Importance of Supply Chain Management for Organizations
| ✓ Paper Type: Free Assignment | ✓ Study Level: University / Undergraduate |
| ✓ Wordcount: 6114 words | ✓ Published: 06 Jun 2019 |
Why has SCM become a necessity for organizations today? – Requirement of SCM in organization.
Logistics practices were being used by militaries around the world since many centuries. Without robust logistics it would not have been possible for Alexander or Genghis khan to move their enormous armies across continents. During 19th & 20th century, factories were usually self-reliant for parts and raw material required for production and suppliers/customers were located nearby. Purchasing departments were perceived merely as order takers and placers. Statement of Henry Ford “You can have any colour as long as it’s black”, signifies predominance of seller’s market. Rules of game are now changed. In 21st century customer is king and customer satisfaction is prime motto of organizations, which means that today customer wants their demand to be satisfied faster and accurately while getting best value for money. It is not product offering but consumer that brings revenue.
There are many forces behind this change like globalization, informed customer, diminishing trade boundaries, shifting customer demands, supply constraints, fluctuating raw material prices, technology and innovation, stricter environmental compliances, spread of supply & demand base and government polices & laws. Everybody is interested in how these forces affect their business and SCM is best capable of answering those questions. Every organization’s main goal is to make money & factors like speed & efficiency costs money and an effective SCM can help in achieving balance. With help of SCM now a product can be developed in USA, manufactured in China & sold in Australia. With a scale & volume like Walmart (11,000 stores in 27 countries and $32 Billion inventory), every process is tied to supplier & only SCM can provide 360o view of supplier network. SCM helps organization to achieve following objectives:
- Not only assuring continuous supply, distribution &to-fro flow of products, services & information but also its responsiveness /reliability
- Marinating good SRM & CRM
- Spend management
- Risk management & compliance assurance
- Removing waste out of system using lean, six sigma & TQM
- Help predicting future trends, demand, consumer preferences using tools like cloud computing, big data, ERP & WMS software.
- Finding ways to reduce & avoid cost associated with inventory, labour, transaction, warehousing, distribution etc.
- Time management
- Defining Performance measurement criteria & its measurement & control.
What has forced the change? – reasons that compelled use of SCM/
There are various factors which compelled organizations to adopt SCM:
- Globalization has that intensification supply chain complexity and spread supplier and customer bases across glob. This will lead to innumerable threats and risks against which firm has to be very vigilant.
- Each & every company doing business is dependent upon some other company to distribute its product offerings to customers, hence it is important for each organization to see its place in supply chain and make all efforts to strengthen its position.
- Intense cut throat competition
- Reducing product pricing & margin and increasing input material and R&D prices. Continuous increasing purchasing cost & production cost,
- Shortened & complex product life cycle
- Changing statutory compliances, laws & regulations, political & macro-economic scenarios leads to focus on green SCM & reverse logistics.
- Rise of super markets & e-commerce websites: As humble corner grocery shops are turning into mammoth super markets having billions of $ in revenues, manufacturers are taking back seat. Supply chain becomes more complex and its importance has increased tremendously.
- Technology: More complex business scenario requires digitalization of SCM solutions to get holistic, integrated & real-time supervision of whole system. Moreover it helps to solve issues in optimization of logistics /supplier-customer Network /Inventory/ warehouse/ transportation using modern tech like ERP, simulations & analytics, RFID, Barcode, GPS, IoT, cloud computing, AI, machine learning etc
- Modular SCM model: Companies becomes more adaptive & agile wrt changing consumer demand, market dynamics, competition etc by utilizing plug-play type models like make2stock, configure2order, virtual factory, make2order or engineer2order manufacturing profiles
- Firms are now realizing importance of people factor like trust, well-being, open communication, good faith, and relationship building among all stakeholders.
- Broader view: for long term sustainability firms are designing strategy based on growth & wellbeing of whole industry, environment, country, future generation and not just their own company and taking up practices like CSR, green SCM, emission control and regulatory compliance
- Other factors like shrinking margin, outsourcing, heavy customization, demand planning at the end of SCM pipeline.
- Lack of Trustworthy logistics arrangement
- Matrix value chain: now a days firms are compelled to collaborate with partners in extended SC network. Partners bring together their capabilities, asset, infrastructure, communication network, knowledge & skills.
- Changing customer demands
- Elevated risk at various levels: external risk (globalization, competition, monetary policy, taxes etc) internal risks (resource scarcity etc)
- Firms have to mould their supply chain to satisfy consumers and as per selling price mentioned on sticker
- Now consumers want convenience over place of purchase, hence supply chain strategy has to ensure that material reaches on time.
