14-19 Age in Education and Teaching: Policies and Legal Framework for Teachers
| ✓ Paper Type: Free Assignment | ✓ Study Level: University / Undergraduate |
| ✓ Wordcount: 6970 words | ✓ Published: 06 Jun 2019 |
Carry out a research and write a report on the following:
• National policies and initiatives for the education of the 14–19 age range
• Legal framework and key legislation relating to teachers working with the 14–19 age range
Include at least 2 of the following current national policies and initiatives:
- Widening Participation, Success for All, Skills for Life strategy, 14-19, Curriculum (Curriculum 2000), Every Child/Learner Matters, Apprenticeships, meeting Ofsted schools standards, addressing needs for social and workforce developments, blended learning approaches, Wolf Report, PLTS (personal, learning and thinking skills)
In this essay we will research on how important it is to give the opportunity to all Every Child/Learner the opportunity to be protected by by national legislation. These legislations should allow all children free safe to learn.
Every Child/Learner Matters was the England and Wales government initiative. It was launched in 2003 shortly after the death of the young lady named Victoria Climbie from the Ivory Coast. Every Child/Learner Matter (ECLM) was the most significant policy that has been initiated in relation to children’s service in the last decade. Every child/Learner Matter was policy of three government papers that led to the Children Act 2004. ECM covers children but also young adults up to the age of 19 or 24 for those with disabilities. Anyone working with children or if you are parent so you can come across with ECLM. It has been created in order to be applied to well-being of every child or young adult from their birth until they reach the age of 19. The main objective is that every child no matter of their individual circumstances or background should receive support throughout their life. There are five key principles attached to the policy which the Government believe every child should have support with. These principles are:
- To be healthy
- To stay safe
- To enjoy and achieve
- To make a positive contribution
- To achieve economic well-being
This policy is functional to everybody who is charged at any capacity of children or young adults until the age of 19 and also for young adults with disability. This includes parents, professionals such as teachers, social workers, foster carers, hospital personnel, and the police, and also voluntary groups or charity with who works with children. in order to make sure each child get the best start in life.
The best way to put this policy in practice is to allow those in charge with children to meet through seminar, conference, or workshops in order to share experience and information about how they can work together to to promote the needs of children and also help them gain the most out of life. This policy also benefits children or young people by asking them to share their issues that can prepare other children avoid or tackle them in case they appear on their ways. This is a good opportunity for children or young people knowing that their voices and views can be heard. This is also good news for families who may think that their children’s needs may be forgotten by the society. This policy has been of course implemented but in order to be efficient, children or young people need to work in partnership with different organisations or groups.
Since the implantation of this policy the government has appointed children’s commissioner in order to help with this process. The responsibility of this commissioner is to give children and young people a proper opportunity to have their views and thoughts known.
This policy is really done in part through work with community groups and children’s organisations groups, giving meticulous focus to the needs of those deemed to be in a vulnerable position.
This policy is overall welcome by those who are working with children and young people every day.
Meeting OFSTED school standard
The office for Standards in Education (OFSTED) is a government agency, headed by Her Majesty’s Chief Inspector of Schools. Its responsibility is to inspect and report on English local education authorities LEAS). LEAS preserves schools, sixth form colleges and other education for 16-19 years old. It also maintains teacher training instruction and early year child care minders. LEAS is also responsible for inspecting independent schools when they apply for registration or when there is a concern about standard.
OFSTED Inspection: OFSTED is in charge of inspecting state schools every six years. When the school is doing well, it may expect a short inspection but when the school is not doing well the inspection can be full taking in account all national curriculum subjects and other aspects of the school’s life. The inspection team essentially report on the quality of the work produced by the school, the educational standard accomplished in the area such as financial resources made available to the school have been managed properly and also the spiritual, moral, and cultural development of pupils at the schools. Before an inspection the school has to prepare for this event. The school has to organise a meeting between the inspector and the parents of the children in order to allow the inspector to hear the parents view. The school director and all the staff are not allowed to attend the meeting in order to allow the children’s parents to express themselves freely.
After the inspection the inspectors meet the governors of the school in order to discuss their findings when the inspection is over within six weeks. The inspectors have to send a written report to the governing body, to the LRA and the OFSTED. The copy of the report is also sent to the parents. The full report and the summary have to be available for anybody who wants a copy. When there is a concern about the standard in a particular school the inspectors place school in one of the three groups: There schools requiring special measures (which can lead to the schools to be closed down), the second group is the schools with serious weaknesses (these schools are given a year to improve), and the last group is the schools with underachievement. In this case the governors of these schools have to make detailed proposals about how they will improve their weaknesses. This type of schools must be given extra support by the LEA and they have to be monitored closely by the LEA and the OFSTED inspectors.
