Success Factors for Online Fashion Retail Business
Info: 7351 words (29 pages) Dissertation
Published: 17th Aug 2021
Abstract
This report will discuss key factors that drive Zalando towards success and the key challenges that could be faced in the future. The paper begins with the explanation of some facts and figures of the online retail industry, the reason why this topic was chosen for the report, followed by company background. The next part of the paper will be examining key factors that make Zalando successful by exploiting theories and link it to real-life situations that Zalando faces in the business. There are seven key factors that will be discussed in the paper; Good Customer Targeting and Business Model, Strong Workforce, Unique Customer Service, Social Media, Localisation, Brand Names, and Strong Corporate Values. The next part will discuss the challenges lying in the future for Zalando. To finish off, a conclusion is written to summarise the whole report.
Table of Contents
2. Key Success Factors of Zalando
2.1 Good Customer Targeting and Business Model
1. Introduction
1.1 Research Background
The online retail industry or ecommerce has been growing steadily in recent years. The industry in Europe managed to generate €530 billion in 2016 and is expecting to generate approximately €602 billion by the end of 2017, which is an expected increase of 14% compared to the previous year (Ecommerce News, 2017). The UK has the highest percentage of consumers that purchase products online in 2016, which is 87%, followed by Germany; 84% and Denmark; 82%. These statistics prove that the online retail industry is popular among consumers and it has a bright future ahead as consumers prefer to do online shopping rather than going to high street stores (Bradshaw, 2017). Companies such as ASOS, Zalando and Boohoo are some of the major players in the online fashion retail industry and consumers are fond of the products and services offered by them.
This report will be focusing on a successful ecommerce fashion retail company known as Zalando. The author will be identifying the key factors that drives the success of the start-up and key challenges lying ahead. The reason this topic was chosen is because the author is interested in running his own ecommerce business. In order to do that, the author would like to further comprehend and analyse the key factors that could turn an ecommerce company into a great success and also analyse the challenges that the company could potentially face in the future. By writing this report, the author can gather all the importance points and use the knowledge gained from the research to potentially run his own effective ecommerce business in near future. This report will use theories and adapt to the real-life scenarios that is occurring surrounding the success of the ecommerce company known as Zalando.
1.2 Company background
The ecommerce fashion retailer Zalando was established in 2008 (Zalando, 2017b). The co-founders of the company are David Schneider and Robert Gentz, and the headquarter is in Berlin, Germany. Zalando initially started their business by selling shoes in a reachable and easy way for customers to purchase online. Later, they added other product categories such as sports products, home accessories and fashion clothing for both men, women, and kids, and now offer more than 1,500 worldwide brands (Wauters, 2014). As of March 2017, Zalando services are currently available in 15 countries; Germany, Austria, Netherlands, France, Italy, United Kingdom, Switzerland, Sweden, Belgium, Spain, Denmark, Finland, Poland, Norway, and Luxembourg (Zalando, 2017b). The company has hired over 12,000 employees worldwide. Zalando took less than ten years to be known as Europe’s major ecommerce fashion retailer (Shotter, 2017). The company managed to generate a revenue of €3.64bn in 2016, while the gross profit is €216.3m. Moreover, Zalando went public in October 2014 on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange and was recognised as the greatest Initial Public Offering for a tech company since year 2000 (Mac, 2014). Hence, it comes to no surprise how Zalando is dominating the ecommerce fashion industry and continue flourishing to achieve greater success.
2. Key Success Factors of Zalando
2.1 Good Customer Targeting and Business Model
Fashion or luxury products are subject to the changing needs and expectations of the customers. For most of the luxury consumers, their aim is to identify brands that suit their tastes and preferences and all the concerted efforts to fulfilling these needs (Arora, 2017). Zalando entered the luxury market as a new competitor but had to address the challenge of an uncertainty barrier coming from the clients (Giovannini et al., 2015). However, the success of the retailer is much attributed to the adaptability of the fashion industry. In principle, Zalando’s market entry strategy was on the differentiation of the fashion goods and services, and as such, the aim was to evoke repeat purchase behavior among customers (Blázquez, 2014; Suryandari and Paswan, 2014). In return, the retailer embraced high-end media as a platform to interact with clients and from this, product messages were easily disseminated with the detailed description of the product benefits. Accordingly, Arora (2017) indicates that first online purchases have direct impacts on future purchase behaviors as they can lead to repeat purchases in future or drive away customers from the product. Conversely, customer satisfaction specifics apply within the online retail sector because as one gets the products that fit needs and expectations, there is the high likelihood of remaining loyal to the brand (Suryandari and Paswan, 2014; Magrath and McCormick, 2013). The success of the Zalando stems from the fact that the retailer entered the market with the emphasis on maintaining or improving customer loyalty, especially providing unique online purchase experience by pinpointing the tastes and preferences, and then presenting products that meet those needs through unique and exceptional services.
