Regulatory Strategy for Variations of Registered Products
Info: 9832 words (39 pages) Dissertation
Published: 9th Dec 2019
Tagged: BusinessBusiness Strategy
- OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY
The objective of this topic is to give knowledge and better comprehension of the administrative necessities for changes improved the situation an endorsed medicate items in various directed markets of United States, Europe and South Africa. For technical advancements, there may be situations which necessitate modifications for an approved drug products. The changes must be in conformance with the regulatory requirements of the Regulatory authority, the ultimate authority for the Drug related approvals in respective regions. The progressions can be significant, direct or minor relying upon the progressions prone to influence the quality, security and viability of the item. Independent of the classification of the progressions, each change is to be conveyed to the notice of the Regulatory specialist in stipulated design that are suggested for the administrative headways. It is the in charge of guaranteeing item quality. The objective is outstanding, the segments requiring change are surely knew and portrayed and the procedure very much characterized. The varieties direction means to build up a straightforward, clearer and more adaptable lawful system for the handling of variations to marketing authorisation of medicinal products, while ensuring a high level of protection of public health.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 32
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


- METHODOLOGY
Variation: A change to the terms of marketing authorization.
Guideline: A document providing guidance on the scientific or regulatory aspects of thedevelopment of medicines and applications for marketing authorisation. Although guidelines are not legally binding, applicants need to provide justification for any deviations.
VARIATIONS (EUROPE)
An advertising authorisation sets out the terms under which the promoting of a restorative item is approved in the EU. A promoting authorisation is made out of:
- a choice allowing the advertising authorization issued by the applicable expert; and
- a specialized dossier with the information put together by the candidate
The Variations Regulation oversees the methods for the correction of the
choice allowing the advertising authorisation and of the specialized dossier.
VARIATION CLASSIFICATION:
All post endorsement changes can be advised to the office through variety documenting. This approach can be material for all classes of uses, for example, Central system (CP), National technique (NP), Decentralized methodology (DCP) and Mutual acknowledgment strategy (MRP). Varieties can be characterized in to four classifications, for example,
- Minor varieties of Type IA
- Minor varieties of Type IB
- Major varieties of Type II
- Extensions
Minor variations of Type IA
Type-IA
These varieties don’t require any earlier endorsement, yet MAH ought to advise inside a year (“Do and Tell”).
Type-IAIN
It requires prompt notice after execution.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 33
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


Minor varieties of Type IB
These must be advised before execution. The holder must hold up 30 days to guarantee that the warning is esteemed adequate (“Tell, Wait and Do”).
Significant varieties of Type II
These varieties require endorsement of the important equipped specialist before usage.
Extensions
These notices will be assessed as like introductory MAA. The expansion can either be conceded as another MA or will be incorporated into the underlying MA to which it relates.
VARIETIES CHANGES
Variety changes are isolated in to four classifications, for example, 1. Authoritative 2. Quality 3. Security, Efficacy and Pharmacovigilance and 4. Particular changes to plasma ace documents and immunization antigen ace records. In view of the adjustment in the post endorsement arrange, MAH ought to take after the EMA suggestions for archive accommodation and execution. Figure-3 speaks to the post endorsement changes groupings.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 34
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS
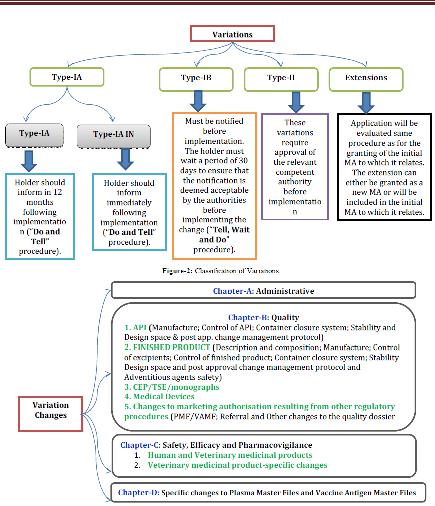
Figure 4 Variation changes


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 35
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


VARIATION GROUPING:
Varieties can be submitted with a solitary warning to the same significant specialist, or to aggregate them with different sorts of varieties. MAH can gather the varieties, for example, sort IA/IAIN varieties or sort IA/IAIN varieties and sort IB varieties or all classifications of varieties in one medication item or in various items moreover. The nitty gritty gathering approaches are spoken to in the beneath figure
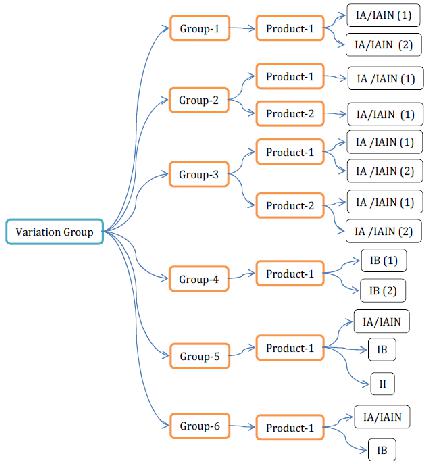
Figure 5 Variations grouping approaches


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 36
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