The parents who have their children in one of these schools have to read the copy of the full report. The most important section is the list of the recommendations. In order to best understand, parents have to ask the school for the copy of the OFSTED framework documents and handbook which contains the guidelines on how inspector monitors school’s quality. Parents have to check the governors’ action plan which normally have to be sent to the parents. (GOV.UK, 2011)
- Include at least 2 of the following current provision, eg National Curriculum in schools, focus on academic performance (GCSE/AS/A Levels), national vocational qualifications (NVQ), work-based learning post 16, Foundation Learning, Key Skills transition to Functional Skills, ‘taster sessions’, age restriction on workplace and work-based learning, structured work experience, academies, city academies.
Based on the targets set by by the National Curriculum.
National Curriculum in schools: In England, state schools have to teach a range of subjects. This has been established in 1989in order to make sure that the same standards of teaching and learning are applied nationwide. The National Curriculum covers learning for all children aged 5-16 in state schools and set out:
- Which subject should be taught
- The knowledge and understanding your child should achieve in each subject base on the child age
- Targets: so, teachers can measure how well each child is doing in each subject
- How information on each child progress should be passed to the parent.
The National Curriculum has been divided into four stages that children are going through during their school life. Key stage 1 is designed for year 1 and 2for primary school. Targets defined in National Curriculum are assessed at the end of each key stage.
See the following table
| Key stage 1 | Ages 5-7 | Years 1 and 2 |
| Key stage 2 | Ages 7-11 | Years 3, 4,5, and 6 |
| Key stage 3 | Ages 11-14 | Years 7, 8, and 9 |
| Key stage 4 | Ages 14-16 | Years 10 and 11 |
The programme of learning sets out what teachers have to teach in every subject during each key stage. The programme of study sets out four teaching requirements which apply across all subjects. These requirements specify that teachers should:
- Use language effectively
- Use information and communication technology (ICT) effectively
- Follow health and safety guidelines
- Provide teaching including different ethnics minority viewpoint
A new National Curriculum has been introduced for secondary school’s pupils (learners in key stages 3 and 4 aged 11-16). It has also been introduced for years 7 and 8 and also started to be applied for year 9 since September 2010. This new National Curriculum is to give more flexibility to schools and teachers regarding what they teach this means that teachers will have time to plan their lesson, it also gives teachers more opportunities to assess their learners and provide more support for those who have learning difficulties. There is another objective of this new National Curriculum. This objective is to make sure that learners who are interested in new national diplomas receive support and guidance when approach the end of key stage 4 (aged 16) in order to help them find a path that interests and motivates them. The new National Curriculum also embraces two non-compulsory programmes of study which are wellbeing and financial wellbeing (BBC, 2007).
National Vocational Qualification (NVQ): It is a work baked qualification that identifies the skills and knowledge a learner requires to perform a job. The candidate has to exhibit and prove their competency for the job they have chosen. NVQ provides different advantages. It is a flexible way to become in the workplace with without a n examination. It is also a practical demonstration of the individual’s skills, knowledge, and understanding. NVQ is also the opportunity to demonstrate that you have met a national standard for an occupational role (Anon., 2001)
- Include at least 3 of the following legal framework and key legislation: equality and diversity, Equality Act 2010, Every Child/Learner Matters, Equipping our Teachers for the Future, CRB requirements, duty of care, KS4 requirements, Equal, inclusive practice, education acts, Kennedy, Wolf
Equality and Diversity:
- Equality: Is ensuring that individual or groups are treated equally but on the basis of their specific protected characteristics such as race, gender, disability, religion, or belief, sex orientation and age.
- Diversity: its objective is to recognize, respect, and value peoples’ differences to contribute and realize their full potential by promoting an inclusive culture for all students and staff.