- Seamless communications with consumers which is two way and not just selling products through blitzkrieg of promotions.
- Outsourcing: impact of outsourcing is such that more that 80% of companies outsource some part of other of their business. Outsourcing involves suppliers and contractors located all across the world. Only supply chain has the strategy & capability to control them, monitor them and to get best out of them.
- Rapidly changing way of doing business: earlier it was local manufacturing unit, and then changed to assembly unit with parts suppliers across world to online supermarket. E-commerce is giving tough competition to brick n mortar shops. Both are developing competitive supply chain strategy to become more sustainable in market and gain strategic foothold.
These factors forces firms, regardless of manufacturing location or supply base, to think about rest of world in their strategy formulation. Firms can no longer ignore & isolate themselves from external factors, innovation, and competition.
Quote an example of an organization that uses SCM effectively. – successful SCM (Dell)
ZARA is an Spanish firm considered as most successful and dynamic apparel business in world. Apparel is highly competitive market where ZARA has management to create its brand leadership though some innovative SC integrations. What they did right:
- All stores are linked with global headquarter, so better SC vibility. Employee can see changing demand in real time & they device strategy & design accordingly,
- Demand led procurement: As demand trend is known firm response faster with leaner inventory level and less wastage. Deign2market time 15 days.
- Vendor categorization: sophisticated design article they make in Spain, rest they procure form china. They have broad supplier base that offer more options in design, fabric, quality etc (which is necessity of apparel business).
- In house sewing: most critical part is sewing which ZARA has kept with them to get more control over quality. For supplier operations also they have strict control through various SOPs.
- Postponement: final design changes happen at delivery location DC, which reduces risk and inventory level.
- Centralization: rapid production is coordinated and consistent way.
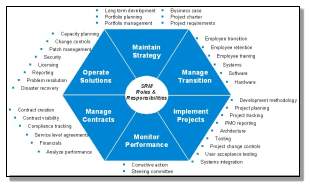
To what extent does SCM act as the center or focal point in the network of suppliers and customers?
Modern day SC functions are non-linear and not poin2point, but rather a complex maze involving several stakeholders with intermingling identities.

The very foundation of SCM is laid up relationships & networks and it is spread across all hierarchy level of both within & outside organization. According to Johnsen and Ford, 1999, following activities are prerequisite to build a network:
SCM & Customers:
It has been proven by authors that an organization that consistently satisfies its customers, enjoy higher retention levels and greater profitability due to increase customer loyalty (Wicks & Roethlein, 2009). All levels in SC directly or indirectly work towards fulfilling customer requirement or creating value for them. Your Customer could be anywhere in the world laced with more product knowledge, purchasing powers & options. They are becoming more demanding, expecting higher service level, unique/differentiated product with better quality; in nutshell they want more value for their money. To sell a product, companies are now relying on 4C’s (customer, cost, convenience & communications) instead of 4Ps. Also a loyal customer itself is a strong barrier to thwart competition, e.g. however hard other android phone makers try to lure, but Apple iPhone has very loyal customer base which is very difficult to crack. Hence SCM is a key to build & sustain customer network through various strategies & performance management tools.
SCM & Suppliers:
Suppliers are backbone & life support system of any SCM network; they are the one who feeds this enormous engine of growth. Product quality is directly related to quality of RM used, hence it is important to track Monitoring supplier quality, delivery and relations. In order to tackle challenges posed by customer a strong vendor base is required. Since so much is at stake, an effective supplier collaboration is required to reduce inventory & operations cost it can be achieved by seamless information sharing & cooperation. Hence SCM is a key to build & sustain supplier network through various strategies & performance management tools. Supplier network is necessary to enable company to Identify new suppliers, market opportunities enablement, connectivity and registration, Catalogue management, Order management, Payment management & Peer networking.
How and why? SCM act as the center or focal point in the network of suppliers and customers
How
It is important to build and maintain win-win relationship with key suppliers and customers backed by trust and seamless communication & information sharing. In an ideal SCM scenario suppliers and consumer are interlinked and they are sharing data, information, feedback, status update.
We can safely say now that both supplier and customer are essential for business to survive and SC is crucial link which hold them together. Partnership could be operational, strategic, tactical etc, based upon how much organization involves customer and suppliers in decision making/planning and sharing data/information/Intellectual Property/business plans/asset with them. Operational level partnership is easy and can be implemented in all companies as it involves lesser degree of sharing. At strategic level however boundaries become blurred, info/data is shared seamlessly and more involvement in decision making, investment & asset sharing.