Proper marketing targeting is an indication of effective business models being used at Zalando. From its earlier years, the company had successfully managed to reach out to a large online target market (Zentes et al., 2016). A lot had been invested in advertising the brand, both on mainstream media like TV and the online platforms. All market targeting approaches succeeded in drawing the attention of luxury and fashion lovers to the brand. High expenditure in the market had paid off since, by the time of its entry, the company had achieved an outstanding overall brand awareness of about 90% (Hendrich, 2017).
Nonetheless, proper market targeting and fulfilment of the needs and expectations of the customers were majorly attributed to the unique website layout. A view of the online store’s website shows a well and clearly-structured as well as an easy-to-navigate platform. The ease of use of the site is also evident from the manner in which visitors have different ways of narrowing down their searches by selecting specific preferences like the brand, colour, size, and price (Bullinger, 2014). Besides that, the advertisements include some of the additional provisions like free delivery, complimentary service-hotline and 100-day return (Bullinger, 2014). Customer service is available on a twenty-hour basis and as such, improves the interaction and communication with the clients.
Proper customer targeting is done through Search Engine Optimization which has also been continued as part of the business strategy and model (Bullinger, 2014). For Zalando, a search on the Google ranks the company as one of the primary search results or outcomes. Zalando is currently ubiquitous on the mainstream internet. When one is looking online for shoes or clothes, it is very easy to come across Zalando. In essence, the company uses article marketing whereby specific search words and key terms around relevant themes such as fashion or shoes (Wedel and Kannan, 2016). The retailer has also applied a unique combination of terms which has equally provided customers with exceptional outcomes thereby presenting customers with a variety or combination of products to assess and choose from. Article marketing has enabled the retailer to market its website through articles and from this, visitors are finding it easier to explore information through videos, texts, games, graphics, and pictures which document the various products offered at the company thereby leading to more customer base, higher revenue, continued growth and expansion.
The success of the retail store also stems from retargeting initiatives as an implication the company is available on every website (Ryan and Jones, 2012). Retargeting is built on the notion that customers regularly leave online shops without buying items although they have listed items in their shopping baskets or wish list. (Lambrecht and Tucker, 2013). Zalando has implemented this strategy whereby it uses giant and vibrant banners that last for many weeks on its website or other popular sites. As such, a click on the banner, in particular on the “buy-now-button” leads customers directly to the shop basket that they left earlier when they were browsing the website (Bullinger, 2014). The action is a constant reminder that evokes a second consideration and purchase behaviours when visitors repeatedly get to view the items being sold; thus, retargeting has made Zalando a successful company. Retargeting follows the reinforcement theory whereby messages are reinforced and retargeted at the clients to attract and convince them to consider purchase behaviours or intentions (Boerman et al., 2017).
The success of Zalando can also be attributed to the proper targeting of the market using appropriate media. Notably, the company adopted the use of TrustedDialog as a model offering companies with latest email quality standards thereby forging and cementing trust with the esteemed customers (Bullinger, 2014). The model has features that ensure safe delivery by authenticating the sender as well as having provisions for customer-specific email contents including product suggestions, special offers, and also personal shopper’s style. Due to this provision, it only took a small amount of time for Zalando to begin expanding. As of late, the company has a wider representation in the European region. Equally, there are plans to expand to Eastern Europe as well as the adoption of internationalization approach to expand to other global markets (Adegeest, 2016).
