Cloud Computing and the Development of Mobile Cloud Computing
Info: 18067 words (72 pages) Dissertation
Published: 10th Dec 2019
Tagged: Information TechnologyComputing
In recent years, cloud computing has appeared to be one of the fastest-growing segments of the IT industry. It was observed that now businesses are shifting towards the cloud. It brings a great change by providing on demand self service entry to the universal group of virtual and physical computing resources via internet network. It is a model for providing and hosting application over the internet. It has many advantages; one of the main advantages of cloud is to provide the users or clients with a huge amount of information without investing much on the infrastructure. Its growth in a short span of time is very much visible and is extraordinary.
Abstract
With all the information on cloud, the biggest concern of this technology is the security and privacy of the customer's data. Sometimes, many challenges may arise while accessing any services on the cloud. In this report, we have talk about the theory of cloud computing, along with its history and architecture and benefits of using cloud. We have also shared information regarding the growth of cloud over the years. We have also analyzed the need for moving to cloud from the traditional network. This paper also provides an overview of mobile cloud computing, its importance, along with its advantages and disadvantages and the challenges we face in mobile computing. Challenges of using cloud are also discussed. The main plan of this paper is to give a better understanding about the idea of cloud computing along with its security concerns. In this paper, some main concepts of cloud computing are discussed and provide a number of important research guidelines in this new and responsive area. Table of Contents Abstract ......................................................................................................................................................... 2 Introduction .................................................................................................................................................. 5 History ........................................................................................................................................................... 6 Cloud Architecture ........................................................................................................................................ 7 Switch from Traditional Technology to Cloud .............................................................................................. 9 Growth of Cloud Computing ....................................................................................................................... 10 Service models(IaaS, Saas, Paas) ................................................................................................................. 14 Data Centers........................................................................................................................................ 14 Information as a Service(IaaS) ............................................................................................................ 14 Platform As A Service(PaaS) ................................................................................................................ 15 Software as a Service(SaaS) ................................................................................................................ 15 Comparisons of Cloud Service Models ................................................................................................ 17 Models of Cloud Computing ....................................................................................................................... 17 Deployment Models.................................................................................................................................... 18 Private Cloud ....................................................................................................................................... 19 Public Cloud ........................................................................................................................................ 19 Hybrid Cloud- The Best of Both Worlds .............................................................................................. 20 Community Cloud ............................................................................................................................... 20 Technological Issues .................................................................................................................................... 21 Characteristics of cloud computing ............................................................................................................ 22 Virtualization in Cloud Computing .............................................................................................................. 22 Hosted Hypervisor............................................................................................................................... 23 Bare-Metal Hypervisor ........................................................................................................................ 23 Benefits of Virtualization .................................................................................................................... 24 Summary of papers ..................................................................................................................................... 24 Paper_1: Connecting Fog and Cloud Computing [24] ......................................................................... 24 Paper_2: Mobile cloud computing for computation offloading: Issues and challenges [25] ............. 27 Paper_3: The Use of Cloud Computing in SMEs [26] .......................................................................... 30 Paper_4: Cloud Computing and Inter-Clouds - Types, Topologies and Research Issues [27] ............. 33 Paper_5: A Study Literature of Critical Success Factors of Cloud Computing in Organizations [29] .. 35 Paper_6: Utilizing Cloud Computing to address big geospatial data challenges [30] ........................ 37 Paper_7: Comparative Study of Information Security Risk Assessment Models for Cloud Computing systems [31] ........................................................................................................................................ 39 Merits and Demerits of Cloud Computing .................................................................................................. 40 Merits of Cloud Computing: ................................................................................................................ 41 Demerits of Cloud Computing............................................................................................................. 41 Challenges of Cloud Computing .................................................................................................................. 43 Impact of cloud Computing ........................................................................................................................ 44 Cloud Computing Security .......................................................................................................................... 45 Cloud Computing Security benefits .................................................................................................... 47 Grid Computing ........................................................................................................................................... 48 Comparison between Cloud and Grid Computing .............................................................................. 48 Mobile Cloud Computing(MCC) .................................................................................................................. 49 Importance of Mobile Cloud Computing ............................................................................................ 49 Advantages of Mobile Cloud Computing ............................................................................................ 50 Disadvantage of Mobile Cloud Computing ......................................................................................... 51 Open Challenges in Mobile Cloud Computing .................................................................................... 51 2017 Cloud Computing Trends ................................................................................................................... 51 Future of cloud ............................................................................................................................................ 53 Conclusion ................................................................................................................................................... 55 Bibliography ................................................................................................................................................ 56Introduction
Cloud computing is an emerging internet based technology which helps in sharing information, data and resources to other devices on request. The term cloud computing came into picture in the year 2006 after Amazon's elastic computing cloud (EC2) [1]. "As defined by National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) : Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction [2]". The aim of the users/consumers is to have an infrastructure having the minimum cost on one hand and providing the Quality of Service (Qos) on the other hand. Hence, it is one of the best option with maximum recourse utilization and minimal cost to the users. The main aim of cloud computing is to use the resources to maximum level, combine them to get higher throughput and to solve large computation problems. Cloud computing has several features such as scalability, interoperability, virtualization, flexibility, mobile access and pa-as-you go service principle [3]. Fig 1 show the structure of cloud computing: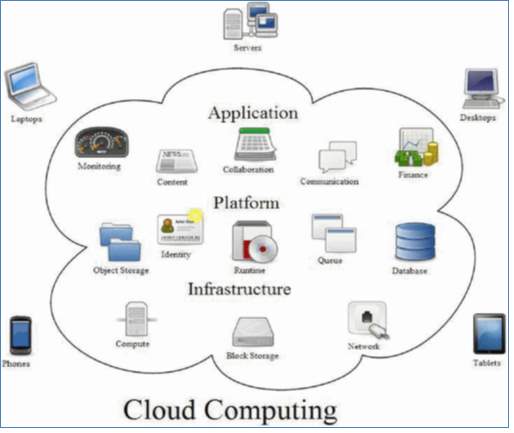 Figure 1 Cloud Computing Framework [1]
Figure 1 Cloud Computing Framework [1]
History
In the MIT Centennial conference in the year "1961, John McCarthy said that, The computer utility could become the basis of a new and important industry", which implied the basic concept of cloud computing. The main characteristics of cloud computing were introduced in the year 1966 for the first time by Douglas Parkhill, in his book, the challenge of Computer Utility [3]. In 2006, cloud computing was launched by Eric Schmidt in his discussion on Search Engine Strategies [4].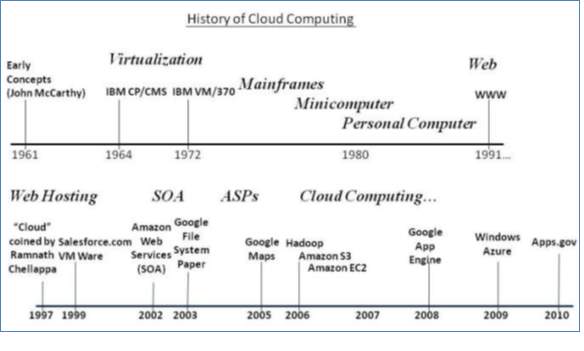 Below is the summary of the occurrences [5]:
"* 1961 – Professor John McCarthy propose computing be organized as a “public utility”.