SUBMISSION OF VARIATIONS NOTIFICATION (HANDLING)
Centralized Procedure:
1. Type IA variations:
The Agency will audit the warning inside 30 days, without contribution of the rapporteur for the item concerned selected by the CHMP or CVMP. Nonetheless, a duplicate of the Type IA warning will be presented by the Agency to the rapporteur for data. In the event that few minor varieties of Type IA are submitted with one notice, the Agency will obviously illuminate the holder which varieties have been acknowledged or dismissed. While on account of minor varieties of Type IA, inability to give all important documentation in the application won’t really prompt the quick dismissal of the variety if the holder gives any missing documentation instantly on demand of the Agency, it ought to be featured that a minor variety of Type IA may in particular conditions be rejected with the outcome that the holder must stop to apply officially actualized varieties concerned.
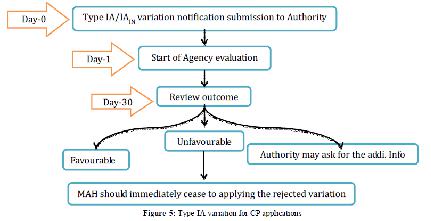
Figure 6 Type IA variation for CP applications


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 37
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


2. Type IB variations
Office recognizes the warning inside 7 logbook days. On the off chance that the proposed variety is not viewed as a variety Type IB then the holder should ask for the office to amend its application and to finish it as per the necessities for a variety Type
 II. If the variety considered as sort IB then appraisal technique will be started. The rapporteur will be associated with the audit and it will take 30 days. In the event that the Agency has not sent the holder its evaluation comes about inside 30 days then the warning will be esteemed satisfactory. If there should arise an occurrence of an Unfavorable result, the holder may change the notice inside 30 days. On the off chance that the holder does not change the warning then the notice will be rejected. In the event that revised at that point, Agency will educate the holder of its last acknowledgment or dismissal. On the off chance that the variety warning is gathered with different class of varieties at that point, organization will obviously advise the holder which varieties have been acknowledged or dismissed
II. If the variety considered as sort IB then appraisal technique will be started. The rapporteur will be associated with the audit and it will take 30 days. In the event that the Agency has not sent the holder its evaluation comes about inside 30 days then the warning will be esteemed satisfactory. If there should arise an occurrence of an Unfavorable result, the holder may change the notice inside 30 days. On the off chance that the holder does not change the warning then the notice will be rejected. In the event that revised at that point, Agency will educate the holder of its last acknowledgment or dismissal. On the off chance that the variety warning is gathered with different class of varieties at that point, organization will obviously advise the holder which varieties have been acknowledged or dismissed

Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 38
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS
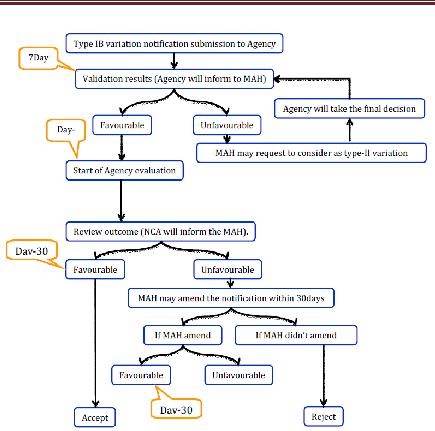
Figure 7 Type IB Variation for CP Applications
3. Type II variations
Office will recognize receipt of a variety warning and after this, Agency will begin the evaluation. All in all, appraisal period is 60-days and this period might be lessened by the Agency in view of desperation of the issue or might be stretched out to 90 days. Inside the evaluation time frame, organization may ask for the supplementary data. The strategy will be suspended until the receipt of the supplementary data. Suspension period is up to 1 month. For broadening the suspension time frame from 1 month, the MAH ought to send a support to the Agency (Maxi. 2months).
Assessment results


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 39
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


Endless supply of a conclusion of the CHMP/CVMP, the Agency will advise to MAH inside 15 days in the matter of whether the variety is acknowledged or dismissed. Where a few Type II varieties, or a gathering of Type II varieties with other minor varieties have been submitted as one application, the Agency will issue an assessment mirroring the ultimate result of the method. The holder may pull back single varieties from the gathered application amid the system. The endorsed real varieties of Type II requiring correction of the Commission choice giving the MA inside 2 months may just be executed once the holder has been educated by the Commission as needs be. Where revision of the choice conceding the MA is not required inside 2 months, or where the endorsed variety does not influence the terms of the Commission choice allowing the MA, the variety might be executed once the holder has been educated by the Agency that its sentiment is great. Varieties identified with wellbeing issues must be executed inside a time span concurred between the Commission and the holder.
Extension assessment
Upon receipt of an extension application, the Agency will handle the application as for an initial marketing authorization application in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 726/2004.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 40
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS
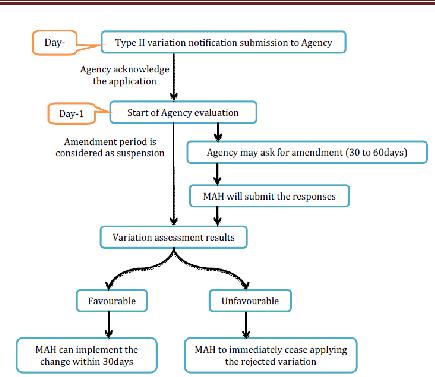
Figure 8 Type II Variation for CP applications
MRP PROCEDURE:
1. Type IA variations
Office will recognize the variety warning and survey inside 30days. MAH can gather Type IA/IAIN varieties and changes can be actualized before accommodation of the notice. Be that as it may, in the event of un-ideal result, MAH ought to promptly stop applying the rejected varieties. By Day 30, the RMS will educate the evaluation results to holder and CMS. On the off chance that the MA requires any change to the choice allowing the MA, all CMS will refresh the choice conceding the MA inside a half year following the receipt of the result of the audit sent by the RMS, gave that the records important to the correction of the MA have been submitted to the CMS. Where one or a few minor varieties of Type IA are submitted as a major aspect of one
Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 41
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