2.2 Strong Workforce
Equally, the success of Zalando is much attributed to the employees and the human resources as part of the internal competencies of the company. As such, the executive management has created conducive atmosphere whereby employees are taught to value customers and the spirit of excellent services to the individuals (Zalando, 2017a). Particularly, there is more to the employees working in the online retail shop that has led to its success and expansion. Zalando’s employees have an open spirit which leads to the unique customer experience. On the other hand, workers have a broader portfolio of knowledge and expertise necessary for a company operating as a retail store to provide or present the essential services and expectations to the customers (Zalando, 2017a). In the case of the Zalando as an online retailer, it is accurate to infer that the success and growth are achieved by applying proper human resource management approaches and strategies that exhaust skills and competencies in meeting the needs and expectations of the customers (Kehoe and Wright, 2013).
The experienced workforce has been applauded for the timely delivery of orders to the customers. For example, the strategic location of the warehouses allows for timely delivery of which they are positioned in areas where it takes less than nine hours for the customers to receive their products (Zentes et al., 2016). In e-commerce, customer delivery is one of the determinants of success of which customers are always in need of brands that deliver their orders in time; the modern consumer is more inclined to be impatient because of how life has been made convenient through e-commerce (Einav et al., 2014). The company’s skilled employees have been useful in collecting data about demand and consumption in the market for which products are designed depending on the trends or current fashion thereby providing the consumers with a wide variety of options. In reality, the choice of individuals working within the company can be explained as a company that uses proper staffing approaches and employee training and development to present goods and services that befit the market or meet the needs, expectations and the changing market needs as a characteristic of the fashion industry (Phillips and Gully, 2015).
2.3 Unique Customer Service
The fashion industry is also service driven, especially for the online retail stores (Pantano, 2014; Kim et al., 2016). The experiences that the customers get through the purchase process have profound implications on their loyalty to the brand as well as the trust that they have on the specific business (Carmignani and Zammori, 2015; Walsh et al., 2017). For the online purchase experience, there are no intermediaries involved (Ko et al., 2016). In this case, success depends on how the company has tailored its services and approach towards effective customer management to improve the experience and ensure that clients will consider repeat purchase behaviors in future. From an expert opinion perspective, customer service has been regarded as the element that companies use in making up as well as earning the trust of their esteemed shoppers, especially in the online business environment (Kastanakis and Balabanis, 2014; Vecchi and Buckley, 2016). However, in Zalando, the manner in which customers are handled is by ensuring that they are engaged of which efficiency in customer service is given priority. The company is quick to respond to the customer orders, and requests as the customer care unit is committed to using different communication mechanisms and media like email and text messages to forward the request to the inventory department. As Zalando has expanded to other markets in Europe, delivery networks are established around Europe whereby employees in each host country is attached to the customer care service so that they can assist the customers in any language or help with the differences in the payment process. Moreover, there is an integrated approach to customer service management of which an IT system approach is embraced in the company, and as such, the emphasis is on quality dimensions like accessibility, consistency as well as the taking up the liability for customer experience (Chandon et al., 2016).
2.4 Social Media
The fashion industry is subject to the changes in the socio-cultural aspects of life (Chandon et al., 2016). Principally, the major trend setters are the social forces like the younger generations while conservative fashion is more common with the older generation (Tuten and Solomon, 2015). From this, businesses are currently increasing their social media presence as a way of interacting with their customers to know or understand the current trends in consumption. For a fashion retailer, greater levels or extent of social media presence is necessary for success in the modern business environment.
Zalando is a company whose executive management understands the principle and necessity of being present in the social media sites especially Facebook and Twitter as they are mostly used. Accordingly, Ngai et al. (2015) confirmed that as of currently, every fashion retailer is using social media in reaching out to the customers to help them with the improvement of customer engagement and managing relationships with the client base. The implication is that social media has a huge crowd and if utilized, a company stands to gain from a large customer base because the platform is readily available. Social media has also enabled e-commerce by providing opportunities for advertisements and promotions (Trainor et al., 2014). Zalando, as an online retailer, has been established as one of the major retail stores with an extensive online following.