Below is the summary of the occurrences [5]:
"* 1961 – Professor John McCarthy propose computing be organized as a “public utility”.
- 1964 – IBM CP-40 Operating Systems uses Virtualization
- 1972 – IBM VM/370 is a virtual machine operating system
- 1991 – The World Wide Web popularizes the internet
- 1997 – First use of the term “Cloud Computing”
- 1999 – Salesforce.com and VM Ware launch
- 2002 – Amazon Web Services (AWS) launches and SOA emerges
- 2003 – Seminal Google File System (GFS) paper published
- 2005 – Google Maps is a watershed event for browser-based apps (introduces AJAX).
- 2006 – Hadoop launched, shortly followed by Amazon S3 and Amazon EC2
- 2008 – Google App Engine launches
- 2009 – Microsoft Azure launches
- 2010 – GSA’s apps.gov launches (and federal Cloud-first policy)."
- Amazon: In 2006, Amazon introduced its Elastic Compute cloud (EC2), structure data storage service (SimpleDB) and object storage service (S3) under the name of Amazon Web Service (AWS). Amazon cloud computing is based on server virtualization technology. Because of its demand in the market and cheep cost it, AWs become the first company to start Infrastructure as a service (IAAS).
- Google style was based on technique known as scientific sandbox. It is a kind of Platform as a Service (PaaS). Google App Engine (GAE) was introduced to public in 2008 [4].
- On June 7, 2012, Oracle announced the Oracle Cloud. While some feature of this are still in development, this cloud is the first to provide a combine set of IT solutions such as Service layers PaaS, IaaS and SaaS.
- Microsoft Azure was announced in the year in 2008 and was released in Feb 2010.
- IBM Smartcloud was introduced by IBM to support smarter planet.
Cloud Architecture

Figure 3 [6]
Cloud computing is one of the most trending technologies driving the world. With its advantages of storage, flexibility, sharing, multi-user, it is being used by many IT companies. Apart from all the big companies, individual companies are also using cloud. It is a service provided through Virtual Network; especially the Internet [6].Cloud architecture is divided into 2 parts:- Front-End
- Back-End
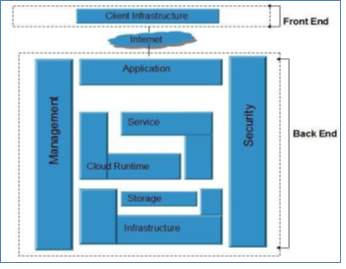
Figure 4 Graphical representation of Cloud architecture [7]
Both the ends are connected to one another through an internet. There are many other resources like middleware, cloud resources that are part of the cloud architecture. Front-End: It is visible to the users or customers. It consists of the user's computer and the network required accessing the cloud system. Different user interfaces can be accessed by different computing systems. Services like e-mail can be accessible through different Web Browsers like chrome, IE or Mozilla Firefox. Some systems use unique application that provides network access to their client. Back- End: It makes the cloud of the computing device as it contains different servers, computers and data storage system. It is the side which is used by the service providers. A dedicated server is assigned to manage each application in the system. Back-end has the below tasks towards its client:- Employ rules for communication between the networks
- Manage traffic and provide security method
Switch from Traditional Technology to Cloud
All the organizations from large scale to small scale are looking for new and better means for managing their web hosting needs. Clouds give a way of increasing the capacity of the infrastructure and reducing the overall cost. This is why every company should rethink about their current infrastructure and see the benefits which cloud computing are going to offer [9]:- Reduced Capital Expenditure: Large amount of money can be saved by moving to cloud as there is no purchasing on installation cost.
- Improved Resource Utilization: All the required resources are available on cloud thus reducing the cost and making it more useful when needed.
- Anywhere Access: With the help of internet connection, we can access the cloud based services and applications from any location. With all the data and application stored on the cloud, customers can work on the same project simultaneously and share their progress.
- Scalability: It is the one of the major advantage provided by cloud computing. It helps users to respond to their IT needs and add or subtract resources when required.
- Disaster Recovery: A backup of the data is always available on cloud, so if in case any company loses is data it can be retrieved by its back up.
- Quality of Service: Cloud service provider will offer you 24/7 customer support and immediate solution in case of any crisis.
- Quick and Easy Implementation: As there is no need to installation of the software or buying the hardware, the company can set its cloud environment in very less time.
- Guaranteed Uptime: Cloud service provider will make sure that your required data is always available and accessible.