And this relationship can only be built upon foundation laid by honesty, Trust, goodwill, expertise & willingness.
- Strategic: Requires formulating structure & configuration of collaboration between firm & its suppliers & customers. Main Tasks are to build channel/network design, postponement, contract term finalization, joint product development, segmentation etc.
- Tactical: Involves planning & coordination among various channels of SC like supplier, buyer, logistics, warehouse, production etc and interlinking of various tasks like load building, planningforecastingreplenishment, distribution, resource availability Vs task in hand & product allocation. Establishing system for performance measure & KPI, monitoring/controlling/feedback of processes. E.g.: integrating production, distribution, sales
- Operational or Transactional: include routine transactional activities like placing & issuing order, invoicing, material issue/ receipt/ loading/ unloading, inventory & material tracking
- Internal relationships: Strong coordination between all departments like production, warehouse, procurement, logistics etc, sales as if marching in lockstep.
- Segmentation is utmost important as 1 size dosnt fit all, as it enhance profitability by formulating SC strategy as per segment.
Customer
Strategy: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is key strategy to manage all customer requirements, relationship building, grievance redressal.
Performance management tools: to measure the level of customer satisfaction are as follows:
- On-time product delivery
- Order completeness
 Error & damage free shipment
Error & damage free shipment
vendor
Strategy:
- Improve transactional capabilities using efficient processes & category management
- Improve TCO by strategic sourcing
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) is key strategy to manage all suppliers.
- Capture value across BU, products & dimensions by putting enterprise interest above all
- Vendor managed inventory
http://www.esourcingwiki.com/images/3/31/Srm2.jpg
Performance management tools:
- Product quality & compliance
- Quantity Ordered versus Quantity Received
- ASN Accuracy (advanced shipment notifications)
- Delivery On-time
- Rejections % (delivery accuracy)
Often vendors are segmented according to spend, product type etc. Business partnerships are developed with Key vendors by resource pooling on continuous improvement basis Hence suppliers are very important in SCM.
Why SCM act as the center or focal point in the network of suppliers and customers
Because of various factors related to suppliers and customers affect overall performance of SC it is important to control them. Some of them are mentioned below:
- Bullwhip effect leads to distortion of actual demand
- Sharing resources & value co-creation is essential to sustain
- Inefficient processes at suppliers & customer requires more collaboration
- Various external factors & seasonality affect performance & demand of customer & supplier
Give an example of an organization that has used SCM to create competitive advantage and explain how this was achieved.
Firms could have either productivity or value advantage or both, but competitive advantage is must haves for every company now. E.g. 3 sellers selling same product at same price in same market targeting same consumer group still one seller is making more profit. Reason?. He may be operating at lower cost, giving better quality; faster delivery, flexibility, after sale services or its brand value is more. These are some of the differentiation tool to gain competitive advantage.
We will see how Samsung electronics has created resilient SCM as competitive advantage to become world’s 2nd largest smartphone maker.
Challenges in front of Samsung (smartphone market):
- Highly competitive cut throat competition
- Fragmented market (each market has its own demand, India cost conscious, EU high specs better camera etc)
- Very short & complex product life cycle.
- Competitors are also suppliers, suppliers are also customers, customers are competitors
- High R&D cost
- Near saturation market
Facts Samsung understood very early:
- Competition is not between firms, but in-fact among network.
- Measure SCM performance on the basis of customer expectation
Samsung used following tools & its implementation:
- Extended value chain integration:
- including supplier & customer in mutual growth plan
- holistic association provide better value chain visibility & flexibility toward highly volatile market
- Customer involvement in product development (SCM re-engineering)
- Continuous agility improvement by
- Increasing value chain visibility
- Speed of implementation & production (use of Six sigma)
- Reduce delivery time by strategically locating production site
- Vendor collaboration:
- Enhance capability of suppliers by training, system & procedure training, CSR, HR
- Joint venture with SMEs with core technology thus encouraging invention & joint product development
- Vertical integration of suppliers:
- Gain more control over supply chain
- Become both OEM & part supplier for flash memory, chips & OLED screens for which Apple is main customer.