As I wrote in my previous assignment, promoting equality and diversity is very important for the learners and the teachers. When you promote equality and diversity, it is for the benefit of students. It creates multi-cultural society in the classroom. Student can learn from his peer culture or background. As the world is now globalizing via internet promoting equality and diversity at school enables learner to better know each other and create positive learning relationship. By better knowing each other students can offer mutual support to each other by helping those with difficulties. By encouraging equality and diversity the school creates a good reputation worldwide and good references in the global world. With the development of the internet communication between people became very easy. People from different social groups can now interact on the internet within minutes. Some social media such as Facebook and Twitter allow people to share information on the internet. People from different countries can exchange information via internet. The use of the internet allows everybody to know about the happening events, situation, and living conditions of all people in all countries. (KB, 2007)
Equality Act 2010: : It has been implemented in October 2010 to replace all existing laws in order to fight against different types of discrimination at school, workplace and the society. The Equality Act, 2010 prevent discrimination against race, sex, gender, sexual orientation religion, belief age, ethnicity etc. Based on the Equality Act 2010, everyone should be treated fairly.
Inclusive Practice: The term inclusive practice refers to the principle that a service or school has to be responsive to the needs of all users or students and that diversity should be acknowledged and respected. Inclusive means that schools or services must not discriminate against people or student or even treat them unfairly.
Word count – 1500 -2000
Evidence: Report
Drawing on your research, write a reflective journal on your own role and responsibilities in relation to working with the 14–19 age range and evaluate the impact on your own practice of the legislation relating to working with the 14–19 age range
- Address at least 4 of the following role and responsibilities in your reflective writing: working within organization policies and procedures, meeting requirements of compulsory sector, acting in loco parentis, promoting inclusive practice and student inclusion, challenging inappropriate behaviors, celebrating successes, encouraging self- and peer assessment, encouraging reflective practice, enabling opportunities for building study skills and functional skills
- Also, address how at least 3 of the following legal requirement impact on your practice: recognition of qualified teaching status for teaching 14-19, establishing relevant guidelines and codes of practice, sector-specific CRB checks, meeting Ofsted schools standards, up-dating personal and professional skills when dealing with young people, retraining in required personal skills, developing appropriate learning and teaching strategies.
: Working within organization policies and procedures: Based on what I wrote in my previous assignment, as a teacher my responsibilities are to apply the policies of the school where I teach in order to promote equality, diversity and inclusion. I have to treat all my students fairly. If a student has a specific need it is my responsibility help him or her to the administration in order to create a contact between the student and the specialized agency. I also have to make sure that during the lesson all the students have a clear understanding of the lesson and for those who have visual impairing I have to the colours to help them clearly for the projection. By creating group activities students will have opportunities to develop a friendly relationship.
Challenging inappropriate behaviours: As I said in my previous assignment, negative behaviour is the fact that someone behaves in appropriate way such disruptive in the classroom or the school environment. In order to challenge this kind of attitude it will be better to prevent it before it occurs. To do this as a teacher I have to identify the reasons why students may have negative behaviours. The reasons of challenging behaviours may be medical such as autistic seeking attention because they might be frustrated, bored, finding difficult to manage a particular task. In the case of medical reason as a teacher I have to seek for help from line manager. In attention case I have to pay attention to that particular student or provide a peer support. I have to make sure that the student is well monitored and I also have to talk to him. As a teacher I have to talk regularly to my students if they seek special supports so that I can provide advice or refer them to specialized agencies (Cumann Muiteo, 2012). That will also promote equality and diversity in the school.
Celebrating successes: : It is very important for the school or an organization to celebrate every achievement. For example, as a project manager when your team achieve an important project it is important to celebrate the team so they can perform well for the next project. In the case of school celebrating achievement will motivate students to achieve more in order to be celebrated. For example, school can organise off school dinner, so that all students can socialize together. By socialising together, the success celebration also promotes inclusion practice.