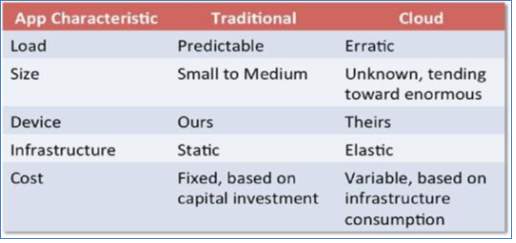 Figure 5 Comparison between Traditional Network and Cloud computing [10]
Figure 5 Comparison between Traditional Network and Cloud computing [10]
Growth of Cloud Computing
According to Compound annual growth rate (CAGR), cloud computing market is growing 22.8% from 2014 to 2018. Companies investing in SAAS applications are growing at a rate of 17.6% CAGR from 2013 to 2018. "The State of the Cloud Report 2015 shows that cloud adoption is still in its early stages. “We believe this still a multi-decade transformation that we’re being part of, and we can think of this as the early innings for the public knows and understands as the cloud industry “, says Byron Deeter" [11]. Main findings of the report are as below [11]: Cloud computing market is expected to reach $127.5B in 2018 as it is growing at a 22.8% CAGR. In 2014, the largest amount was spent on private cloud ($ 26B) and the total cloud computing market was $56.6B.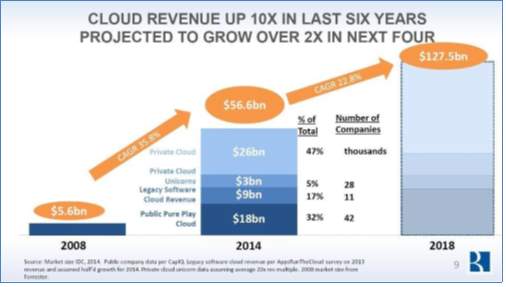
Figure 6 Growth of cloud computing market [11]
Out of all the application spending, 30% goes to SaaS based applications which is expected to increase at 17.6% CAGR from 2013to 2018. Software spending based on location is predicted to decrease at2.8% CAGR in the coming years.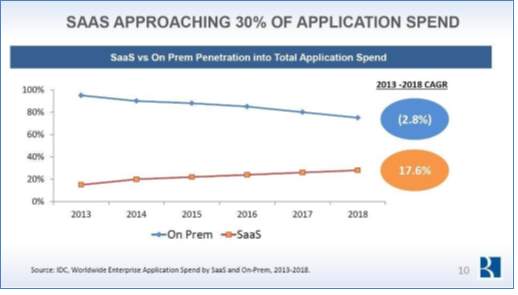
Figure 7 Worldwide Enterprise application spend by SaaS and On-Prem [11]
By 2018, 62% of all the CRM software will be carried through cloud. From 2013 to 2018, cloud based CRM is increasing at 19.6% CAGR.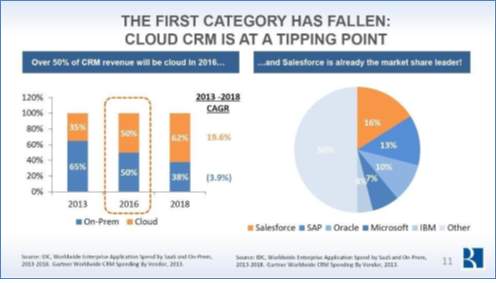
Figure 8 [11]
As per 2015, vertically focused enterprises have a $25.2B market cap. Vertical market capability joint with the facility to deliver new apps on cloud, results in building new customer, more reliability, and finally high market estimations.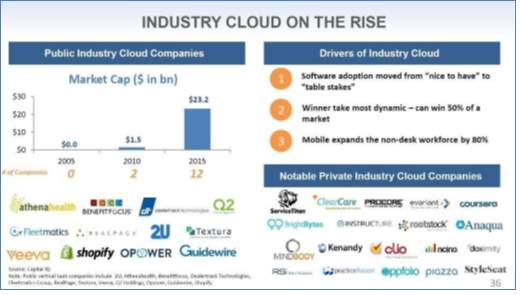
Figure 9 Industry cloud on the rise [11]
Tremendous growth is seen in mobile impact on cloud market development. Maximum internet is now used through the mobile device. 73% of global penetrations of Smartphone are recorded. Below picture will give the Bessemer's study in the area of mobility.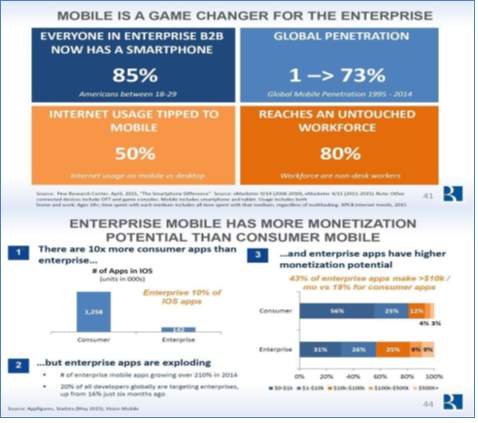
Figure 10 Mobile as the Game Changer [11]
By 2020, BVP cloud is expected to reach $500B market cap. Below graph shows various growth situations, the index grows 64% CAGR from 2010 to 2014.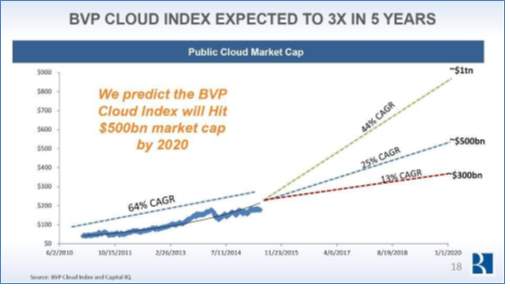 Figure 11 BVP Cloud Index [11]
Figure 11 BVP Cloud Index [11]
Service models (IaaS, Saas, Paas)
Clouds are constructed on the new data centers. It includes services like infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). These services are provided to customers as utilities and then they have to pay as per their usage [12]. In this type of environment, all the layers are treated as a service. Fig 3 shows that what can be treated as a service in all the layers.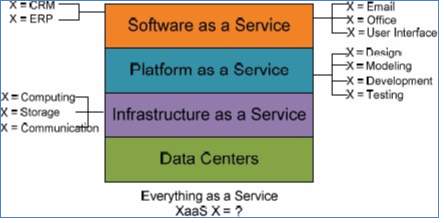 Figure 12 Hierarchical View of Cloud Computing [12]
Figure 12 Hierarchical View of Cloud Computing [12]
Data Centers
Data centers are known as the basis of cloud computing. It gives the hardware where the clouds run. They are established in an area which is less prone to disasters, having a low energy rate and less population. Nowadays, datacenters consist of thousands of interconnected networks.Information as a Service (IaaS)
It is the lowest layer of the infrastructure. It consists of the hardware and other network resources such as routers, switches, etc. It is based on the concept of virtualization. It virtualizes the network, storage and power from the data center, and provides this service to the customers. These are then used by the consumers as per their requirement. Example of this layer consist of Amazon's product EC2, Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure, Flexiscale, etc [12] [13]. Characteristics of IaaS [14]:- Facility of self service
- Efficient pricing model
- Resources are distributed
- Large amount of resources are available with several users using it
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
It is the second layer of the computing system and often known as the cloud ware. It provides a platform for development with a number of services to help in the design, development, deployment, testing and monitoring on the cloud. It does not require any prior software installation and enables different distributed team to work simultaneously. Some of the examples of this layer is Google App engine, Amazon Map reduce, Microsoft Azure, etc. Characteristics of PaaS [14]:- Multiple user architecture
- Rough control on sharing and security
- Strong Workflow capabilities
- User friendly interface
- Flexibility
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is the top layer of the infrastructure. In this layer, the software is given to the user as a service on demand. This software is used by many end users at the same time and is updated automatically. End users don't have to go through the problems of deployment and maintenance. All the applications are accessible as requested and once their use is over they will be rolled back. With these main characteristics it can be integrated with many different applications. Some examples of this layer are Google Gmail, Microsoft Hotmail and many more. Characteristics of SaaS:- Host software on their own or on third party location
- User friendly as software's are updated automatically
- Helps in scalability
- Data and services available from any location with the help of internet.