notice, the RMS will illuminate the holder which varieties have been acknowledged or dismissed. The MAH must not actualize the rejected varieties.
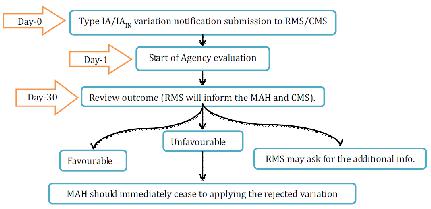
Figure 9 Type IA Variation for MRP Application
Type IB variations
The RMS will recognize the notice inside the 7 date-book days. In the event that the warning is right and finish then evaluation will begin. On the off chance that the notice not considered as sort IB, the holder will be asked for to change its application and to finish it as per the prerequisites for a Type II variety application. The appraisal time frame is 30days. In the event that the RMS has not sent the appraisal comes about inside 30days then the warning will be regarded adequate. In the event of an un-positive outcome, the holder may revise the notice inside 30 days. In the event that the holder does not revise the notice inside 30 days as asked for, the variety will be esteemed rejected by all CMS. Inside 30 days of receipt of the revised notice, the RMS will advise the holder of its last acknowledgment or dismissal. Where a gathering of minor varieties were submitted as a major aspect of one warning, the RMS will illuminate the holder and the CMS which varieties have been acknowledged or dismissed. Where fundamental, the pertinent specialists will refresh the MA inside a half year following conclusion of the system by the RMS. In any case, the acknowledged minor varieties of Type IB variety might be executed without anticipating the refresh of the MA.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 42
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS
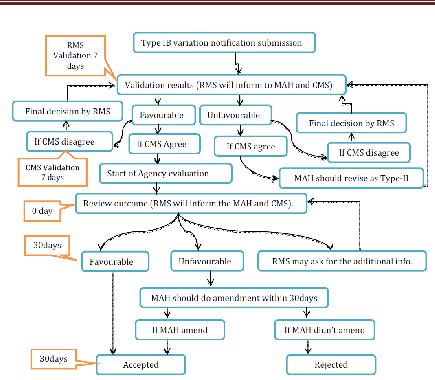
Figure 10 Type IB Variation for MRP Application
Type II variations
Organization will recognize the warning and appraisal will take 60days. This period might be lessened by the RMS in light of the earnestness or might be reached out to 90 days. RMS will set up a draft appraisal report and a choice on the application as per the imparted timetable and will course them to the CMS for remarks and to the holder for data. The CMS will send to the RMS their remarks inside the due dates set out in the timetable. Inside the assessment time frame, the RMS may ask for the MAH to give supplementary data and this period will consider as suspension. By and large, a suspension time is one month and it will reach out up to 2months in light of the holder demand to the RMS for understanding. After receipt of the holder’s reaction, the RMS will finish the draft evaluation report and the choice on the application and will flow them to the CMS for remarks and also to the holder for data.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 43
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


Assessment Results
Before the finish of the assessment time frame, the RMS will settle and present the evaluation report and its choice on the application to the CMS. Inside 30 days following receipt of the appraisal report and the choice, the CMS will perceive the choice and educate the RMS as needs be. Where an application concerning a gathering of varieties that incorporates no less than a variety Type II is alluded to the coordination gathering, the choice on the varieties not subject to the referral will be suspended until the point that the referral system has finished up. In any case, just the varieties in regard of which a potential genuine hazard to human or creature wellbeing or to nature has been distinguished will be talked about by the coordination gathering and in the long run by the CHMP or CVMP. The RMS will illuminate the CMS and MAH about the endorsement or dismissal. On the off chance that MAH presented the gathered varieties as one application, RMS will illuminate the holder and the CMS which varieties have been acknowledged or dismissed. The holder may pull back single varieties from the gathered application amid the method. After a positive choice is conveyed in regards to varieties with changes to the outline of item qualities, marking or bundle flyer, the holder ought to submit, inside 7 days, interpretations of the item data writings to all CMS. After endorsement of the varieties, the skilled specialists of the CMS will, where vital, change the promoting authorisation to mirror the varieties inside 2 months, gave that the reports important to the revision of the MA have been submitted to the CMS. The acknowledged real varieties of Type II can be actualized inside 30 days. In those situations where the application has been the protest of a referral, the varieties must not be actualized until the point when the referral system has inferred that the varieties is acknowledged. Be that as it may, the varieties in the gathering not subject to the referral might be actualized if so demonstrated by the RMS. Varieties identified with security issues must be executed inside a time span concurred between the RMS and the holder.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 44
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS
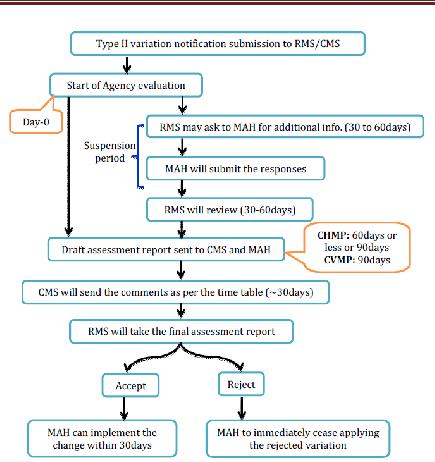
Figure 11 Type II Variation for MRP application