Promoting inclusive practice and student inclusion: In my previous assignment I developed that as a teacher in order to promote student inclusion you must be creative, caring, patient, innovative, resourceful, structured, and flexible. The school have to collaborate with families to assist students of all ability levels to achieve many skills. All teachers at the school and the rest of the staff have to work together to teach and reach each student. When planning a successful inclusion teachers have to take in consideration allocating the time, resources, strategies, interventions, and appropriate students supports. As a teacher in order to promote inclusion I need to work with the whole class, small groups, and individual students. The school has to inform teacher about which students direct skills instructions. I need to have expectation for my students and always highlight their strengths. This practice will create student’s self-confidence (universitiesuk.ac.uk, 2014)
Establishing relevant guidelines and codes of practices: Teaching and learning activities in the school have to be guided by the codes of practice for teachers and students. The responsibilities of teachers and students are considered to be reciprocal so that the responsibilities of one group implies the rights of the other. Both teachers and students have to comply with these guidelines and codes of practice. In the case students, they have to be aware of the policies and practice of the school, and the rules and regulations regarding the use of the school computing, library, and other facilities of the school. Students have also to meet the deadlines of the submission of their work. Students gave to accept joint responsibility of their learning and respect the working environment of others in all the premise of the school. Students also have to respect the rights of all the staff members (monash.edu.au, 2007). In the other hand as a teacher I have the responsibilities towards my learners. I have to make available all the policies and regulations of the school to my learners. I have to develop my student’s knowledge, understanding, skills, and attributes as defined in the school course by providing them with my teaching programs, course materials, activities, and tasks appropriate to development of their attributes. I also have to provide my students with opportunities to be involved in the structuring of their learning experience and also encourage them to take joint responsibilities of their learning. My responsibility is also to take in consideration my student’s prior backgrounds, knowledge, and abilities when I am planning my teaching activities. I have to help my learners to learn from their assessments tasks by providing them timely and constructive feedback. I have to make myself available in order to discuss assessment results with my learners. I have to encourage and enable my students to evaluate their own and each other work critically. As teacher I have to provide advice and support to those who are in need (universitiesuk.ac.uk, 2014).
Sector- specific CRB check: Everyone who is employed directly or indirectly by the school is eligible for an enhanced CRB check because there is a possibility to be in contact with children. CRB or DBS is designed as a safeguarding measure. It is a response particularly to the Sohams murders in 2002. CRB check will include any unspent/spent convictions, cautions, warmings, and reprimands an applicant may have received (criminalrecordandbarringservice.co.uk, 2004). CRB check also include any additional information police deem worthy and barred list searches if they are appropriate. As a teacher I have to comply with the CRB check. It will give the opportunity to my employer to acknowledge my criminal record because I will be in contact with young people all the time.
Developing appropriate learning and teaching strategies: As a qualified ICT teacher it is my responsibility to develop appropriate teaching and learning strategies based on a specific need of my learners. There different types of teaching and learning strategies. These strategies include activities-based strategy. It is a strategy that helps student to improve achievement by engaging them in individual or group experiential learning opportunity such as purposeful conversation, project planning, hands-on enquiry, and analysis, and product creation (Gauntley, 2005). As a teacher I can also use direct-instruction strategy. That is a personal and timely intervention of the teacher I am. My words and actions have to guide and model the learning, whether to a large or small group or to an individual student. With the growth of new technologies, as an ICT teacher, I also have to use ICT-based strategies. It will help students to improve their learning by attaching the power, innovation, and potential of information and communication technologies. The use of ICT includes digital and or electronic data and applications in order to create, modify, and transmit information. Word processing, database, and spreadsheet software improve productivity while the internet, email, and web browser improve telecommunication. The use of ICT also includes the of desktop publishing and graphic and photographic programs heighten visual display. I will advise my learners to do some researches through the internet which can help them to gain additional information on the top of what they got from my direct intervention teaching strategy.
Word count – 1500 -2000
Evidence: Reflective writing
(1.2)
Task 2: Analyse the relationship between schools and other providers of learning for the 14–19 age range
Research and write a report on at least 3 of the following: widening choices, developing links to industry, alternative to academic for those wishing to continue formal vocational education, more specialized teaching, opportunities for applying learning in employment context, increasing level of challenge, higher-level qualifications, working towards providing skilled workforce, increasing flexibility of provision.
Word count: 500 – 750
- Widening choices: The NFER recently produced a work relating to 14-19 years old education in order to better understand how young people of this age group are navigating through complex choices of qualification and location of the study. Recently there were changes in year 14-19 curriculum. These changes mean that young people have to make decision at this stage across four path-ways. These path-ways are: GCSE and A Level, Apprenticeship, Diplomas, Apprenticeship, and Foundation Learning Tier. Young people have also to decide on the specific subjects they will study and the location of that study. Schools and colleges have to support those young people who did not choose GCSE and A Level pathway in order to make successful transition post 14, post 16 into further education or employment. The research of NFER showed or informed how people make or helped to decisions in the context of wide range of available options. These options have been created as a result recent policy developments. They include:
- The Increased Flexibility Programmed IFP) introduced in 2002. This programmer encourages schools, colleges, and training provider to work in partnership in order to provide vocational learning opportunities for students at key stage 4
- The young Apprenticeship programmer: It has been introduced in 2004 through which young people work to a level 2 qualification and undertake a prolonged period of work experience in an employer organization
- The skills for work: It has been designed in Scotland in order to provide a vast range of learning opportunities for young people. This programme allow young people of school age to take courses which will help them to develop their skills and knowledge in the work environment. (nfer.ac.uk, 1998)
- The introduction of Foundation, Intermediate and Advance Diplomas: It helps young people while they may be studying to undertake professional training.
