television show. Role play provides an outlet of creativity for young children.
PLAY THEORY
Though a great number of historical theories have been criticised but they are still relevant today as their influence in the value of play in the life of young children can be over emphasised. For example play is used in everyday activity, from classroom play to break time and to sport activities, play has played a huge role in the life of young children, through play children has learn to communicate effectively, able to control their emotions, solve problems and work as a team. Children use play to mimic adult such their teachers and parents, play has been and will continue to be use as a therapy for children. These are some of the approach that theory has influence and will continue to make impact in the life of children ( Jennesia 2018).
Play and Educational Theory
Maria Montessori is an advocate of adult guided play, she believes that children learn fast using their senses, instead of insisting what to play and how to play on them. In other to promote learning, Montessori suggested that educators should make available all necessary play material for children to explore and discover skills. She believe so much in toys and puzzles, she is of the opinion that children will learn more skilful skills using these toys (Lorina 2018)
Montessori’s Theories in Practice
Educators will ensure that children are given uninterrupted time to play
Children are given support learning opportunities
Children are provided Montessori materials and equipment to explore
Encourage independence, give children the opportunity to choose
Avoid criticism and absorb learning through different experiences
Lev Vygotsky
Vygotsky stressed the importance of relationships, interaction and communication between children, teachers or peers. He also emphasised on the role of language development of in children’s thinking ability, he also see personal and social interaction as inseparable because they complement each other (Lorina 2018)
Vygotsky’s Theories in Practice
Vygotsky’s zone of proximal development describes that children learn through watching people around, some especially their role model. .
The theory of Vygotsky is available to help educators to know when a child needs help, and how to support the child through their learning difficulty..
After from playing with their peers, children also need to interact with their educator, these kind of conversations will help assist them further.
Jean Piaget
Piaget believed that all children’s thinking and development progressed through stages, he further stated that a child must master a stage before that progress to the next stage hence if that cannot master a stage, they will never reach their full potential. Research now argues that thinking develops through complexity rather than stages as believed by Piaget. Piaget also believed in what he called “Concrete Learning”, is the process of how children learn using their five sense, he emphasised that by telling children facts about a thing, without letting them feel, touch or experience all such thing, will not really make sense to them (Lorina 2018)
Jean Piaget particularly stressed on the development of knowledge in children and he is recognised as one of the most influential theorists of child in the twentieth century. He identified two cognition; Accommodation and assimilation. According to Piaget, accommodation is the process whereby child transfer based on their perspective in the environment, while assimilation is the process whereby such believe or perspective is being practice in real world context. For example when children act base on their mindset. Piaget further emphasised on the compatibility of child development and intellectual development in children. He believes that children develop in stages, therefore each stage of development must correspond with the type of play activity for children. Piaget also carried out an observation on three children, to justified how his six stages of child development congruent with the stages a child’s play (Jennesia 2018).
Piaget theory emphasised how cognitive development in children helps their growth development. He is of the opinion that children reflect on things differently compare to adults. According to Piaget children’s development is widely based on quick their brain mature and how active they are able to explore their surroundings. He further proposed some principle hat principle that supports all cognitive development.
Children are active to learning
Children must be allow to explore their environment. The fact that children see and think differently from adults, they should be given the opportunity to experiment their opinion. Though the stages of cognitive development for all children are the same but they progress through this stage differently. Looking at this stages of development in children from infant to school-aged school, their thinking and ability is so different that you will definitely notice the progression, from their think strategy to problem-solving skills.
Piaget believed that children cognitive development can the related to their role model. That is, the progress of a child can be determined by her role model or guidance. Though he stated that their progress will increase as they pass through the stages of cognitive development and maturity (Children’s services 2019)
Piaget’s Theories in Practice
Educator’s advocate should be suitable for the individual child’s stage of thinking. For example; play toy should be provided based on children’s age.
Early years educator should understand each children ability based on their age and intellectual ability.
Educators must ensure that activity offered to children is what they are capable of doing and what is too difficult for them to handle.
Encourage children to participate in their own development by listening to their ideas and providing them the support that they require.
As an educator, we must understand that each child will use play material differently. For example Pre-schoolers will explore differently from toddlers.