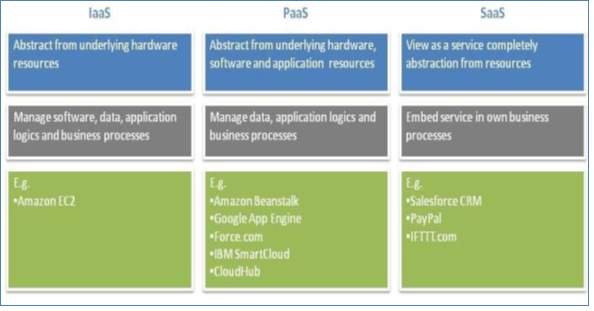
Figure 13 Comparison between Cloud service layers [15]
Fig below shows the hierarchical structure of the layers but it is not necessary that lower layer has to be constructed immediately below its top layer for example IaaS can have Saas as its upper layer instead of PaaS. Features of one layer can also be considered as a part of other layer.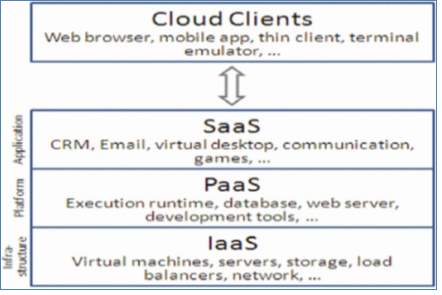 Figure 14 Hierarchical structure of Service layers [16]
Figure 14 Hierarchical structure of Service layers [16]
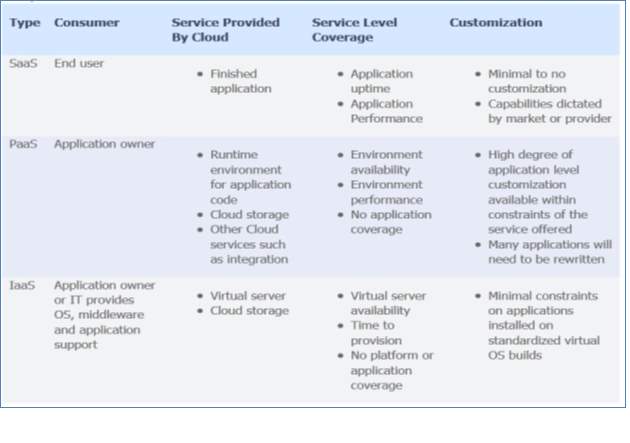
Comparisons of Cloud Service Models
Models of Cloud Computing
There are four different models for cloud computing. All the models consist of some essential characteristics and key attributes [18]. Let us first talk about this before describing the deployment models. Characteristics:- Network Access: All the services are available to the end users through the network and are accessible using Desktops, laptop, mobiles, Tablets.
- On demand Service: The end user is having an option to use the resources like storage, networks, processors etc as required and without any other user's disturbance.
- Elasticity: resources are dynamically allocated to the users as required and then released. Thus giving them an impression of unlimited availability of resources for the users.
- Resource Pooling: Resources are being used by many consumers at the same time. This process is not affected by the location as the consumer is not concerned with the physical location of the resource.
- Measured Service: Utilization of the resources is measured properly so that the user is billed as per the quantity of its own usage.
Key Attributes
Below are the different key attributes for the cloud models:- Shared Service: Design to use by a large crowd instead of a single consumer.
- Elastic Scaling: Dynamic in nature and construct to meet the increasing number of demands. Solution Packaged: Consist of all the required resources in 1 package User-based Pricing: Consumers are billed as per their usage.
- Self Service: User friendly provision of application and services. Access: Easily accessible through the Internet
Deployment Models
There are various types of clouds depending upon the cloud service provider. Each cloud is having its own advantage and disadvantage. The 3 main deployment models are: private, public and hybrid. One more model is community model but this less commonly used as compared to these 3 models. The features and comparison of each of these models is discussed below. Figure shows the overview of the deployment of these three models: Figure 16 Cloud Deployment models [19]
Figure 16 Cloud Deployment models [19]
Private Cloud
Private cloud infrastructure is created for a particular organization. This organization may contain many different business units. This type of infrastructure can be located within the organization's building or at a distant location and is used particularly for the organization's benefits. It is maintained and supported by the organization, third party, or combination of both. They are also known as internal clouds. They are developed by the IT department of the organization to optimize the utilization of resources by using the concept of virtualization and grid. It has advantages of cloud like virtualization, low administrative cost and availability of services. However, maintenance and management of the infrastructure is organizations responsibility, thus increasing the operating cost.
Public Cloud
Public cloud infrastructure was created to use by anyone in the network. Cloud service provider makes it available for the public and is hosted at the their location. It may be supported by any public organization. Deployment and development of this type of infrastructure is done with the minimal cost as compared to the other deployments options. They can be maintained by any individual or any other type of organization. They are monitored by a third party over the internet and charged on the basis of usage. They are also known as provider clouds. Public cloud shares reliable and trustworthy application quickly but the only main concern is confidentiality.
Hybrid Cloud- The Best of Both Worlds
Hybrid cloud is a combination of both private and public cloud. It is the new concept of combining the internal and the external providers. This type of infrastructure consists of large number of different clouds and allows data or applications to move from one cloud to another. It is an advantage for the enterprises as they can utilize the public cloud for their all-purpose computing and can use the private cloud for their business sensitive data.