- Developing links to industry: Working closely with industry enables students to be up-to-date with the industry trends. Schools have to develop learning approaches that are industry-led, benefitting from practical work. During the learning time examples and courses have to be designed in order to encompass current practice and demands. The collaboration between schools and industry improves student’s employment prospects.
- Increasing flexibility of opportunity: The increased flexibility of provision for year 14-16 programme has been introduced in 2002 by the department for education and skills DFES) in order to provide vocational learning opportunities at key stage 4. The increase flexibility for 14-16 year olds programme is provided by means of partnerships between a Lead of partner, which uses to be a college of Further Education, partner schools, and sometimes other providers. These providers can be training provider and employers. This partnership has to work towards a number of targets identified relating to achievement of qualifications, progression after year 11 and attendance through the programme.
Working towards skilled workforce: As an ICT teacher I have to promote the efficiency among my learners because from the school students have to know how to guide their life in professional way. In order to show my students how to be good future professional I have to set my teaching agenda through the year or term. I have also to keep my teaching simple in order to help my learner to understand what I am teaching. I also have to encourage innovation among my learners for example for those who have a very knowledge of ICT. To be a good teacher I have to listen to students through unnamed survey that can help to improve the area where necessary.
Evidence: Report
(3.1)
Task 3: Analyse teaching, learning and assessment approaches for use with 14–19 learners
- Your analysis for Teaching and learning should address experiential(Kolb),ILT(information and learning technology) and at least one of the following: learner-centered to develop cognitive and psychomotor skills(Bruner),multisensory approaches,workshopsfor practice of skills,project work to develop research skills(GENERIC)
David Kolb has published his learning style model in 1984. After the publication he developed his learning style inventory. Kolb’s experimental learning theory is based on two levels: a four-stage cycle of learning and four separate learning styles. The vast majority of Kolb’s theory is concern with the learner’s cognitive processes. David Kolb acknowledge that learning involves the acquisition of abstract concepts that can be applied flexibly in a range of situations (Mcleod, 2013). According to Kolb (1984, p. 38), learning is the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience.
The experiential Learning Cycle: Kolb ’experiential learning style theory is characteristically characterised by a four-stage learning cycle in which the learner touches all the bases.
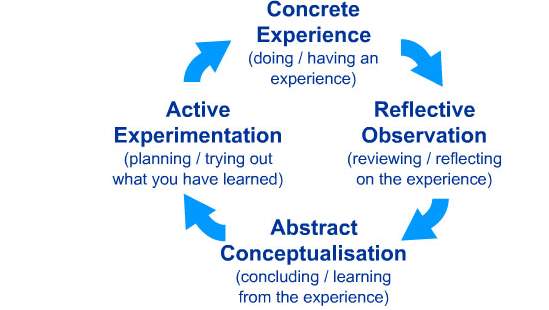

(Mcleod, 2013)
Effective learning is seen when the learner moves through a cycle of four stages:
- Having a concrete experience followed by: 2) observation of and reflection on that experience which leads to:3) the formation of abstract concepts (analysis) and generalization (conclusion) which are then: 4) used to test premise in future situation, leading to new experience
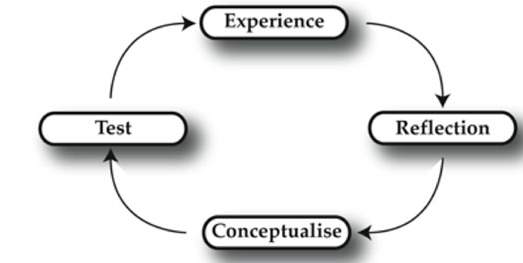
Kolb (1974) saw learn as combined development with every stage jointly supportive of and feeding into the next. There is possibility to enter the cycle at any stage and follow it its logical sequences.
However active learning happens when a learner is capable of executing all four of stages of the cycle.
Learning style: Kolb’s’ learning theory (1974) sets out four different styles. These styles are based on a four-stage learning cycle. Kolb clarifies that different people naturally prefer a certain different learning style. People [referred style can be influenced by by different factors such as social environment, educational experience, or the basic cognitive structure of the individual.