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 45
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


NATIONAL PROCEDURE:
1. Type IA variations
NCA will audit the Type IA warning inside 30 days. In the event that the MA requires any revision to the choice giving the MA, NCA will refresh the choice allowing the MA inside a half year. For the gathered variety, NCA will advise the holder which varieties have been acknowledged or dismissed. In the event that the variety has been dismissed then MAH ought to promptly stop to apply officially actualized varieties.
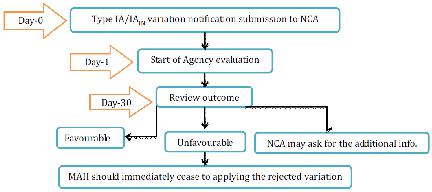
Figure 12 Type IA variation for NP Application
- Type IB variations
NCA will check whether the proposed change can be considered as Type IB variety or not. If not considered, at that point the holder will be asked for to update its application and to finish it as per the necessities for a noteworthy variety of Type II application. The survey time frame is 30days. On the off chance that the NCA has not sent the holder its assessment on the warning inside 30 days then the notice will be regarded satisfactory. On the off chance that rejected, at that point holder may revise the warning inside 30 days to assess the reason for the disapproval of the variety. On the off chance that the holder does not alter the warning inside 30 days as asked for, the variety will be regarded dismissed by the NCA. Inside 30 days of receipt of the changed notice, the NCA will illuminate the holder of its last acknowledgment or dismissal of the varieties. Where a gathering of minor varieties were submitted as a major aspect of one notice, the NCA will advise the holder which varieties have been acknowledged or dismissed. Be that as it may, the acknowledged minor varieties of Type IB might be actualized without anticipating the refresh of the MA.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 46
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS
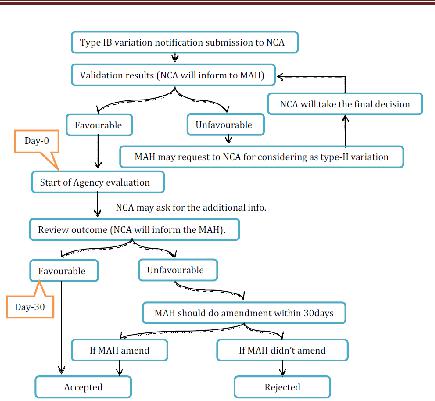
Figure 13 Type IB variation for NP Application
3. Type II variations
NCA will recognize receipt of a substantial variety Type II application and audit begins from the date of affirmation. When all is said in done, the audit time frame is 60-day for human and 90days for veterinary drugs. This period might be diminished or might be stretched out to 90 days. Inside the assessment time frame, the NCA may ask for the holder to give supplementary data. The method will be suspended until the receipt of the supplementary data. When in doubt, a suspension of one month will apply. For longer suspension the holder ought to send a defended demand to the NCA for assention. The assessment of reactions may take up to 30 or 60 days relying upon the unpredictability and measure of information asked for to the holder.
Assessment Results


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 47
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


Before the finish of the assessment time frame, the NCA will advise to the holder about the endorsement or dismissal. For gathered varieties, NCA will illuminate the holder which varieties have been acknowledged or dismissed. The holder may pull back single varieties from the gathered application amid the technique. After endorsement of the varieties, NCA will correct the MA to mirror the varieties inside 2 months gave that the archives important to the alteration of the MA have been submitted to NCA.
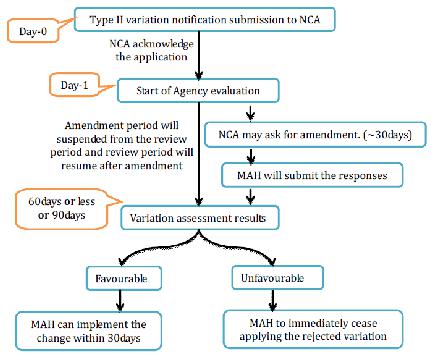
Figure 14 Type II Variation for NP Application
Acknowledged varieties of Type II can be executed after acknowledgment of the varieties by the NCA, Variations identified with wellbeing issues must be actualized inside a time period concurred between the NCA and the holder.
Extension assessment
Endless supply of an expansion application under the common acknowledgment or the simply national technique, it will be dealt with as an underlying MAA.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 48
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


REJECTED VARIATION HANDLING
On account of a negative result from the organizations and not met and thus a resubmission is required or in light of the fact that documentation is lacking. If so, Agency may request that the MAH finish a presumed quality deformity notice shape and give a Risk Assessment provide details regarding the effect of the item available by means of email to qdefect@ema.europa.eu inside 7 timetable days from the date of the dismissal letter. Such asks for are relied upon to be extremely extraordinary.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 49
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