Community Cloud
The cloud infrastructure is used by a number of different organizations having the same interests. This helps in reducing the expenditure cost as the money invested is shared among all the organizations. It can be maintained or supported by one of the participating organization or by the third vendor or by the combination of both. It can be located in the organizations place or at a remote location. Comparison of the Cloud Deployment models: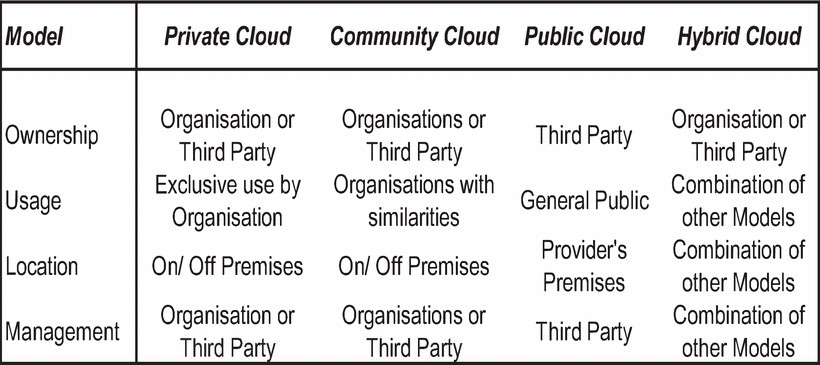 Figure 20 [18]
Figure 20 [18]
Technological Issues
Several current technologies are being used by cloud computing thus it is highly possible that it carries the issues relate to them. Due to several novel characteristics of cloud computing many researchers and scientist are behind to examine the QoS it provides. They have found two main sensitive areas: Data Management and Network Configuration [22]. Data Management: To ensurehigh availability, cloud computing uses layer storage area which helped in running computing cycles and less duplicity of data. With the flexibility in the architecture of cloud, it provides the users with infinite amount of resources. This structure offers the users with a reliable, stable and parallel computing engine. Some scientist is focusing on creating a distributed programming structure which will help in easy data-parallel application. The construction of this structure will help in long-term storage of large quantity of data and provides a framework that will activate distributed datasets by allocating some work to each member if the dataset. This structure will ensure data management but will raise concerns related to data mining. Exploitation of available resources and avoiding pointless functions should be taken care by the methods of data mining. Cloud computing has always encourage new options in automatic data management. Search engines nowadays use cloud computing to create a semantic web. Networking: Two different network exist in cloud computing: a) Physical Network: consisting of physical servers and physical network devices and b) Logical Network: consisting of virtual machines installed on physical severs and connected by logical links. This kind of network needs a optimize flow and limited amount of bandwidth for communication purpose.Characteristics of cloud computing
There are different characteristics of cloud computing are as stated below:- Cost savings: There are number of reasons that indicates that by using cloud we can lower the cost like: a) infrastructure is not purchased b)initial and recurring expanse is low c) billing mode is pay as per use and many more [9].
- Multi-sharing: As the cloud is distributed and shared, multiple services and applications can be used at the same time.
- High scalability: It helps in servicing the requirements for a large number of audiences.
- Agility: It shares resources among users, while being more efficient and agile.
- High availability and reliability: Due to minimum infrastructure failure servers are easily available and more reliable.
- Managed metering: With the use of meter, customers are billed as per their usage. Meters are used for managing and optimizing the service and provide billing details to users.
- Measured Service: All the features of cloud service are controlled and managed by service provider for efficient billing and optimal resource utilization.
- On Demand Self Service: Any customer can use the service when needed without any interference from the provider.
- Shared Infrastructure: Allows the sharing of storage, resources, services and network among a large number of users.
- Network Access: Can be access through internet from a large number of devices like smart phones, computers, laptop and Tablets.
- Elasticity: Consumers can use services as per their requirement.
- Maintenance: All the maintenance is done by the service provider thus the consumers are least bothered about the up gradation of any service or application.
- Reliability: Removing of unnecessary and unwanted sites helps in building consumers confidence and also helps n disaster recovery [3].
- Mobile accessible: Mobile users have increased efficiency as the services and data is available from anywhere.
- Resource Pooling: Resources are assigned and reassigned as per the demand of the users.
- Less IT knowledge is required for accessing the services on the cloud.
- Per as per you go helps in measuring the usage of services on regular basis.
Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization is one of the major changes in the working of all the IT companies. Virtualization in cloud computing helps to separate the hardware on which it is working from the operating system. Virtualization has the capability to let one physical resource to behave as multiple virtual resources and vice versa [23]. With the help of virtualization we can allow multiple virtual servers to work as one physical machine. Virtualization helps in easy migration of one physical machine to another. It has its own advantages like reducing the cost, energy saving and helps the organization to increase the profit. In cloud virtualization, the machine on which the operating system is running, is separated from the hardware with the help of a virtualization layer. This layer is called as hypervisor. They are classified into 2 types: a) Hosted Hypervisor and b) Bare-Metal Hypervisor.Hosted Hypervisor
In this, hypervisor is hosted on top of the operating system and then the operating system is mounted on the hardware. On this hypervisor, an instance of OS is installed.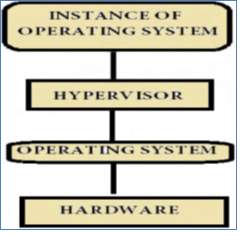 Figure 21 Hosted Hypervisor [23]
Figure 21 Hosted Hypervisor [23]
Bare-Metal Hypervisor
In this, the hypervisor is hosted straight above the hardware and then an instance of operating system is installed on the hypervisor. This is mostly used by desktop computers.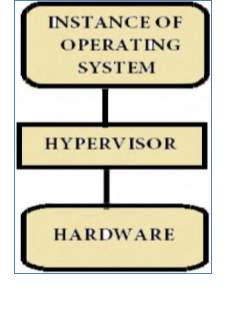
Benefits of Virtualization
- Reduced Cost: Virtualization in cloud computing helps in reducing the cost in following manners: 1) installation of physical machine 2) hardware maintenance 3) annual maintenance cost 4) power [23]
- Hardware Independence: Ability to move from 1 machine to another without any changes in the OS, drivers or applications
- Server Consolidation: Possible to run large number of virtual machines on a physical server thus reducing the need of several physical servers.