2.5 Localisation
Various approaches are currently being adopted worldwide to improve product offerings. Localisation is a concept that is fast gaining ground to counter the effects and negative implications of globalization on product innovation and embracing diversity in manufacturing and production (Zhao et al., 2014). For Zalando, the retailer is currently distributing its products to around 15 countries, but if it standardized processes and product offerings, then the uniqueness of each market would be limited while different needs and expectations of the customers would not be met (Zentes et al., 2016). In retrospect, the retailer is adopting localisation in its website design and layout, of which the focus is on adding value and improving accessibility to different localities where the company operates. The success of Zalando in the different localities is much attributed to the fact that the websites are personalized for every country with the aim of meeting the needs of the locals. For instance, the sites are translated into different languages to fit the particular locality while the company ensures that the online service provision including distribution adopts the distribution systems as well as embracing fashion patterns within the local area of operation. Therefore, Zalando can be argued as a case of an online retailer where localisation approach is integrated into growth and expansion, and the company desists from the standardization of products (Rask, 2014).
2.6 Brand Names
Branding has become such a consideration in the modern dynamic business environment as consumers now look for products attached to renowned and valued brands in the market (Bik et al, 2015). In the same context, Zalando has extensively invested in branding its products since the company comprehends the necessity of brand consciousness and the positive connection or relationship with customer satisfaction, loyalty and increased online purchases (Popescu, 2015). The implication is that the more individual customers are interested in the brand, the more likely they are to check on the latest productions and styles provided by the specific brand (Verma et al., 2016). Zalando is a large brand name because in the past ten years, it has established itself as a major player in the market. Searching through styles and fashion on Google, customers are more likely to stumble upon Zalando, and from this, they check the latest products and fashion trends offered in the online retail store. Furthermore, the company is attached to many big brands, of which various reputable brands are currently sold for the first time through the retailer. From this provision, the retailer benefits from the exceptional brands through awareness as well as gaining from their target market groups. As mentioned earlier, Zalando has allowed over 1500 brands to be adopted through its brand name and influence (Wauters, 2014).
As of currently, Zalando has a large assortment of brands using its platform to sell their products and reaching out to the target customers. The company is attached to major global brands like Adidas, Tommy Hilfiger, and Nike which each have a strong following and customer loyalty (Zalando, 2017c). On the other hand, the global brands are further complemented through high or major local brands like Morgan, Modstrom, and Minimum (Zentes et al., 2016). Zalando includes other fashion brands that have been helping the retailer to stay or keep updated with the current fashion or trends in the market. For instance, fast fashion brands including Vero Moda, New Look, and Jack & Jones are all included as part of the companies helping with the marketing and targeting in the brand (Zalando, 2017c). To target different customers, in particular for the prosperous as well as luxury shoppers, the retailer has offered the customers with a myriad of premium brands including Aigner and Hugo Boss (Zalando, 2017c). Furthermore, for the sport and specific outdoor brands, the company has included such brands like Adidas, Asics, and Patagonia in targeting customers whose emphasis are on engaging in sports as well as leisure activities or those who would prefer the sporty look (Zalando, 2017c).
Zalando is also working with private label brands, including its brands like Zign, mint&berry, and even & odd all aimed at covering a broader range of trends and fashion styles (zLabels, 2017). The brands originate from Berlin and have been enjoying an excellent market response. The private brands include different assortments like shoes, accessory and apparel collection for women, men and children, which have equally contributed to the success of the company. Particularly, the company has its private label designers currently working to introduce new ideas to respond to future fashion trends and as such, has developed Zalando to be ranked among the largest employers in Berlin’s fashion industry (Bearne, 2015).
Additionally, brand partnerships have equally contributed to the success of the retailer. Some of the executive brand partnerships include the collaboration with Mango as well as Topshop as some of the major brands in Spain and Britain respectively (Zentes et al., 2016). From this, the store offers fashion labels that are updated and representing unique brand stories. Another form of the partnerships are the brand shops of which particular areas are reserved for the brand partners of which opportunity is left to tailor the brands towards satisfying customers (Zentes et al., 2016).
2.7 Strong Corporate Values
Corporate governance has become such a vital consideration in the modern business environment of which considerations are on fulfilling the needs and expectations of all stakeholders (Walsh et al., 2017). For Zalando, much of its success is attributed to the embedded corporate values which are customer-centric. Customer satisfaction is crucial towards the success and growth of the company (Zalando, 2017a). The aim of the company has been on exceeding customer expectations while equally surprising them with product offerings, as well as impressing them so that their trust can be earned. All the daily operations of the company are embedded in unique and distinct aspirations considered as the foundations to the company’s success.