It is important to discover what children are interested in, then plan around it and make it enjoyable for them, if children are interested in repeating a play activities, give them the opportunity to do so.
If educator’s can understand how children learn, they will be able to provide a conductive environment for children to learn and explore (Lorina 2018)
Erick Erickson
Erickson theory focused on psychosocial life of each individual. He identified individual uniqueness, that each person is different in development hence each child such be observe as a individual in other to meet their needs. He develop eight stages of development and stressed that there may be issues to overcome before a child can proceed to the next stage.
Erikson’s Theories in Practice
It is inevitable that educators will form attachment with children
As educators we learn to respond warmly to children’s needs.
We must ensure to talk to babies politely, if we cannot attend to their needs immediately.
Educator’s must ensure to offer support to children and encourage to do things by themselves
To make available different play material for children so that they can have choices and able to explore.
Allow a child to be ready for toilet training before training them.
Educator’s must also ensure there is a enough space for children to play
Give children the opportunity to decide on what to do or play with.
Invite them when deciding a play activity and allow them to say their opinion
Do not interrupt them during play and give them enough time.
EVALUATION
Jean Piaget states that “Play is the answer to how anything new comes about.” Play is the corperate language of childhood. Children develop their communication skills through play, they learn to understand each other, during play they develop emotions and try different skills. Play is the process through which children perceive the world and make sense out of their experience (KCCCI 2019)
In my opinion and from what I have learnt all through the course, play is not just play as we think, from this course I have learnt how play is important to children, as an educator how we can use play to observe and discover if a child is experiencing any learning difficulty. Play is not just play, there are various ways in which play impact the life of children, physical will help with their muscles and bone development, while social play helps children to how to treat other, they learn to share and to co-operative with their peers.
Play has also helped children to develop their communication skills, children who are very sky and timid as often been cheerful through play. An example of this is from my work experience, there is a TC who was very shy and hardly play or talk to any of her peer, any time they invite to play she always nod no but one day she adhere and join them, they all agreed to pretend play and she offered to be the doctor, the role helped her because she had to choice but to communicate with the patient, as she was acting this role, looking at her you can see the excitement, this is one of the way play can help a child communication skills.
CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATION
I have learned and discovered the value of play in the life of young children and how educators can help in the development of children. Children’s play has fascinated educators, child psychologist and theorist for centuries. In my opinion, children should be provided with conductive environment, including resources and equipment needed to explore and experiment their intellectual ability in other to reach their potential and development all necessary skills needed as they grow.
In Conclusion, Play is fun for children and can be enjoyable if less interrupted by adult. Though adult should be around to supervise play or even involve in a group play but children should also be given time to play, for example ‘free play’ where children can choose an activities to do on their own, through this they learn decision making.
The importance of the early years education has been emphasised through research as a great start for children education, children learn through everything that they do, play, talk, see, hear, share, smell or even taste.
APPENDIX


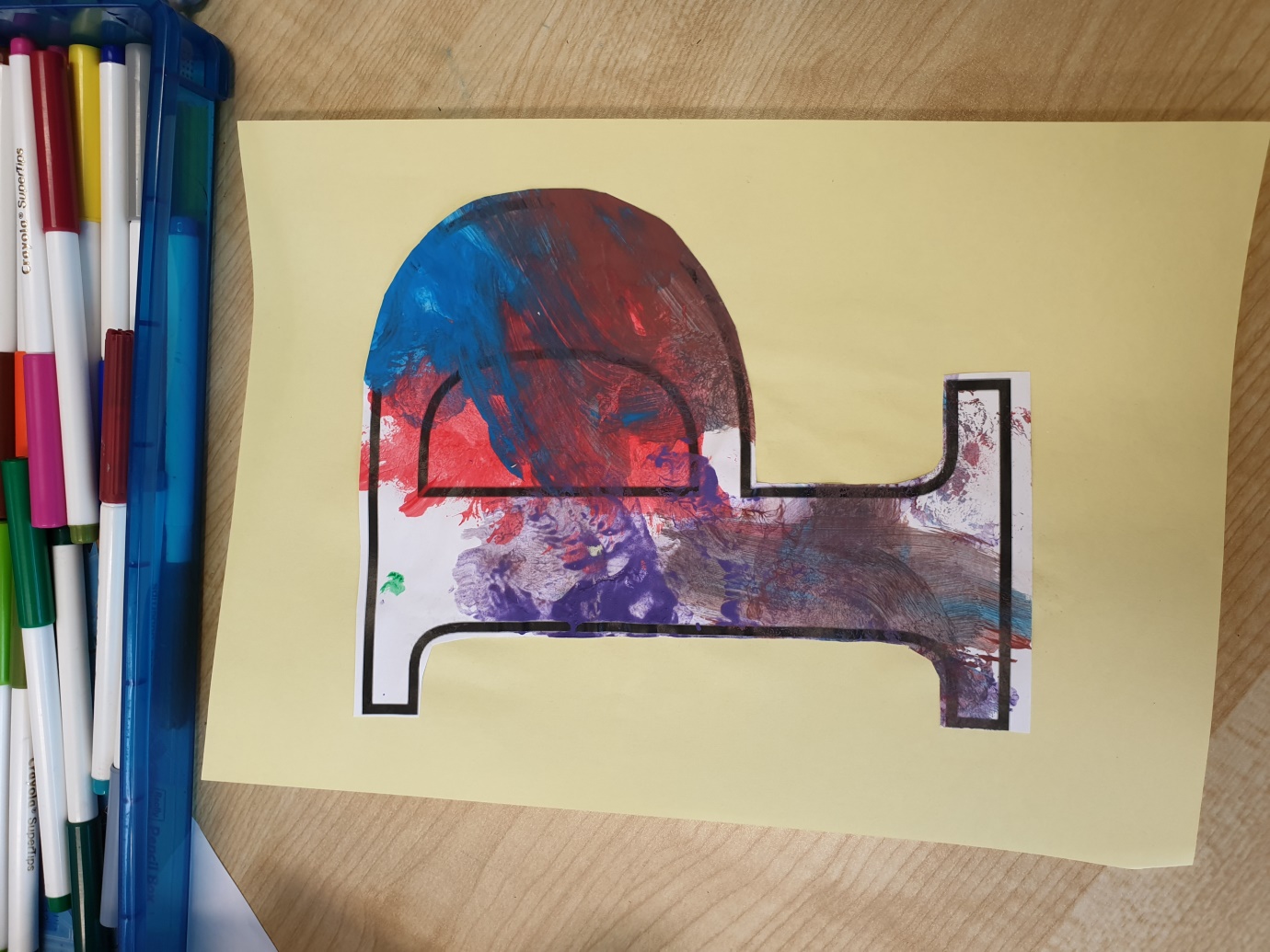

REFERENCES
- Aussie Childcare Network (2019) Child Theorists and Their Theories in Practice. Available at https://aussiechildcarenetwork.com.au/articles/childcare-articles/child-theorists-and-their-theories-in-practice [Accessed 5 April 2019]
- Fisher Price (2019) Importance of Play in Early Childhood Education.Available at: https://www.fisher-price.com/en_US/parenting-articles/playtime-and-toys/importance-of-play-in-early-childhood-education [ Accessed 11 April 2019]
- Jennesia Pedri (2019) Theory of Play. Available at: https://www.jennesiapedri.com/theories-of-play/ [Accessed 9 April 2019]
- Learninh4Kids (2019) Available at: https://www.learning4kids.net/play-activities-by-age/ [Accessed 24 March 2019]
- Sielearning (2019) Child Development Thoerist. Available at: https://sielearning.tafensw.edu.au/MCS/CHCFC301A/12048/chcfc301a/lo/12020/index.htm [Accessed 11 March 2019]
- Unicef (2019) The Lego Foundation. Available at: https://www.unicef.org/sites/default/files/2018-12/UNICEF-Lego-Foundation-Learning-through-Play.pdf [Accessed 15 March 2019]
Eduloxsa (2019) It’s Child’s Play: Why Play in Child Development Is so Important. Available at: https://www.edubloxsa.co.za/why-play-in-child-development-is-so-important/ [Accessed 20 July 2019]
- Childcare Committee County Kildare (2019) Learning and Developing Through Play. Available at: https://www.kccc.ie/Quality/KCCC-Quality-Outreach-Programme/Learning-and-Developing-Through-Play [Accessed 15 March 2019]
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