- Attain economies of scale & exploiting bottleneck in system
- Customer collaboration
- integrate client requirements into product since design stage helps in differentiated product, faster development process hence less time to market & ultimately customer loyalty
- build client recommendation & feedback in SCM processes (e.g.: swift delivery system)
- Demand focussed
- Most accurate sales & demand forecasting (S&OP) helps in taking complex trade off decisions
- Better inventory optimization
- Team as Value Chain: leverage organizational ecosystem to drive SC implementation
- Seamless information sharing, innovation led free communication culture, collaboration instead of competition among teams
- Employees are encouraged to take risk, prepared for urgency, thus getting faster response, less beurocracy, flexible to change
- Near shoring: reduce lead-time, distribution cost, time2market, less cost etc. E.g. plants in Mexico to cover USA etc
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
- Extensive use of technology e.g. automation/robots in production, robust SCM solution software which gives end2end visibility.
- Six Sigma & Lean manufacturing
- Risk management integrated in SCM
What Samsung achieved through competitive advantage:
- Cost leadership
- Reduced time2market
- Product service differentiation
- Innovation
- Strategic market positioning
- Talented & expert staff (due to six sigma black belt training)
How does SCM play a role in customer retention and service quality?
Service quality & customer satisfaction are vital for business to grow. Both are interlinked with each other and their value is increasing every day.
Customer retention
It has been proven by authors that an organization that consistently satisfies its customers, enjoy higher retention levels and greater profitability due to increase customer retention (Wicks & Roethlein, 2009). An effective SCM network integrates both upstream & downstream logistics by building strong Vendor Company Customer relationship. There by achieving competitiveness & customer retention. By applying various SC strategies like strategic partnership, postponement & information sharing companies can achieve better service quality & customer retention. Each entity in SCM is supplier & customer and are interdependent hence a upstream & downstream integration of supplier & customer respectively is vital
- Strategic relationships:
- Supplier: maintaining long term strong relationship means sharing risks & rewards, seamless communication across SC, better understanding of demand & expectation. It also helps in sharing product knowledge & scheduling delivery as per their requirement. Moreover a win-win situation where we get better product quality, reduced lead time and agile service response. (Thatte, 2007).
- Customer: By integrating SRM with SCM & marketing, firms achieve closer customer relationship which means better product differentiation, increased brand perception, loyalty. Firms can mould their SC as per consumer requirement. E.g. Consumer wants a product which elevates their prestige, performs exceptionally, gives better value for money, delivered faster & backed by great service support. Hence to provide so, company deliver a quality product with higher brand value, available at doorstep and on call 24×7 service support and manage its SCM & logistics network to make it happen. As a result they will get happy customers who prefers to come again.
- Supplier postponement: It is the practice of moving forward one or more operations or activities; making, sourcing and delivering to a much later point in the supply chain (Van et al, 1998). It helps firms to develop differentiated products as per customer needs. E.g. Zara sends plain skirts, laces, and buttons separately to central location near country of sale. As per feedback of marketing regarding current trends they stich laces & button. Hence they achieve less obsolete inventory, flexible to meet demands, hence loyal customer.
- Information sharing means provide product status, sales data or any type of data which enable to monitor & control SC processes.
- Info sharing is worth only if;
- Data is accurate, reliable, relevant, real time & easy to retrieve
- A powerfull software to monitor & analyse data
- Skilled people to make most of it & use info to device strategy before competition (e.g. enter new market, launch new product, M&A decision) or sensing risk and plan beforehand its mitigation action.
- Supplier-firm-customer to make better decision jointly, enhance operational synergy
- Better supply chain visibility,
- Accurate prediction of market trends,
- Better understanding of bottlenecks in performance deliverance,
- Better response to market so less inventory, and more flexibility to change as per on-going trend
- As they work as single unit customer feels themselves as part of process and remains loyal to firm.
- Info sharing is worth only if;
- Understanding customer needs: After ensuring above practices are being followed manufacturer has better understanding of:
- What customer want: differentiated products with lesser R&D cost and less time wastage in trial & error during product designing. E.g. Honda understood Indian youth wants uniqueness in bike they launched a base model with plenty of customization options like headlight covers, flayers, seat, stickers etc.
- When they want: right time to launch a product or as per season or product delivery before deadline
- Where they want: For products delivery options like home delivery, click & collect and for service delivery 24×7 oncall, home visit, service delivery in own language, mobile apps etc.

What price: try to bundle maximum in desired price range, go an extra mile to serve without charging much.
- Customer loyalty: It is the act of buying same brand or same company repeatedly over a period of time, regardless of competition, price & other parameters. Loyalty is achieved when a firm is able to provide pre & post purchase satisfaction to customers. Satisfied customer loyal customercustomer retention. As Phillip Kotler once said “customer don’t buy product or service they buy aspiration, value. Hence to satisfy a customer one must provide product as per their perceived expectation”. According to Cacioppo (2000), an increase in customer loyalty by 5% can lead to an increase in company’s profits by 25-85%. According to article published in IIDM, customer loyalty can be built upon following factors:
- Perceived Quality:
- Perceived Value
- Corporate Image
- Hence by gaining customer loyalty a firm achieves:
- A loyal customer is strong barrier in itself to competition
- A predictable demand for its product hence less fluctuation and smooth supply chain.