Information and Learning Technology: As an ICT teacher I can use technology in different ways to enhance my teaching practice. For example, I can show documentary or film during my teaching session, I can use PowerPoint presentation. I can also use technology to research on the internet or to keep records of students’ progress. I also use the technology to support my teaching practice and my students learning in or out of the school. The use of ILT during our teaching practice has a broad of benefits. It gives the opportunity to students to access a variety of resources, it makes teaching of higher quality, it organizes our course, it provides an efficient keeping of our student records. It also provides support to student basic needs. ILT also contribute to build on learners existing IT skills.
Workshops for practice and skills: As an ICT teacher I have t keep update the growth of the technology. In order to improve my teaching practice, I have to participate to workshops. These events will help me improve where I have some weaknesses. The workshops will give me the opportunities to meet my ICT teacher’s colleagues who have more experience in the teaching. I will also use this opportunity to ask questions .
Assessment is an integral part in all GCSE courses of students’ teaching and learning. When teachers are planning and delivering GCSE courses they need to use assessment in different ways. Assessment is not only done formally to meet the requirements of a qualification. Teachers use formative assessment for an ongoing basis in order to help their students to achieve the best of their abilities. Assessing students can be by questioning. Questioning is the centre of teaching. When a teacher makes a good use of questioning, that is more than asking questions in lessons. Teacher needs to ask himself whether the questions in the classroom make cognitive demands on the students. By asking probing or cognitively demanding questions is indispensable to developing students’ thinking skills. Teachers have to use a mixture of open-ended questions in order to het students involved in classroom. Teachers have also to connect teaching to the real world. They can support learning knowledge application and knowledge transformation by putting learners’ prior knowledge into context or by relating learning to real life situations. To do this, teachers have to provide opportunities for learners to feign a real-life problem in the classroom.
Another approach to teach 14-19-year olds is to raise their confidence. Teachers have to help their students to develop self-confidence. To do this, teachers have to start with classroom activities. During these activities they must (students) start with relatively easy questions which can become more difficult as long as learners progress. The other way is to students to develop independence of thoughts and learning by allowing them to express themselves during the classroom discussion. Teachers have also to vary their teaching style by providing opportunities for group work as well as encouraging student to work at his own in order to develop individual application of knowledge.
Teachers have also to develop group cohesiveness. 14-19-year olds students are very self-conscious. In this year gap they can be sensitive as to how they relate to others and also can be sensitive to how others perceive them. Sometime some students may not want to accept each other maybe because they lack social skills to interactor work together. As a teacher you have to enable a sense of a team or togetherness in the classroom. The role of a teacher is to foster an atmosphere cooperation within your learners. Another way to promote group cohesiveness is to organise pre-lesson session where whole classroom has to part in a practical discussion. Teachers have also to encourage students to take responsibility in their learning.
Assessment refers to the different methods or tools that a teacher or trainer can use to evaluate or measure the academic readiness, learning, progress, skills acquisition or educational needs of a learner (edgeglossary,org, 2015). A teacher has different options in order to assess his or her learner’s knowledge or understanding on a particular subject. My analysis will be focused on two types of assessment such as initial and diagnostic assessments. Initial assessment: It is a relatively brief assessment at the beginning of the programme in order to establish a starting point for learning. For example, initial assessment in literacy and numeracy is to establish student’s level of confidence in English, maths or ICT in order to make suitable proposal about the programme of functional skill teaching (toolkits.excellencegateway.org.uk, 2010). As an ICT teacher I will use initial assessment to acknowledge the basis understanding of all of my students in ICT. As I wrote in my previous assignment. during an initial assessment on a learner I realized that a student has a partial visual impairment. I met this learner needs by providing large font on my slides and on written material as well as using a colored paper of their choice to aid in their learning. I acknowledged this particular need before the course started that why I was able to plan for it. This is important so that learning can take place and any barriers to learning can then be eliminated. As a teacher it is my responsibility to create a safe environment for my learners that will promote equality and value diversity. Therefore, learners need to feel welcomed, valued and part of the group in a classroom setting or environment. Identifying learner’s needs during initial assessment will help both the learner and teacher alike.
Formative Assessment: It is the monitoring of the student’s learning in order to provide on-going feedbacks. These feedbacks can be used by the teachers to improve their teaching or by the students to improve their learning. Formative assessment is a variety of methods that teachers used to conduct in-process of evaluation of students’ comprehension, learning needs, and academic progress during a lesson, unit, or course. This process helps teachers to identify concepts in which students are struggling, to understand skills in which they have difficulty or lesson standards where they have not achieved in order to make adjustments to lessons, instructional techniques, or academic support (Reform, 2011).