VARIATIONS (UNITED STATES):
The New Drug Application (NDA) is the vehicle through which the medication supports formally propose the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for approving the marketing of new pharmaceuticals in the United States (US). NDA provides the complete information regarding the quality, safety, efficacy and other characteristics of the product. Changes are inevitable at times for an approved NDA, but reporting the changes are mandatory and are to be in compliance with the regulatory requirements of FDA. This article details the regulatory requirements and the ways of reporting post approval changes of an NDA to the FDA.
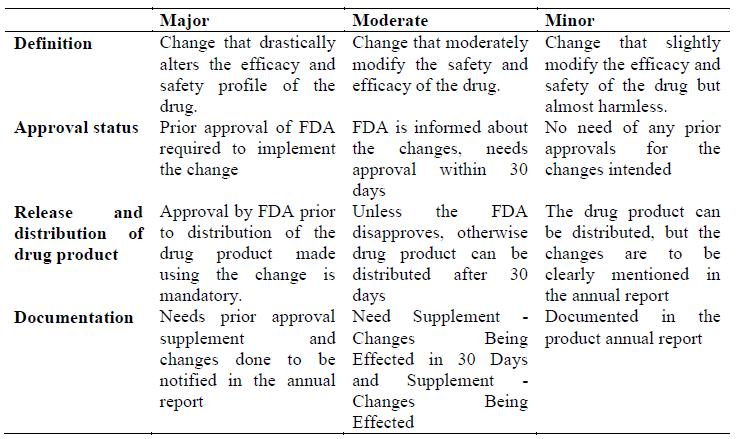
The post endorsement changes are to be as per area 506A of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the Act) and § 314.70 (21 CFR 314.70). The post approval changes are categorically reported as
- Major changes
- Moderate changes
- Minor changes
- Major change:
A noteworthy change is a change that has a considerable potential to adversy affect the character, quality, quality, immaculateness, or power of a medication item as these elements may identify with the wellbeing or adequacy of the medication item. A noteworthy change requires the accommodation of a Supplement and endorsement by FDA before conveyance of the medication item rolled out utilizing the improvement. This sort of supplement is called, and ought to be unmistakably named, an “Earlier Approval Supplement”. A candidate may solicit FDA to speed up its survey from an earlier endorsement supplement for general wellbeing reasons (e.g., medicate deficiency) or if a postponement in rolling out the improvement portrayed in it would force a phenomenal hardship on the candidate. This kind of supplement is called, and ought to be plainly named, an “Earlier Approval Supplement – Expedited Review Requested”. FDA is destined to concede demands for facilitated survey in view of remarkable hardship for assembling changes made fundamental by calamitous occasions (e.g., fire) or by occasions that couldn’t be sensibly predicted and for which the candidate couldn’t design.
2. Moderate change:


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 50
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


A direct change is a change that has a direct potential to adversy affect the character, quality, quality, immaculateness, or intensity of the medication item as these components may identify with the wellbeing or viability of the medication item.
There are two sorts of direct change. One sort of Moderate change requires the accommodation of a supplement to FDA no less than 30 days before the conveyance of the medication item rolled out utilizing the improvement. This sort of supplement is called, and ought to be plainly marked, a “Supplement – Changes Being Effected in 30 Days”. The medication item rolled out utilizing a direct improvement can’t be conveyed if FDA illuminates the candidate inside 30 days of receipt of the supplement that an earlier endorsement supplement is required. For each change, the supplement must contain data controlled by FDA to be suitable and must incorporate the data created by the candidate in surveying the impacts of the change. In the event that FDA educates the candidate inside 30 days of receipt of the supplement that data is missing, dissemination must be postponed until the point when the Supplement has been revised to give the missing data. FDA may distinguish certain direct changes for which dissemination can happen when FDA gets the supplement. This sort of supplement is called, and ought to be unmistakably named, a “Supplement – Changes Being Effected”. On the off chance that, after survey, FDA opposes changes-being affected in-30-days supplement or changes-being-affected supplement.
3. Minor change:
A minor change is a change that can possibly adversy affect the personality, quality, quality, immaculateness, or intensity of the medication item as these variables may identify with the wellbeing or viability of the medication item. The candidate must portray minor changes in its next Annual Report. Under § 314.70(e), a candidate can submit at least one conventions (i.e., equivalence conventions) depicting tests, studies, and acknowledgment criteria to be accomplished to show the nonattendance of an unfavorable impact from determined sorts of changes. A likeness convention can be utilized to diminish the revealing class for determined changes. A proposed similarity convention that was not affirmed as a major aspect of the first application must be submitted as an earlier endorsement supplement..
GENERAL PRE-REQUISITES
submitted data (e.g., remedy of spelling or typographical blunders, reformatting of group records), a candidate must inform FDA about each Change in each condition built up in an endorsed application past the


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 51
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


variations already Provided for in the application. A supplement or yearly report must incorporate a rundown of all progressions contained in the supplement or Annual report. On the rundown, FDA suggests that the candidate depict each adjustment in enough detail to enable FDA to rapidly decide if the suitable revealing classification has been utilized. For supplements, this rundown must be given in the introductory letter.
In yearly reports, the rundown ought to be incorporated into the synopsis area. The candidate must depict each change completely in the supplement or yearly report.
Table 3 Summary Types of Post-Approval Changes and Their Implications
Valuating the Effect of Manufacturing Changes a) Assessment of the effects of the change
The approved application holder under section 505 of the Act must measure the impacts of the change before conveying a medication item rolled out with an assembling improvement. For each change, the supplement or yearly report must contain data controlled by FDA to be fitting and should incorporate the data created by the candidate in evaluating the impacts of the change. This sort of data must be included in supplemental application or in an annual report.
1) Conformance to specifications


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 52
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