- More sales per customer, easy to identify key customer and easy to implement CRM policies and targeted promotional plans
- Gain competitive edge over competition, can utilize experience of one market into other new market.
- More repurchases decisions and more commitment to remain with supplier.
- Helps in deciding what level of information, asset, resources, and investments to be shared with preferred partner.
On the contrary a dissatisfied customer not only stop buying himself but able to influence others also not to buy, moreover with social media a word of mouth bad publicity is enough to close shutter of any successful businesses.
SERVICE QUALITY
Customer satisfaction is very meticulously interlinked with service quality. Service quality is ultimate culmination of all direct & indirect efforts company make to satisfy its customer like feel of product, exceptional service, polite & friendly behaviour of staff. Service quality is defined as ability to provide desired level of service accurately and with consistency. Krishnamurthy and Sivashanmugham (2011) identified five factors which affect service quality:
- Policy: includes factors like no. of SKUs/brands, inventory level, feedback system, payment methods(Cash/ EFTPOS), promotional
- Physical Aspect: includes physical Assets which adds to convenience to customer like well-planned store layout, labelled racking system, availability or spare parts & nearby service stations.
- Personal Interaction: Soft skills of interacting PoC staff like behaviour (friendliness, politeness, willingness), knowledge & skills.
- Assurance: Trust aspect of service delivery like delivered as promised, genuine product, sales slip, small queues etc. Other attributes like empathy, tangibility, and assertion are also important.
- Problem Solving: includes customer service counters or phone numbers, robust compliance lodging & speedy redressal system
- Reliability: includes brand and product reliability, error free delivery & invoicing. Product life exceeds warranty by far.
- Product: includes performance & operational features of product, its quality & price. It also includes aspiration attached with brand
Other factors which affect service quality are:
- SERVQUAL model to measure the service quality is proposed by Raven and Welsh (2004) which includes attributes of service like Credibility, Reliability Responsiveness, Empathy & Tangible.
- Speed, ease, accuracy of service delivery
Service quality Measurement: apart from above parameters use following tools to measure service quality:
- Getting accurate feedback/complaints (surveys, follow-up, complaint & call center data, Mystery shopping, service rating)
- Objective Service Metrics like Customer churn rate, Customer Satisfaction Score (% of satisfied & unsatisfied customers). Queuing Ratio, Problem Resolution Time
- Social Media Monitoring (#tag, visits & liks to official posts etc)
Some e.g.: we received 20% fewer questions about exporting this month, so the reworking we did in the app saved us 12 hours of support time already!” or When our email time to first response goes above four hours, we see consistent dips in customer satisfaction.” Or “Answering billing questions takes us three times the average ticket length”.
Outcome of service quality:
- Positive word of mouth
- develops the positive relationship and impression
- customer involvement boost service quality
USE MORE SUPPLY CHAIN ASPECT
Give an example of a company that used SCM to support customer retention.
Apple is famous for three things Steve Jobs, innovation& Design and its die-hard loyal customers, who can spend days standing in queues outside Apple store to purchase their new iPhone or iPad and use same phone brand year after year.
The key for this extremely loyal customer base and strong customer retention lies with equally innovative & adaptive supply chain which is considered best in world (by research firm Gartner). Current CEO of Apple Tim Cook has risen to these ranks from being in charge of supply chain.
SCM- the Apple way:
- Continues improvement in solutions and strategies.
- Control over whole ecosystem: strategic approach on what it will own Vs exerting control over partners, gives better control over things
- Strong leadership: Apple is fortunate to have leaders like Steve Jobs and Tim Cook. Cook believes that ““inventory is fundamentally evil” he says “You kind of want to manage it like you’re in the dairy business. If it gets past its freshness date, you have a problem.”
 SC Cycle: design parts & fix specification select best vendors (pre-qualification, qualification assessment & selection of vendor)purchase materialship to assembly plant in India & China Online Consumer order onlinedirect delivery through UPS/Fedex
SC Cycle: design parts & fix specification select best vendors (pre-qualification, qualification assessment & selection of vendor)purchase materialship to assembly plant in India & China Online Consumer order onlinedirect delivery through UPS/Fedex
Final product ship to CW at California, USAship to retail storesconsumerat the end of product cycle return to CW or Apple store
- Lean System: Reduced inventory & warehousing cost, less risk of obsolete inventory (sudden announcement from competitor change everything)
- Supplier: Reduced no. of vendors from 100 to 24, thus forcing them to compete for business share.