Use of peer-assessment: It is the fact that students taking responsibility for assessing the works of their peers based on the set assessment criteria. They can so provide feedback to their peers. (University of Reading, 2013)
Self-Assessment: is the process of looking in aspects in which as student you are not performing well. It is one of the motives that drive self-evaluation, along with self- verification, and self enhancement. According to Sedikides (1993) self-assessment motive will prompt student to look for the information to confirm their uncertain self-concept rather than certain self-concept. Students also use self-assessment to improve inevitability their own knowledge.
Summative assessment: It is the assessment used to measure students learning at the end of instructional term. This learning is compare against some standard or benchmark.
Online assessment: It the use of technology in different ways of assessment such as educational, assessment, and health assessment. This type of assessment uses computer connected to a network. It includes multiple choice, online submission, and computerize testing.
Project based to allow building of understanding: Project based learning is a dynamic way to teaching students in the range of 14-19-year olds. It helps students to explore real-world-problems and challenges, simultaneously developing cross-curriculum skills while working in a small group. Project based learning inspires students to gain profound knowledge of the subject they are studying. Students remind better the project they develop themselves than what they read in the books.
- Your analysis for assessment should address initial or diagnostic to establish needs,formative to encourage learning, use of peer-assessment, self-assessment to buildconfidence, summative assessment to measure achievement, onlinetesting and at least one of the following: projectbasedto allowbuildingofunderstanding,observationofpractice to allowskillsdevelopment and holistic approach, normorcriterionreferenced tosuitneeds and context
Word count: 1000
Evidence: Report
(3.2, 4.1, 4.2, 5.1, 5.2)
Task 4. Plan, deliver and assess learning sessions for 14–19 learners, taking account of:
•own analysis of teaching, learning and assessment approaches for use with 14–19 learners
•curriculum requirements
•individual learner needs
Evidence: Complete a Lesson Plan and submit an Assessor’s Observation of your teaching practice
Evaluate own practice in working with 14–19 learners and identify areas for improvement in own practice in working with 14–19 learners
Evidence: Complete a Self-Evaluation based on your teaching practice
5.1 Own practice, e.g. planning variety of appropriate learning and teaching activities, timing of activities, sequencing and pacing to specific learning group needs, actively engaging students, embedding functional and wider skills.
As ICT teacher, during my teaching session I planned variety of appropriate and teaching activities. For example, during the session I created games for learning booster. Learners have to use computers to create a name writer system which allows them to get their name in the system as soon as they enter their date of birth. Other activates consist of creating a coding program which allows them to work on an E-commerce website to enter their user name and the information they want. The timing of these activities is well managed in order to give us opportunities to move forward to achieve our learning outcomes of this topic. The way to avoid the clunky lesson pace is to ensure that students know clearly what they will taught for this particular day and what they have to do. As a teacher I make sure that I meet the needs for those students who have some particular learning difficulties. During my teaching session I actively engaged my students for example by asking them to read the slides or answer some questions that asked during the teaching time. As ICT teacher I have the responsibility to embed my learners on functional and wider skills. At particular time of the lesson I gave my learners to practice their knowledge in math by converting binary numbers to decimal numbers. This practice helps them to exercise on multiplication and division. I also embed them by asking them to read the slides this helps them to practice their reading and spelling.
5.2 Assessment methods, e.g. engaging students, encouraging self-assessment, check-and-correct, medal-and-mission, standards of observation of practice, online testing, value added.
As ICT teacher I used different types of assessment to check and level the understanding of my students. I first engaged my learners by giving them responsibilities to develop their own coding program and activate it by entering data. By giving them the responsivity to develop their own coding program I encourage self-assessment for each learner. If for example there is a student whose coding program is not working for some reason I check-and-correct it to give the opportunity to use the coding program. I also assess my learners by practicing Medals-and-Mission method. This means that when I provided feedback to my learners, I identified where they well and grade them. But I also identified the areas where they did not perform well and them the opportunity to improve. As ICT teacher during my teaching session some time I give opportunity to my learners to present some researches they perform using PowerPoint presentation. Each student has the opportunity to come before the classroom to present his/her work. During this presentation I make notes in order to provide feedback. This practice is standards observation and practice. I also encourage my learners to use online submission in order to give me the opportunity to evaluate their work electronically. They can use for example turnintin or viper to submit their work. This online testing is reliable because it helps teachers to mark the work and provide feedback adequately. As an ICT teacher I always provide initial assessment for all my learners at the start of the term. This give me the opportunity to know the level of ICT knowledge of each of my students. After certain time have to submit their assignment. At this point I grade the work of each student and compare the result with the result with the work of other student from other schools. For clever students their result is nationally recorded (added value).