- Encapsulation: Virtual machines can be treated as complete package containing the hardware, operating system and the virtual resources.
- Isolated: All the virtual machines on single physical servers are independent of each other.
Paper_1: Connecting Fog and Cloud Computing [24]
In this article the author started by saying his experience in an event about Internet of Things (IoT) where he was left thinking with the fact that IoT is very systematic yet very complicated to define. Though we have things that have a mind of their own but still we are facing challenge in processing data from this external device. According to Cisco cloud traffic is going to increase by 3.7 fold by 2020. As per him, IoT is all about processing data in a meaningful manner and cloud computing is about controlling data from storage. The problem IoT faces with respect to cloud is the time taken by the cloud to transfer data from the server to the public cloud which is very high to meet the needs of IoT. The solution to this problem is to build data or information on the edge of the network which can handle all data assembly and processing. With the help of an example he proved that how centralized computing complicates the process of sending the information to the remote which is located thousands of miles away instead of using the data centre which is located on that particular location. And to make it worse we are using open internet for transmission. The solution to this problem as discussed by him can be processing the data which is needed by the device immediately. However, the data will be ultimately sent to centralized cloud for storage and future processing. As IoT needs to react quickly to data created by any device or server, so by performing this process it will give better performance and efficiency. This process is given a name by Cisco known as Fog Computing. The aim of fog computing is to reduce the latency for critical applications by shifting the course of data processing and transfer to the edge of the cloud near to the IoT device. Benefits of Openfog:- With the help of a standard structure and technology, approach to edge computing has become simple but in a reliable way.
- Able to provide with a good development layout, that can be followed and influenced by the software builders and network devices.
- Able to deal with security issues in a reliable way.
Figure 23 [24]
As latency is one of the major issue with IoT, so keeping IoT on the edge of cloud is a very fundamental concept. Latency will always remain a concern for the developers and administrator doesn’t matter how speedy is the network. Thus the concept of fog computing is trying to promote the idea of computing at the edge for cloud and non cloud deployments. At the end, the author concluded by saying that now people are creating alternatives to the process of keeping all the data and information on public cloud. As some times public cloud can be risky. With the help of IoT, we can think differently and combination of fog computing with cloud computing is something we can look in the future.Paper_2: Mobile Cloud computing for computation offloading: Issues and challenges [25]
Nowadays, mobile users are asking more from their mobile devices. They are expecting to access computing services through their smart phones. This paper talk about the combination of mobile devices with cloud in order to expand the competence of mobile devices. Many researches are being carried out to provide mobile users with the ability to use computing resources like infrastructure and software. The 2 main highlights of this paper are:- Analyzing recent computing offloading structure
- Discussing the open issues related to Mobile Cloud Computing(MCC)
Figure 24 [25]
Computation Offloading: It came into picture around 1970's. It is known as the process for sending computation services to the remote server. Large number of offloading techniques has been developed for application in mobile devices. Mobile offloading technologies depends upon the technologies such as wifi or cellular network. Computation offloading is considered useful only when the mobile device consumes more time and energy as compared to the offloading overhead. Offloading Approaches: There are 3 main offloading approaches: Offloading Steps; Framework Access; Framework mechanism. Offloading is mainly done in 3 steps:- Application partitioning: It divides the components in 2 parts: offloadable and non-offloadable components. The decision of a component being offloadable or not is based on the information provided.
- Preparation: This step helps the offloadable components to be used in the mobile application. It includes the transfer and installation of code along with the selection of remote server.
- Offloading Decision: It is the final step for offloadable components before its execution started.
- Static offloading framework
- Dynamic offloading framework
- Based on virtual machine
- Based on code offloading
Table 1 Comparison between offloading framework
| Framework | Partitioning | Preparation | Decision | Offloading mechanism | Contribution | Granularity level | Autom ation | Year |
| VM Cloudlet | The entire migrating image of the running application is offloaded to the designated remote server while the mobile device provides a user interface and serves as a thin client | It requires the cloning of the mobile device application processing environment to a remote host | Not available | VM: the mobile device transmits all the states of the application to the cloudlet<comma> which applies it to the base VM to launch and execute the VM | Cloudlet-based resourcerich mobile computing | Entire App | Not availabl e | 2009 |
| Phone2Cloud | The application can be partitioned or entirely offloaded | Applications need to be manually modified in order to be executed on cloud servers | Static: the offloading decision is based on user’s delay-tolerance threshold and static analysis | Code: the remote execution manger gets required input data<comma> it executes offloading computation on the cloud server<comma> and sends back results to the offloading proxy | Enhancement of the application’s performance and improvement of energy efficiency of smartphones | Part/Entire App | Semiautoma tic | 2009 |
| MAUI | Annotate each individual method as local or remote | It creates two versions of a mobile application (for mobile device and cloud). It uses programming reflection to identify which methods are marked offloadable or not | Dynamic: decision is based upon the input of the MAUI profiler and MAUI solver | Code: MAUI does not support executing only portions of a method remotely | Energy-aware code offload | Method | Manual | 2010 |
| Mirror Server | The framework does not require a partitioning so the entire application is offloaded | It creates a mirror for a smartphone | Not available | VM: During the copying process<comma> no operation from user is authorized | Reduce the workload and increase the resources of smartphones in a virtual manner | Entire App | Not availabl e | 2010 |
| Cuckoo | Partitioning is made based on the existing activity model in Android. The graphical components remain on the mobile device while the services can be offloaded | Destination running a Java VM | Dynamic: method invocations to services are received and Cuckoo framework will then decide whether to offload it or not while checking the availability of the remote resources | Code: the framework receives method calls and evaluates whether to offload the method using heuristics information | Simplifying the development of smartphone applications while benefiting from computation offloading | Method | Manual | 2010 |
| CloneCloud | The partitioning is made based on static program analysis and program profiling | A duplicate of mobile device’s software stored on the cloud server | Dynamic: threads are migrated from the mobile device to the clone in the cloud | VM: offloaded components of an application are running inside a virtual machine | Elastic execution between mobile devices and clouds while adapting the application partitioning | Thread | Autom atic | 2011 |
| Jade | An application is partitioned at the class level in Jade. A class must implement one of two interfaces to be offloadable | It checks the application and device status by monitoring the communication costs<comma> work load variation<comma> and energy status | Dynamic: have updated information concerning the status of the application and the device | Code: an offloaded object can be executed on the remote server | An energy-aware computation offloading system | Class | Autom atic | 2015 |
- Platform diversity
- Privacy and Security
- Automatic mechanism
- Fault Tolerance and partition offloading
- Offloading cost
Paper_3: The Use of Cloud Computing in SMEs [26]
In this paper, the author discussed the growth small and medium enterprises with the help of cloud computing. Cloud computing helps the SME's to grow their business and to advance their technology in a more effective way. Recent researches has showed that cloud computing has helped to boost SME's growth and encourage industrial practices at all stages. This paper discusses survey results of 7 different European countries to find out the lack of knowledge and areas of improvement or options to build new competences. It also discuss about the objective of IN-Cloud European project. The author first shares the definition of cloud computing given by NIST followed by its advantages with respect to SME's. Issues related to SME's moving to cloud are also described. Few of the issue that impact the decision of SME's to opt for cloud services are described below:- Cost related to infrastructure
- Lack of understanding about the structure
- Needs and requirements of different companies
- Time Factor
- Pro-activeness of a SME's to opt for cloud services
- Education people about the benefits of cloud computing
- Training employees to use computing services and technologies in their companies. Designing VET qualification based upon the usage of cloud in the companies.