An evaluation of the impacts of a change on the character, quality, quality, virtue, and strength of the medication item ought to incorporate an assurance that the medication substance, intermediates, in-process materials, as well as medication item influenced by the change comply with the endorsed particulars. A determination is a quality standard (i.e., tests, expository techniques, and acknowledgment criteria) gave in an Approved application to affirm the nature of medication substances, tranquilize items, Acceptance criteria are numerical cutoff points, ranges, or other criteria for the tests depicted (§ 314.3(b)). Conformance to a detail implies that the particular, will meet the recorded acknowledgment criteria.
2) Additional testing:
In Notwithstanding affirming that the material influenced by assembling changes keeps on meeting its particular, it is prescribed that the candidate play out extra testing, when proper, to survey whether the character, quality, quality, immaculateness, or power of the medication item as these components may identify with the wellbeing or viability of the medication item have been or will be influenced. The appraisal ought to incorporate, as proper, assessment of any adjustments in the compound, physical, microbiological, organic, bioavailability, and additionally solidness profiles. This extra evaluation could include testing of the post change medicate item itself or, if proper, the material straightforwardly influenced by the change. The sort of extra testing that a candidate should perform would rely upon the kind of assembling change, the kind of medication substance as well as medication item, and the impact of the change on the nature of the medication item. For an Instance: Evaluation of the hardness or friability of a tablet after specific changes.
b) Equivalence
On testing, the applicant should usually assess the extent to which the manufacturing change has impact on the identity, strength, quality, purity, and potency of the drug product. Usually, this is accomplished by comparing test results from before and Post change material and deciding whether the test outcomes are identical.
c) Adverse effect
Some changes can adversely impact the drug product. In most of the cases, the applicant may not implement these manufacturing changes, but sometimes to do so. If an assessment indicates that a change has adversely affected the medicate item, FDA prescribes that the change be submitted in an earlier endorsement supplement paying little heed to the suggested announcing classification for the change. For example, a process change


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 53
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


suggested for a progressions being-affected in-30-days supplement could cause the arrangement of another degradant that requires capability or recognizable proof. The candidate’s corruption capability methodology may demonstrate that there are no security concerns identifying with the new degradant.
By and by, it is suggested by FDA that the candidate ought to present the separate change in an “Earlier endorsement supplement” with suitable data that backings the proceeded with wellbeing and viability of the medication item. Amid the audit of the earlier endorsement supplement, the FDA will evaluate the effect of any unfriendly impact on the medication item as this change may identify with the wellbeing or viability of the medication item. The post endorsement changes are classified as per the category they belong to and the class of change.Table 4 Classes of Post Approval changes
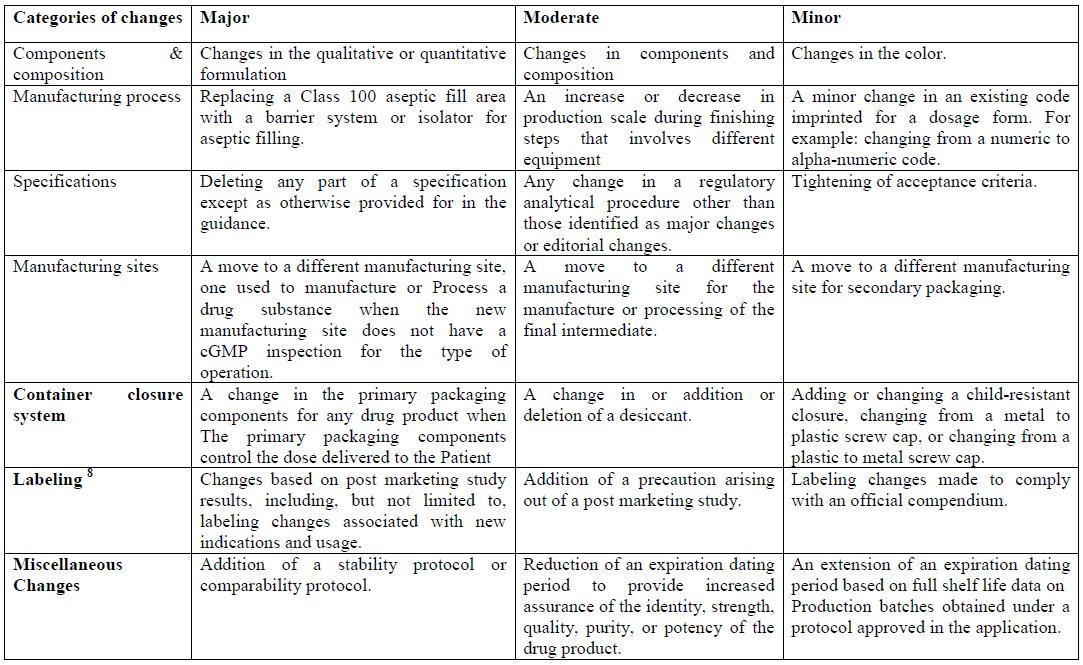
In addition to reporting the changes made, an applicant making a change to an approved NDA under area 506A of the Act should likewise fit in with other relevant laws and controls, including current great assembling practice (cGMP) necessities of the Act (21 U.S.C. 351(a) (2) (B)) and pertinent controls in Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations. Further, the candidate ought to likewise consider all significant CDER direction reports for proposals on the data that ought to be submitted to help a given change.


REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


VARIATIONS (SOUTH AFRICA)
Amendments to the registration dossier are necessary to maintain the safety, quality and efficacy of a medicine and to ensure compliance with current technical requirements, to adhere to administrative aspects, to keep abreast of scientific progress, or to reflect new therapeutic indications / warnings or other safety matters.
It is therefore the objective of the MCC to process, as quickly as possible, amendment applications made by the
- holder of the certificate of registration (HCR) to registered medicines
- Applicant of old medicines
- proposed holder of the registration certificate (PHCR) / Applicant in response to
committee recommendations.
This document has been prepared as a tool to address all matters concerning amendments to
- facilities, (including change in the HCR)
- pharmaceutical and analytical aspects of the medicine.
Comprehensive documentation to support the amendment application should be supplied and the conditions determined by Council, complied with.
1. FORMAT OF RESPONSES TO COUNCIL
1.1 Responses to letters from the Registrar of Medicines should be cross-referenced to the actual questions asked. A copy of the letter from the Registrar of Medicines being replied to should be included for easy reference.
1.2 Council resolutions/Committee recommendations should be addressed by stating the Council resolution/ Committee comments or recommendations followed by the relevant response. The format as per section 6 of this guideline should be used and the requirements of this guideline be complied with.
2. AMENDMENT SUBMISSIONS: FORMAT
2.1 All pre- and post-registration amendment submissions should be submitted with the following in addition to those reflected in section 7 of this guideline:
- Amendment schedule / covering letter in accordance with section 6 of guideline; correct coding is important, as per General Information guideline section 13.
- Administrative amendment fee, if relevant;


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 55
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


- completed MRF1 PART 1A including 1Ac) Amendment history / CTD Module
1.2.1 and relevant front pages of the MRF1 PARTs/SUB-PARTs /CTD module
1.1 ToC
2.2 MRF1 PART 1Ac) Amendment history / CTD Module 1.2.1 f)
- The MRF1 PART 1Ac) / CTD Module 1.2.1 f) Amendment history should reflect the particulars of the pharmaceutical and analytical amendments (if applicable) of all types.
- The current amendment being applied for should not be included in this section as a submission with a response pending.
- If any PARTs / Annexures / Modules or sub-Modules have not been approved, this should be indicated.
- If the response to an amendment is pending, this should be indicated, rather than
not reflecting this amendment at all.
2.3 An amendment application may not address more than one product unless
- the products constitute a range for which a single application for registration dossier was submitted at the time of application for registration
- it is an application for change of only the name or address of the HCR, in which case details for a group of products may be submitted. However, each registration
dossier should be updated in accordance with the change.
2.4 All applications for amendments should be properly bound on the left side. It is preferred that documents be punched (2-hole) and secured. The use of lever-arch files, metal file fasteners and any kind of paper clip is not recommended.
Any single volume should not be thicker than 4 cm, including binder, also depending on the binder used. When submitting more than one volume of an application, they should be tied together.
2.5 All photocopies should be legible and the left margin of documents should be wide enough to allow for legibility after copying and binding. Shading, e.g. in tables, should be avoided.
2.6 The date of the amendment schedule/covering letter should be reflected in black on every page of the submission.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 56
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


2.7 All pages should be paginated and the document indexed according to the existing MRF1 PARTs (e.g. page 3B.1 referring to PART 3B, first page) or tabbed in accordance with the CTD modules.
2.8 Dividers or tabs should be included where applicable to facilitate locating the different sections in the document.
2.9 The front pages of the amended MRF1 PARTs and the amended pages only of the PARTs should be submitted when amendments are made which involve a limited number of pages. The pages to which the amendments refer should be clearly indicated. The relevant ToC for CTD should be updated.
2.10 When extensive updating of the dossier is done, a completely updated dossier should be submitted and the amended PARTs / CTD Modules clearly indicated. The amended pages should reflect the date of the amendment schedule/letter and those not amended should reflect the relevant date of the previous submission/amendment. It is not acceptable to submit selected pages only when a full update is submitted.
2.11 All documents in a foreign language should be translated into English and certified or verified.
2.12 Amendments to applications for registration during evaluation prior to registration by Council are usually not permitted, unless recommended by the committees, or advised by or negotiated with Council.
2.13 Incomplete submissions or submissions which do not comply with the requirements as described or if not accompanied by the amendment schedule/covering letter in the format prescribed in section 6 of this guideline will not be evaluated. These should be collected within 14 working days of notification of the inadequacy, failing which such applications will be destroyed.
3. PROPRIETARY NAME
Changing of the proprietary name during the evaluation and registration phase will only be permitted if the Council has not accepted the name originally proposed by the HCR/applicant.
The policy on proprietary names is detailed in the General Information guideline.
The requirements in addition to those in 2.1 are summarised in section 7.4 of this guideline.
4. HCR-FPRR and/or additional/change of MANUFACTURER, PACKER, FPRC


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 57
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