- Warehouse: shutdown 10 out of 19 warehouse to control excess inventory & 1 Central warehouse integrated with owned stores
- Inventory: 6 days in hand inventory from 30 days. Inventory turnover ratio 5 days i.e. better that Dell(10 days), Samsung(21 days).
- Less SKUs: lesser SKU gives better forecasting & keep production & warehouse cost in-check.
- Push System: surprisingly in technology market, its Apple who dictate terms, it’s all because of Trust consumer have upon Apple, due to its quality, premium, & innovative products and exceptional service quality. This helps in accurate demand forecasting & better control over SC
- Long product life cycle: approx. 12 months for each product. Apple launches upgraded iPhone every year. This not only helps in predictive SC strategy but also give long term contract term negotiation with suppliers so that they achieve economy of scale.
Apple SCM – in numbers:
- During July’11, every piece of iPad 2 was sold, leaving no wastage or dead inventory
- Q1’14, $2.1 Billion in inventory(Vs sales $170 Billion i.e. 1.2% inventory to sales ratio)
- 1 Billion iPhones sold since 2007.
- May’17, cash on hand is quarter of Trillion Dollars, making it most valuable company in world.
Explain Cost reduction, and its importance in a logistics network.
Definition: It is a process of reducing unwarranted expenses so that profitability can be increased & operations become more efficient. Cost saving starts with
- Understanding where money is being spent & categorising them broadly in
- Fixed & variable costs then further bifurcating them according to spend
- Long term or short term
- Defining purpose of cost reduction & benchmarking it against industry standard.
- Factor all costs over sales volume
Cost reduction in Logistics:
Cost reduction is in direct trade-off/conflict with customer satisfaction, e.g. (1) Faster delivery Vs high transportation cost i.e. sea Vs air freight (2) Product shortage due to less inventory Vs buffer inventory & high inventory cost). Also it affects product price, availability, quality (expiry in perishable goods), hence reducing logistic cost is main priority of logistic managers.
- Focus on safety: Avoid injuries which cost company in terms of money, delay & reputation loss, OSHA may shut facility on safety issue
- Labour cost: Time motion studytime taken by each activity & its frequency calculate costweed-out unwanted activities/reduce frequency without affecting operation.
- Promote automation use tech like RFID, Barcode, carousel storage, GPS, forklifts voice-directed picking, WMS etc.
- Labour payment on the basis of job done (per Ton, per packet per trip etc) instead of per Hrs. Train them & treat them well.
- Schedule shifts as per work load, encourage new ideas.
- Quality: Poor quality cause returns & all cost associated with it moreover hampers customer satisfaction. Freeze product specifications.
- Fix preventative maintenance (PM) schedule of plant & machinery, e.g. an hr spent on truck maintenance is better than late shipment due to breakdown. Moreover PM improve machine availability & reduces uncertainty.
- Technology: It saves cost. E.g. wearable voice command tools improves warehouse efficiency, movable racks saves space, WMS helps in automated cycle counting & location & layout control (high turnover SKUs near shipping), efficient lighting etc.
- Supplier Collaboration: involve & collaborate with supplier in cost reduction.
- Stock loss: Avoiding errors, use of robust tracking system, use of technology (GPS, RFID, CCTV etc) reduces misplaced/lost items. Segregation of inventory in terms of high & low value, fast moving & slow moving.
- Process: Freeze SOP for each job to standardize way of working. Work as per roaster in each shift so as to pinpoint who do what in what time with what accuracy.
- Audit: Periodic audits and stock take
- Packaging: Packaging as per need (not over not under packaged), roadworthy & product-worthy, proper labelling with barcode, product details helps proper locating & unloading & storage. Improve bursting strength of packing material to improve vertical stacking etc.
- Delivery cost: Spoke & hub distribution system, scheduled delivery timing, fixed driving routes etc.
- Least inventory level backed by accurate demand forecast, SRM & CRM integration in SCM, integration of sales and inventory data.
- Outsourcing: Firm often outsource to focus on their key expertise. Warehousing, logistics & transportation are most outsourced areas because
- 3rd parties are more efficient, productive and skilful.