- Your job role.
- Everyday use of IT services
- Usage of cloud services in your business
- Not using cloud services in your business
- Problems related to the acceptance of cloud in your company
- Benefits of cloud to your company
"Table 1. Based on Job Role
| Job Role | Italy | Spain | Germany | UK | Greece | Portugal |
| Owner/Director/Manager | 10% | 31% | 21% | 71% | 36% | 80% |
| Employee | 58% | 46% | 46% | 21% | 27% | 13% |
| IT Staff | 16% | 4% | 25% | 0% | 36% | 7% |
Table 2. Everyday use of IT services
| Use of IT on daily basis | Italy | Spain | Germany | UK | Greece | Portugal |
| Word processing/ Ms office | 82% | 92% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 79% |
| ERP | 31% | 42% | 32% | 7% | 18% | 43% |
| CRM | 47% | 50% | 57% | 43% | 18% | 50% |
| Social Media | 37% | 73% | 82% | 64% | 45% | 71% |
| CAD/CAM | 21% | 19% | 14% | 14% | 64% | 14% |
| Numerical Computing | 27% | 27% | 7% | 36% | 55% | 14% |
| Software Development | 38% | 58% | 61% | 7% | 45% | 64% |
| Accessibility software | 18% | 4% | 14% | 0% | 27% | 7% |
Table 3. Usage of cloud services in your business
| Use of cloud services in your organization | Italy | Spain | Germany | UK | Greece | Portugal |
| Yes | 49% | 77% | 75% | 93% | 82% | 73% |
| No | 29% | 19% | 18% | 7% | 18% | 27% |
| No, but in future | 7% | 4% | 4% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Not sure | 15% | 0% | 3% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
Table 4. Benefits of cloud to the company
| Benefits of cloud to the company | Italy | Spain | Germany | UK | Greece | Portugal |
| Cost Efficiency | 58% | 61% | 81% | 71% | 11% | 75% |
| Scalability and flexibility | 47% | 65% | 67% | 36% | 67% | 75% |
| Sustainability | 27% | 22% | 10% | 21% | 22% | 25% |
| Maintenance by cloud provider | 31% | 48% | 48% | 29% | 33% | 67% |
| Security | 33% | 17% | 24% | 29% | 56% | 42% |
Paper_4: Cloud Computing and Inter-Clouds - Types, Topologies and Research Issues [27]
In this paper, the author described the basic concept of cloud computing, its characteristics, architecture (with its 3 service layers), deployment models and Inter-cloud. The main focus of this article is about the concept of inter-cloud, its architecture, types, topologies and research issues related to it. Inter-cloud is defined as the inter connected cloud of clouds. Inter cloud computing refers to the interconnection of several different cloud providers architecture. It is based on 2 important factors namely portability and interoperability. The need of inter-cloud arises because of limited computation resources. It provides advantages like different geographical sites, better services and information, and avoids vendor lock in situations for the client. There are two categories of inter-cloud: Federation cloud: It is a cloud in which several different service providers are willing to join hands to share information with each other by interconnecting their infrastructure. This type of cloud is used for government cloud or private cloud. Different kinds of federation cloud are centralized and peer to peer cloud. Multi cloud: In this type, client uses several self-governing clouds. There is no interconnection and allotment of the cloud infrastructure. Categories of multi cloud include Services and Libraries. The author then discussed the topologies of the different cloud architecture that includes: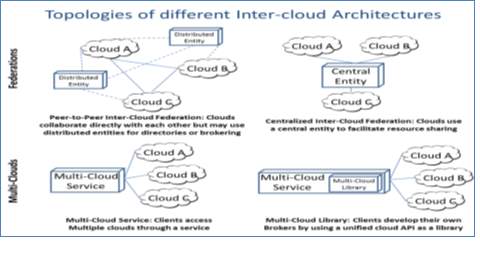
- Peer to Peer Inter cloud Federation:
- Centralized Inter cloud Federation
- Multi cloud Service
- Multi cloud libraries
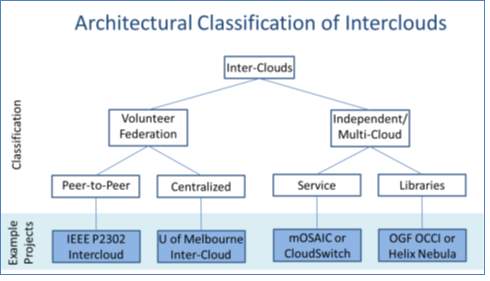
Figure 26 [27]
Research issues in Inter- Cloud: Cloud user's requirements and needs gets unpredictable some times. This leads to a complicated situation in providing the resources. Some of the issues faced in this type of cloud architecture are listed below:- Easy Mapping of services to resources:
- Application Service Behavior Prediction
- Economic Models Driven Optimization Techniques
- Integration and Interoperability
- Scalable Monitoring of System Components:
Paper_5: A Study Literature of Critical Success Factors of Cloud Computing in Organizations [29]
The aim of this paper is to discuss the important factors that assist organizations to use cloud computing in their business process. The major factors found by author were flexibility, cost reduction, redundancy and reliability, collaboration, scalability, efficiency, virtually and availability which plays a vital role in the success of cloud computing in any business. The author started its research with a small discussion on the definition of cloud computing along with its service models. They also gave a brief idea about the architecture of cloud and the different deployments models of cloud computing. In the later part of this article, authors raise a question as to why organizations use cloud computing. As per the study conducted by them, they found out that there are 8 major factors that are making organizations to use cloud computing. These 8 factors are discussed below: Cost Reduction: Cloud computing gives the benefit to consumers of pay as you go. Consumers using the cloud services are billed according to their usage for the services. One more advantage the consumers were getting was that they don’t have to maintain or create any infrastructure. Moreover, cloud servers can do multi tasking, so they were capable of providing the solutions to customers quickly. Flexibility: It can be achieved by accessing cloud resources from any type of device. Service provider's separate their infrastructure from the customers device. Depending upon the requirement of customers, they can modify the use of computing services easily and flexibly. Scalability: Cloud computing interface is user friendly. Thus, we can achieve scalability by expanding the infrastructure. Efficiency: Email services provided by cloud providers like hotmail, yahoo, Gmail are examples of showing the efficiency of the cloud services. It can be achieved easily as users can access their mail from wherever they want. Reliability: Cloud providers having their data around the world are capable of overcoming site failures and ensure reliability. Dividing the load to different clouds saves time and makes the system more reliable. Collaboration: As thereare similarities in the architecture and the services provided by different providers, we can collaborate them. With respect to customer point of view, they can share documents and data in a particular group. Availability: The resources are managed and controlled by the service providers. They haveall the access to the resources and can make them available to the customers whenever they want. Cloud providers who have their data centers spread across the world have the facility to provide fault tolerance by duplicating data in different locations. In the end the author concluded by saying that cost reduction is the most important success factor with comparison to reliability being the less critical success factor.Paper_6: Utilizing Cloud computing to address big geospatial data challenges [30]