4.1 Amendments to any of the above result in an update of the Medicine Register and the issue of an amended registration certificate for registered products.
The original medicine registration certificate should accompany amendments to registered products.
A copy of the medicine registration certificate will not be accepted as the original is to be replaced.
If the original certificate has already been submitted to Council, this should be indicated in the amendment schedule / covering letter (section 6 of this guideline).
4.2 The processing of the application is not a mere formality; each application will be evaluated individually. The authorisation for change is dependent on various aspects including the proposed new HCR / manufacturer / packer / laboratory‟s infrastructure and its compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) in terms of the guidelines as recommended by the SA Guide to GMP and the World Health Organisation.
4.3 In order to assess the suitability of the proposed HCR, manufacturer, packer or laboratory, an inspection by Council Inspectors may have to be performed prior to the authorisation of the change requested.
An inspection by Council Inspectors may be required for manufacturers in countries outside the borders of South Africa other than those with which Council aligns itself.
4.4 An amendment will be considered final only once the HCR has been supplied with the new registration certificate or a letter of approval stating that the new registration certificate will follow for registered medicines, or a final letter of approval of the amendment in the case of an old medicine.
4.5 If the dossier has not been updated during the previous 5 years, or an application for a type C change is lodged, a fully updated dossier in CTD format should accompany an application for transfer of the certificate of registration or change in manufacturer.
4.6 The HCR should be familiar with the requirements in the current Guide to GMP.
4.7 As the processing of these amendments results in the updating of the database/Medicine Register and the issue of amended registration certificates, the HCR should ensure that details with regard to approved facilities are current.
4.8 Should there be a discrepancy between the administrative data submitted with the amendment request and the relevant PARTs / MBR1 Annexures, the data in the Registration Dossier on file will be reflected on the registration certificate.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 58
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


4.9 It is the responsibility of the HCR to
- ensure that details with regard to the facilities / laboratories applied for are correctly reflected in MRF1 Part 1A / CTD Modules 1.2.1, 1.7.1, 3.2.S.2, 3.2.P.3.1
- check registration certificates for correctness and communicate discrepancies to Council within 30 days of receipt thereof.
4.10 If the HCR is of the opinion that the information reflected on the registration certificate is incorrect, the correct approved information together with the letter(s) of approval by the Council should be provided. An amended registration certificate will be issued free of charge should the error have occurred at this office.
4.11 Once a change in HCR-FPRR/manufacturer/packer/FPRC has been approved, the updated pages to the PARTs / Modules are placed on file. Subsequent updates of the dossier should clearly and unambiguously reflect these as approved. (It is often not clear whether the information submitted pertains to the same as the previous or a new amendment).
4.12 The letter of cession from the current HCR should confirm that the complete registration dossier (MRF1/ MBR1 / CTD) and product history have been transferred to the proposed HCR. This letter must be signed by the Responsible Pharmacist as defined in [Section 22C(1)(b) of Act 101 of 1965].
4.13 The FPRR changes when a registration certificate is transferred. The MRF1 PART 1A / CTD Modules 1.2.1, 1.5.2 and 1.7 should be appropriately updated to reflect this change. However, if the dossier has not been updated during the previous 5-year period, a fully updated dossier should accompany the application for transfer of the registration certificate.
4.14 The Registration dossier should be fully updated to the current statutory format and current scientific standards within 12 months after transfer of the registration certificate. In the case of mergers the HCR should adhere to the programme of updating of dossiers as approved by the Council. The date by which the dossier will be fully updated should be clearly reflected in the amendment schedule/covering letter.
However, if the dossier has not been updated during the previous 5-year period, a fully updated dossier should accompany the application for transfer of the registration certificate.


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 59
REGULATORY STRATEGY FOR VARIATIONS OF REGISTERED PRODUCTS


4.15 The proposed HCR should ensure that the registration dossier being acquired has been fully updated recently (at least during the last 5 years) and that the full product history is provided by the current HCR. An HCR should be in possession of all the information relevant to the product.
4.16 The current HCR remains legally responsible and liable until transfer of the registration certificate has been confirmed in writing.
4.17 HCR – FPRR ONLY – NAME ONLY
In this case application to change the name of the HCR may be submitted for a whole range of products. Old medicines and registered products should be dealt with under separate cover.
The requirements in addition to those in 2.1 are summarised in section 7 of this guideline.
The relevant documentation has to be submitted for each product.
4.18 HCR – FPRR ONLY – ADDRESS ONLY
4.18.1 The SMF has to be updated.
4.18.2 The front page of the Registration dossier / PART 1A / CTD Modules 1.2.1 and
1.7 have to be updated.
4.18.3 The letter addressed to the Registrar (section 6 of this guideline) has to reflect the code VAA (for the Medicine Register) and include Appendix 1 (CTD Module 1.5.2.1) reflecting the details of the change of the HCR‟s address.
4.18.4 The requirements for change of HCR will apply as this will result in a change in the registration certificate.
The requirements in addition to those in 2.1 are summarised in section 7 of this guideline.
The relevant documentation has to be submitted for each product.
5. PHARMACEUTICAL AND ANALYTICAL AMENDMENTS
This information is for the amendment of a registration dossier already lodged with the Medicines Control Council, pertaining to PART 3 (PART 3A to PART 3I) / MBR1 Annexures 2 to 13 / CTD Module 3 of the application for registration dossier.
It is practically difficult, if not impossible, to review all pharmaceutical amendments to every pharmaceutical product registered by Council. This document is also aimed at trying not to prejudice the HCR in terms of medicine regulation. It is the HCRs responsibility to ensure that
– the requirements of this document and other policies/guidelines are complied with;


Pharmaceutical management and Regulatory Affairs Page 60
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Business Strategy"
Business strategy is a set of guidelines that sets out how a business should operate and how decisions should be made with regards to achieving its goals. A business strategy should help to guide management and employees in their decision making.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