- Gives business more flexibility, e.g. company can rent more trucks or warehouse in case of peal demand instead of owning them)
- Asset utilization: maximum asset utilization aiming for zero idle time. E.g. instead of owning more trucks to deliver vegetables in morning and idle for day, use lesser trucks and spread delivery throughout day. Shipping in FTL.
- Reverse logistics as cost saving tools e.g. reusing printer cartridge, gas cylinders, exchange offer for smartphones
- Postponement
- Cross docking
Explain capital reduction and their importance in a logistics network.
Definition: Working capital is amount of money need to run business. WC= Current asset – Current liabilities. Asset means inventory, plant & machinery, receivable payment & liabilities include vendor payment. Lesser WC better fund flow e.g. Dell has negative WC.
Strategies for Capital reduction in Logistics:
- Cash management: SC professional working with finance by meeting expenses with lesser fund
- Debtor management: managing suppliers payment like payment cycle, term extensions, forward LC payment etc
- Inventory management:
- Volume reduction :
- Use VMI, JIT, delivery scheduling
- Order frequently thus reducing buffer stock level, replenish fast.
- Share inventory level with vendor to align delivery schedule as per consumption
- Value reduction(unit cost):
- Achieved by reducing purchasing & holding cost by order in EOQ,
- Negotiating quantity discount & long term supply contract, purchase from OEM instead or trader, pool requirement of all Bus.
- Reduce no. of warehouses & DC.
- Giving O&M(operation & maintenance) contract thus reducing inventory value & increasing machine availability.
- Lower inventory level should be calculated very carefully as lesser inventory leads to supply shortage and ultimately customer dissatisfaction and loss of business.
- On the other hand higher -inventory means increasing damage, shrinkage, interest rates and misc. other inventory carrying cost tied up with inventory.
- Improved working capital often termed as positive health of company and increase company share price.
- Standardization of spare parts thus to reduce inventory volume & value
- Postponement to differentiate product at later stage of supply chain thus reducing working capital and obsolete inventory
- Reduce no. of SKUs, focus on most profitable ones, it will remove inventory clutter thus improve working capital.
- Volume reduction :
Steps to achieve capital reduction:
- Benchmarking savings target and clearly define in SCM strategy and saving % to be link with employee performance measurement.
- Formulate performance measure and their tracking mechanism
1699 words
Explain service improvement and their importance in a logistics network.
A product that is well-conceived, excellently packaged and broadly advertised is worthless if it is unavailable when the customer wants it (LaLonde, 1976). Logistic play most crucial part as it ensures last mile connectivity with customer. Customer service is most critical to gain competitive advantage. Main aim of logistics is to satisfy customer requirement & also service performance is determined by the way logistics system is constructed and operated. Despite of being so interdependent upon each other service level and logistics, are always at opposite poles, waging a trade-off. E.g.: higher the service level higher the cost and vice versa.
Hence it is very important to improve service level. Increasingly firms are bundling services with product offerings like 2GB data free with purchase of smartphone, this is done to make product more attractive in eyes of buyer. The aim is to improve sale by adding services as firms know very well service quality is key to achieve higher market share & profitability, e.g. cash on delivery, returns, same day delivery.
- Service improvement work towards integration of sales & delivery process
Main forces responsible for this growth are:
- Ever changing consumer demand & preferences.
- Short product life cycle and
- Excessive competition which has reduced differentiation in products.
According to Lalonde (1976), 3 types of services are Pre-transactional elements Transactional elements & Post-transactional elements.
According to below table proposed by Gilmou P., (1978), in deliverance of customer service, logistics account for 70% contribution.
| Customer service Components | Weightage | Function |
| Delivery time | 21 | Logistics |
| Quality of the delivery | 20 | Logistics |
| After-sales service | 16 | Sales |
| Inform customers about the delivery | 14 | Logistics |
| Product price | 12 | Marketing |
| Competence in doing work | 11 | Sales |
| Delivery accuracy | 9 | Logistics |
| Correct specification | 9 | Quality |
| Convenience for receiving goods | 6 | Logistics |
| Cooperation between buyers and sellers | 6 | Marketing |
| Packing | 5 | Marketing |
Tools for improving Service Quality:
- Managing customer expectations by Service Level Agreement (SLA), which provide a common platform about services, urgencies & accountabilities.
- Service-level trade-off analysis is undertaken by firm to compare type & quality of distribution activities they offer Vs cost.
- Customer segmentation: divide customer in groups and devise separate SC strategy for them.
- VoP (value offering point) suggested by (Holmström et al., 1999).As evident from below diagram at VoP supplier fulfill customers demand in customers demand chain, ideally it is at the end of supply chain. But VoP can be located earlier in suuply chai e.g.. in VMI vendor participate in inventory management thus improving service quality.