Also, the corporate value of the company focuses on continuous development whereby solutions are sought to every problem through innovation (Zalando, 2017a). The team spirit and dynamic working culture have been equally useful in driving the success of the company; Zalando’s employees are seen to have a strong passion for technology, fashion as well as retail-excellence.
Since the corporate value or culture within the company embraces teamwork, the focus is on creativity and the exploration of different solutions (Zalando, 2017a). All the employees within the retailer are encouraged to always think out of the box and as such, are convinced to embrace changes but still maintaining the sight of the individual and company’s goals. Team setting has ensured that innovation is reached to greater levels or extent in the enterprise. Moreover, great ideas are considered not to be exclusively explored or used within formal settings (Zalando, 2017a). The company has created a work environment with the aim of encouraging employees to remain unconventional but being pragmatic in their actions.
3. Key Challenges Lying Ahead
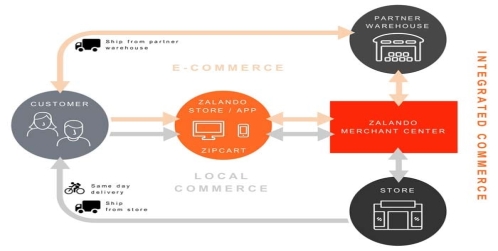
In spite of the much-celebrated success, few challenges lay ahead for Zalando, where the management has to address to sustain its growth and expansion. As the retailer continues to partner with other major brands like Adidas, the challenge lying ahead is how it will be able to connect the online stores and the physical brick and mortar store departments. Recently, Adidas has been welcomed as the first international partner. From the partnership, the Berlin customers are currently able to order online at the retailer and as such, having the Adidas products shipped from Zalando’s store (Hendrlksz, 2016). In this case, the move in Diagram 1 shows the vision that the company currently has in creating integrated commerce to fulfill the demands and expectations of the customers.
Diagram 1 Integrated commerce (Metzler & Bendix, 2016)
However, the challenge now lays on how the company will link its online retail store with the physical stores to ensure that the clients get what they want from major brand partners like Adidas. Creating a connection between the online stores and the physical stores shows the challenge that the company will have in integrating its e-commerce (Pantano and Viassone, 2015). In this case, the increased expansion and partnership with other brands is set to come at the expense of the company’s higher expenditure in ensuring that accessibility is improved and that customers are not disappointed when they make for orders and requests (Pantano and Viassone, 2015). As such, it is also a challenge in already crowded market to ensure that partnerships with brands are effective or will be successful. Therefore, there is a bigger challenge for the retailer to tailor its strategy and business model into meeting the expectations of high-end brands like Adidas and also maintaining its e-retail business model.
Other problems will also come with the advancements in technology, especially on such provisions like machine learning which is poised to change not only the fashion industry but also other industries in general. The concept will change the fashion industry especially how it is influenced or defined by vital social factors or indicators like idols, brands, stars as some of the subsets of fashion. Machine learning as a technology will bring the inherent challenge of recommending and curating fashion through automatic system or approach (Perlich et al., 2014). Machine learning and artificial intelligence will solely depend on the data collected by the companies and brands to identify trends in consumptions and fashion. Nevertheless, the primary challenge lying ahead for online retailers like Zalando is to get to learn the trends in consumption; the inherent necessity to use large and relevant data sets. For example, the retailer currently has data sets in the fashion and consumer behavior on luxury products. On the other end, only bigger companies and the established retail brands will benefit because they have an extensively large customer base of which they will use the machine learning to their scale effects. In this case, the challenge implies that machine learning and artificial intelligence will only make it possible for the larger and established retailers to grow (Fan et al., 2014). Conversely, machine learning and artificial intelligence cannot be used in determining and learning such significant aspects as social, emotional as well as other fashion aspects which are psychologically determined (Perlich et al., 2014).