5.3 Improving own practice, e.g. liaising with others, working with 14-19 specialists, identifying opportunities for CPD, researching issues affecting 14–19 age groups, observation or work shadowing, awarding organization events, retraining.
As a teacher o always work to improve my teaching. In order to achieve that I create working relationship with my peers who have more experience in the teaching career than me. This liaising with other helps me to improve some aspects of my teaching styles. The 14-19 years’ group in one of the difficult group in education. At this ages learners are more disturbed not really focused. In order to keep my student on their study I created a connection with a specialist group called 14-19 specialist. This helps me a lot by providing me some advices and tips on how to deal with my learners. As I have some weakness in my teaching practice. I have identified opportunities for CPD. This is a process to help me develop or learn more in my teaching career. I can also improve my teaching career by practicing observation or work shadowing. I will watch my colleague teaching the subject with me and notice the areas where I can improve when I am teaching. As the technology is improving every day, I also have to attend some workshops events in order to update my knowledge or I can go for retrain to improve my understanding in certain areas of the teaching practice.
Bibliography
Anon., 2001. vocationaltraining.org.uk. [Online]
Available at: https://www.vocationaltraining.org.uk/nvq-overview
[Accessed 05 04 2018].
BBC, 2007. bbc.co.uk. [Online]
Available at: http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/parents/national_curriculum_key_stages/
[Accessed 04 10 2017].
criminalrecordandbarringservice.co.uk, 2004. criminalrecordandbarringservice.co.uk. [Online]
Available at: http://www.criminalrecordandbarringservice.co.uk/dbs-checks-schools-guide/
[Accessed 05 04 2018].
Gauntley, T., 2005. blogspot.co.uk. [Online]
Available at: http://timgauntley.blogspot.co.uk/p/evolving-glossary-of-teachinglearning.html
[Accessed 05 04 2018].
GOV.UK, 2011. Gov.Uk. [Online]
Available at: https://www.gov.uk/guidance/being-inspected-as-a-non-association-independent-school
[Accessed 03 10 2017].
http://policy.monash.edu.au, 2007. http://policy.monash.edu.au. [Online]
Available at: http://policy.monash.edu.au/policy-bank/academic/education/conduct/suppdocs/code-of-practice-teaching-and-learning.html
[Accessed 05 04 2018].
Mcleod, S., 2013. simplypsychology.or. [Online]
Available at: https://www.simplypsychology.org/learning-kolb.html
[Accessed 11 10 2017].
Mcleod, S., 2013. simplypsychology.org. [Online]
Available at: https://www.simplypsychology.org/learning-kolb.html
[Accessed 10 10 2017].
monash.edu.au, 2007. monash.edu.au. [Online]
Available at: http://policy.monash.edu.au/policy-bank/academic/education/conduct/suppdocs/code-of-practice-teaching-and-learning.html
[Accessed 05 04 2018].
nfer.ac.uk, 1998. nfer.ac.uk. [Online]
Available at: www.nfer.ac.uk/publications/smd01
[Accessed 05 10 2017].
Reform, T. g. E., 2011. edglossary.org. [Online]
Available at: http://edglossary.org/formative-assessment/
[Accessed 01 10 2017].
universitiesuk.ac.uk, 2014. universitiesuk.ac.uk. [Online]
Available at: http://www.universitiesuk.ac.uk/policy-and-analysis/Pages/inclusion-equality-diversity.aspx
[Accessed 05 04 2018].
universitiesuk.ac.uk, 2014. universitiesuk.ac.uk. [Online]
Available at: http://www.universitiesuk.ac.uk/policy-and-analysis/Pages/inclusion-equality-diversity.aspx
[Accessed 05 04 2018].
University of Reading, 2013. .reading.ac.uk. [Online]
Available at: https://www.reading.ac.uk/engageinassessment/peer-and-self-assessment/peer-assessment/eia-peer-assessment.aspx
[Accessed 98 10 2017].
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this assignment and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