- Reverse logistics & customer care
- Effective communication method
- Conflict resolution and escalation method & its output should be included in future strategy
words 1552/450
[Words: 2173/1250]
ABBREVIATIONS:
- ERP,
- RFID,
- GPS,
- IoT
- AI
- JV: joint venture
- BTS: Build To Stock
- DC: Distribution Centre
- IT: Information Technology
- IT&C: Information Technology & communication
- M&A: Merger & acquisition
- ROI: Returns on Investment
- R&D: Research & Development
- SCM: Supply Chain Management
- SKU: Stock Keeping Unit
- SOP: Standard Operating Procedures
- VMI: Vendor Managed Inventory
- VCN: Value chain Network
- VCA: Value chain analysis
- USP: Unique Selling Price
- VCS: Value creating system
REFERENCES / BIBLIOGRAPHY:
WEB LINKS:
- https://hbr.org/1979/03/how-competitive-forces-shape-strategy
- http://universalteacher.com/1/disadvantages-of-strategic-alliance/
- https://www.mruni.eu/upload/iblock/bca/Isoraite.pdf
- https://www.cleverism.com/strategy-frameworks-value-chain/
- http://phoenixcg.com/files/Kaplan%20et%20al%20-%20Managing%20alliances.pdf
- http://s3.amazonaws.com/academia.edu.documents/1073236/7pwo48rznkwymis.pdf?AWSAccessKeyId=AKIAIWOWYYGZ2Y53UL3A&Expires=1499736001&Signature=TcD%2BV13vW29poE%2FCilgOglYsK%2B0%3D&response-content-disposition=inline%3B%20filename%3DStrategic_Alliances_and_Models_of_Collab.pdf
BOOKS:
- Dewitt et al, (2001) Defining Supply Chain Management. Journal of Business Logistics, Vol. 22, No. 2, p. 18).
- Alvarado, U., & Kotzab, H. (2001). Supply Chain Management: The Integration of Logistics in Marketing. Industrial Marketing Management, 30(2), 183-198.
- Johnsen, T.E. and Ford, I.D. (1999) “An Initial Conceptual Framework for Managing Collaborative Innovation in Complex Business Networks”, 15th Annual IMP Conference, September 2nd – 4th, University College Dublin, Dublin.
- Essentials of Supply Chain Management By Michael H. Hugos, John Wiley & Sons, 8/07/2011
- Christopher, M. (1998), Logistics and Supply Chain Management – Strategies for Reducing Cost and Improve Service, London, Pitman Publishing.
- Collin, J. (2002), Selecting the right supply chain for a customer in project business, Doctoral Dissertation, Helsinki University of Technology.
- Holmström, J., Hoover, Jr., Eloranta, E. & Vasara, A. (1999), “Using value reengineering to implement breakthrough solutions for customers”, International Journal of Logistics Management, Vol. 10, Iss. 2, pp. 1-12.
- Gilmou P., “The management of distribution: An Australian framework”, Longman Co. Ltd., Melbourne, 1978, p. 11
- Kotler, P., Marketing Management, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 2006
- Christopher, M. (1998), Logistics and Supply Chain Management – Strategies for Reducing Cost and Improve Service, London, Pitman Publishing.
- Chopra, Sunil & Peter Meindi, (2002). “Supply chain management; Strategy, planning and operations, Delhi: Pearson Education
- Gugler, P. (1992) ‘Building Transnational Alliances to Create Competitive Advantage’, Long Range Planning, 25 (1): 90-99.
- Tsang, Eric W. K. (1999) ‘A Preliminary Typology of Learning in International Strategic Alliances’, Journal of World Business, 34:211-229
- Logistics and integrated approach by Michael Quayle 1993 edition, Tudor Publication
- Logistics an introduction to supply chain management by Donald Waters , 2003 edition, Palgrave Macmillan publication
- Logistics & Supply chain Management by Martin Christopher, 4th edition, Pearson publication.
- Modelling Value: Selected Papers of the 1st International Conference on …edited by Herbert Jodlbauer, Jan Olhager, Richard J. Schonberger
JOURNALS & RESEARCH PAPERS:
- Reading material given during lectures
- Thatte A. A., (2007). “Competitive advantage of a Firm through Supply Chain Responsiveness and Supply Chain Management Practices”, Published PhD Dissertation. University of Toledo
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allDMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this assignment and no longer wish to have your work published on UKEssays.com then please click the following link to email our support team:
Request essay removal