The other important or profound challenge with the online fashion retail is consumerism. In the modern business environment, consumers hold too much power. From this, the retail brands are forced to be sensitive to the needs and expectations of the customers (Pantano and Viassone, 2015). In this case, a retailer has to be to present in all the channels of communication and interaction. Therefore, e-commerce is set to increase in the near future with the online retailers like Zalando being put under pressure to fulfill the e-retail services. A major challenge will be the provision of the e-commerce experience while also making profits from the business. On the other hand, consumers are ever in a constant demand for new and various products (Pantano and Viassone, 2015). An excellent example is the fast fashion apparel whereby customers to match the consumerism approach of their celebrities within weeks or days. The trend is set to continue and be the major determinant of consumption in the retail industry. Zalando will equally experience obstacles in meeting the dynamic nature of consumption. Fundamentally, the exponential growth of the fashion and luxury products will put too much pressure on retailers like Zalando. Meeting the vibrant and changing needs of the consumers will become a primary or profound challenge in the coming years for Zalando.
The other most vital challenge to the retail industry or sector is on sustainability and the need for adopting green practices in business management and distribution of products (Boström and Micheletti, 2016). There is a growing trend of the fashion brand websites displaying information and messages about their actions on the community and protection of the environment. In reality, corporate social responsibility has become such a major consideration and a vital aspect of retail management. Consumers have also become aware of their role in pushing for actions and intervention on environmental protection. In this case, retailers are screened for waste disposal, water consumption, labor practices, working conditions, health, and safety (Crane, 2016). The implication is that when a brand has a negative association with the listed elements of environmental and social sustainability, then it risks losing client base. The same challenge lies for Zalando because in the near future, lobbying for sustainability will increase of which the emphasis of consumers will be on identifying with the brands that implement and value sustainable business practices. Balancing sustainability and meeting the needs and expectations of the fast fashion market will be a challenge for Zalando.
4. Conclusion
From the above assessment, significant conclusions can be made regarding the factors for growth and primary or key challenges that need to be addressed in the future. Zalando has become a major giant in the e-commerce environment, beginning as a small online apparel and accessory store to become a major force to reckon with in the online retail market. The success is much attributed to the customer-centric approach whereby meeting the needs and expectations of the customers is the central focus of the business strategy. Also, not to forget all is achieved through a trained and skilled workforce with the experience and knowledge on customer service. Moreover, much is attributed to the targeting strategies that the company employed at the point of its entry into the market. Different approaches were exploited in targeting marketing, including incentives like article marketing through search engine optimization and also the adoption of re-targeting approach.
Proper customer management initiatives had also been adopted, especially the interaction with customers from different platforms like social media. Also, part of customer management stems from the emphasis that the company has put on to ensure that the customer’s issues and concerns are being addressed on a 24/7 basis with a dedicated customer care unit to attend to the needs and concerns of the customers. Partnering with other brands and its unique brands is partly to be considered for the growth and success of the company. The brand provides the company with target markets and exposes the brand to different customers. Localisation is also a factor for success, especially how the company ensures that services or products are not standardized but rather tailored towards meeting the specific needs and expectations of the local markets.
There are significant challenges that the company needs to confront in the future. The emergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning will make it difficult to understand the trends in consumption and fashion. As the company continues to grow and expand, more brand partnerships are being considered, but there is the challenge of linking the physical stores and online stores of the enterprise. Furthermore, problems are set to arise with consumerism, especially how customers determine and dictate what they want in the market. Sustainability will also force the company to focus on embracing environmental and social responsibility at the expense of revenues.
References
Adegeest, D. (2016) Zalando expands fulfillment centers in Europe. [Online]. 2016. Available from: https://fashionunited.uk/news/retail/zalando-expands-fulfillment-centers-in-europe/2016082221493 [Accessed: 3 August 2017].
Arora, A.P., (2017) Buying behaviour of consumers towards luxury fashion brands. Global Journal of Enterprise Information System, 9(2), 123-126.
Bearne, S. (2015) Zalando plots Berlin campus space to accommodate 5,000 employees. Available from: https://www.retail-week.com/sectors/fashion/zalando-plots-berlin-campus-space-to-accommodate-5000-employees/7002292.article [Accessed: 5 August 2017].
Bik, H.M., Dove, A.D., Goldstein, M.C., Helm, R.R., MacPherson, R., Martini, K., Warneke, A. and McClain, C., (2015) Ten simple rules for effective online outreach. PLoS computational biology, 11(4). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003906 [Accessed: 6 August 2017].
Blázquez, M., (2014) Fashion shopping in multichannel retail: The role of technology in enhancing the customer experience. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 18(4), 97-116.
Boerman, S.C., Kruikemeier, S. and Zuiderveen Borgesius, F.J., (2017) Online behavioral advertising: A literature review and research agenda. Journal of Advertising, 1-14.
Boström, M. and Micheletti, M., (2016) Introducing the sustainability challenge of textiles and clothing. Journal of Consumer Policy, 39(4), 367-375.
Bradshaw, J. (2017) Online retail booms as high street struggles. Available from: http://www.telegraph.co.uk/business/2017/01/08/online-retail-booms-high-street-struggles/ [Accessed: 1 August 2017].
Bullinger, C. (2014) Zalando – 7 letters for success in e-commerce. Available from: http://internetinnovators.com/en/post-en/zalando-7-letters-for-success-in-e-commerce/ [Accessed: 5 August 2017].
Carmignani, G. and Zammori, F., (2015) Lean thinking in the luxury-fashion market: evidence from an extensive industrial project. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 43(10/11), 988-1012.
Chandon, J.L., Laurent, G. and Valette-Florence, P., (2016) Pursuing the concept of luxury: Introduction to the JBR Special Issue on “Luxury Marketing from Tradition to Innovation.” Journal of Business Research, 69(1), 299-303.
Crane, D., (2016) The puzzle of the ethical fashion consumer: Implications for the future of the fashion system. International Journal of Fashion Studies, 3(2), 249-265.
Ecommerce News (2017) Ecommerce in Europe: €602 billion in 2017. Available from: https://ecommercenews.eu/ecommerce-europe-e602-billion-2017/ [Accessed: 1 August 2017].
Einav, L., Levin, J., Popov, I. and Sundaresan, N., (2014) Growth, adoption, and use of mobile E-commerce. The American economic review, 104(5), 489-494.
Fan, J., Han, F. and Liu, H., (2014) Challenges of big data analysis. National science review, 1(2), 293-314.
Giovannini, S., Xu, Y. and Thomas, J., (2015) Luxury fashion consumption and Generation Y consumers: Self, brand consciousness, and consumption motivations. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management, 19(1), 22-40.
Hendrich, C. (2017) Elevating the Zalando Brand. Available from: https://corporate.zalando.com/sites/default/files/mediapool/20170620_elevating_zalando_website.pdf [Accessed: 3 August 2017].
Hendriksz, V. (2016) Zalando tackles the challenges with linking online and offline. Available from: https://fashionunited.uk/news/retail/zalando-tackles-the-challenges-with-linking-online-and-offline/2016062120833 [Accessed: 9 August 2017].
Kastanakis, M.N., and Balabanis, G., (2014) Explaining variation in conspicuous luxury consumption: An individual differences’ perspective. Journal of Business Research, 67(10), 2147-2154.
Kehoe, R.R. and Wright, P.M., (2013) The impact of high-performance human resource practices on employees’ attitudes and behaviors. Journal of management, 39(2), 366-391.
Kim, S., Park, G., Lee, Y. and Choi, S., (2016) Customer emotions and their triggers in luxury retail: Understanding the effects of customer emotions before and after entering a luxury shop. Journal of Business Research, 69(12), 5809-5818.
Ko, E., Phau, I. and Aiello, G., (2016) Luxury brand strategies and customer experiences: Contributions to theory and practice. Journal of Business Research, 69(12), 5749-5752.
Lambrecht, A. and Tucker, C., (2013) When does retargeting work? Information specificity in online advertising. Journal of Marketing Research, 50(5), 561-576.
Mac, R. (2014) Zalando Worth $6.8 Billion After Pricing IPO At More Than $27 A Share. Available from: https://www.forbes.com/forbes/welcome/?toURL=https://www.forbes.com/sites/ryanmac/2014/09/29/zalando-worth-6-8-billion-after-pricing-ipo-at-more-than-27-a-share/&refURL=https://www.google.co.uk/&referrer=https://www.google.co.uk/ [Accessed: 2 August 2017].
Magrath, V. and McCormick, H., (2013) Marketing design elements of mobile fashion retail apps. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management: An International Journal, 17(1), 115-134.
Metzler, P. & Bendix, A. (2016) Integrated Commerce and our Merchant Center rebuild. Available from: https://jobs.zalando.com/tech/blog/integrated-commerce-merchant-centre-rebuild/?gh_src=4n3gxh1 [Accessed: 8 August 2017].
Ngai, E., Tao, S. and Moon, K., (2015) Social media research: Theories, constructs, and conceptual frameworks. International Journal of Information Management, 35(1), 33-44.
Pantano, E. and Viassone, M., (2015) Engaging consumers on new integrated multichannel retail settings: Challenges for retailers. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 25, 106-114.
Pantano, E., (2014) Innovation drivers in retail industry. International Journal of Information Management, 34(3), 344-350.
Perlich, C., Dalessandro, B., Raeder, T., Stitelman, O. and Provost, F., (2014) Machine learning for targeted display advertising: Transfer learning in action. Machine learning, 95(1), 103-127.
Phillips, J. & Gully, S. (2015) Strategic staffing. 3rd edition. New Jersey, Pearson Education.
Popescu, G.H., (2015) The competitive nature and effectiveness of online retailing. Psychosociological Issues in Human Resource Management, 3(1), 101-106.
Rask, M., (2014) Internationalization through business model innovation: In search of relevant design dimensions and elements. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 12(2), 146-161.
Ryan, D. and Jones, C. (2012) Understanding digital marketing: Marketing strategies for engaging the digital generation. 2nd Edition. London, Kogan Page Limited.
Shotter, J. (2017) Zalando lifts revenues but signals margin pressure. Available from: https://www.ft.com/content/b0feacf2-fe6a-11e6-8d8e-a5e3738f9ae4 [Accessed: 2 August 2017].
Suryandari, R.T. and Paswan, A.K., (2014) Online customer service and retail type-product congruence. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 21(1), 69-76.
Trainor, K.J., Andzulis, J.M., Rapp, A., and Agnihotri, R., (2014) Social media technology usage and customer relationship performance: A capabilities-based examination of social CRM. Journal of Business Research, 67(6), 1201-1208.
Tuten, T.L., and Solomon, M.R., (2015) Social media marketing. 2nd Edition. Boston, Sage.
Vecchi, A. & Buckley, C. (2016) Handbook of research on global fashion management and merchandising. Hershey, IGI Global.
Verma, V., Sharma, D. and Sheth, J., (2016) Does relationship marketing matter in online retailing? A meta-analytic approach. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44(2), 206-217.
Walsh, G., Schaarschmidt, M., Schaarschmidt, M., Ivens, S. and Ivens, S., (2017) Effects of customer-based corporate reputation on perceived risk and relational outcomes: empirical evidence from gender moderation in fashion retailing. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 26(3), 227-238.
Wauters, R. (2014) Inside Zalando: A deep dive into Europe’s biggest online fashion store. Available from: http://tech.eu/features/339/inside-zalando/ [Accessed: 2 August 2017].
Wedel, M. and Kannan, P.K., (2016) Marketing analytics for data-rich environments. Journal of Marketing, 80(6), 97-121.
Zalando (2017a) Corporate Values. Available from: https://corporate.zalando.com/en/corporate-values-p#fc-303 [Accessed: 5 August 2017].
Zalando (2017b) From start-up to grown-up. Available from: https://corporate.zalando.com/en/start-se#fc-229 [Accessed: 2 August 2017].
Zalando (2017c) Shoes & Fashion Online | Brands. Available from: https://www.zalando.co.uk/brands/ [Accessed: 6 August 2017].
Zentes, J., Morschett, D and Schramm-Klein, H. (2016) Strategic retail management: Text and international cases. 3rd Edition. Wiesbaden, Springer Gabler
Zhao, M., Park, S.H. and Zhou, N., (2014) MNC strategy and social adaptation in emerging markets. Journal of International Business Studies, 45(7), 842-861.
zLabels (2017) Brands. Available from: https://zlabels.com/brands [Accessed: 7 August 2017].
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Business Strategy"
Business strategy is a set of guidelines that sets out how a business should operate and how decisions should be made with regards to achieving its goals. A business strategy should help to guide management and employees in their decision making.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