In this paper, the authors has discussed about the combination of cloud computing with the big data. Earlier big data was known for its 4 V's(Volume, variety, velocity and veracity) but with the help of cloud computing capabilities, new ways were introduced to change the Big Data 4 V's to 5 V's with the addition of value to it. The addition of 5th V (value) is a big concern for processing capacity. Information regarding cloud computing ways to handle big data challenges is discussed in this paper. Geospatial data is produced in large Volume with variety of forms for several different purposes, their precision and ambiguity covers a large area as defined by Veracity, with data producing at a very high velocity. With this unique information, geospatial data can be developed by adding Value to improve its research and development. This transformation leads to big challenges in terms of data mining, management, analyses and system architecture. Cloud computing then appear as a standard to provide computing as a value service with its 5 main features: 1)pooled resources, 2) fast and flexile computing power, 3) pay as per usage service, 4)in demand access of services and 5) broadband access for quick communication. Cloud computing service oriented architecture enables everything as a service including Iaas, PaaS and SaaS. The paper discusses that how cloud helps in the transformation with the below 4 scientific examples: To support climate Analytics: The big climate data seen in the past and replicated for the future must be analyzed and managed carefully in order to understand the impact of climate change on environment and city areas. There are several issues faced by the use of big data in terms with the 4V's of the climate data. The problems regarding the combined difficulties of the 4 V's can be solved with the help of cloud based modern data management policies and its service oriented structure which helps to analyze, manage and process climate data. Supporting Knowledge Mining: Due to the increase in the volume, variety and velocity, spatiotemporal data causes a big challenge for the scientist to access the right data for their research. One solution to this problem is to mine information from the geospatial data for ranking and recommendation. But this is challenged by the big data volume, variety and velocity. There are 2 main challenges to it: 1) Dividing big data into parallelizable pieces so that they can process with scalable computing resources; and 2) how to use the computing resources for processing the divided big data. Supporting land-use and land-cover change analysis: Land Use and Land Cover is one of the major parts in the change of the environment and sustainability research. The Land Change Monitoring, Assessment and Projection (LCMAP) forced the need to create quality land change goods from the real time observations. But there are different data challenges that exeunt: 1) constantly changing LULCC data; 2) managing, storing and sharing huge and use data; and 3) replicating LULCC with complicated algorithm and training sets. Supporting dust storm forecasting: Dust storms can cause severe risk to health, surroundings and the environment worldwide. Whenever dust storm occurs there is great loss of human lives due to traffic accidents because of less visibility and reduction in the efficiency or renewable resources etc. Therefore it's is very important to predict any upcoming storm with big spatiotemporal resolution to reduce its impact. A solution to this requirement is to replicate a one day phenomenon in a 2 hour computational time. While cloud computing helps in addressing many of the challenges in geospatial big data, but few issues are still not addressed:- Data storage and management is one of the highest priorities for geospatial data, including optimization of traditional database management system.
- Security is also a major concern to ensure protection for both sensitive data and user's information. More research is needed to gain trust and safe it from several attackers.
- More spatiotemporal methods should be created to optimize cloud with big geospatial data execution.
- More tools should be created to record the usage of resources and for billing purposes.
- More spatiotemporal methods should be invented to grasp benefits of flexible storage and computing resources.
Paper_7: Comparative Study of Information Security Risk Assessment Models for Cloud computing systems [31]
In this paper, the author has discussed about the problems related to the storage of data and information on the data center. Issues like data theft, unavailability of data, data violation are discussed. In the latter half of the paper, the author provides solutions to overcome this problem. This paper main focus is on the security weakness and problems related to the privacy and secrecy of the client data. Cloud Data Storage Challenges & Issues:
Figure 27
- Cloud storage Issue:
- Identity Management and Access Control:
- Contractual and Legal Issues:
- Cloud data storage issues related: A protocol was introduced by Wei et al, The SecCloud which gives provides security rules for customers data. This protocol not only secures the customers stored data but also give security to computational data.
- Identity Management and access control issue solution: SPICE was the technology used in identity management system. The main feature of SPICE was to provide group signature in cases of unidentified users.
- Contractual and legal Issue solutions: Though customers have benefits from cloud usage but can have face great risk in case of SLA violations. An algorithm was introduced that deals in reducing the risk in case of any violation. This algorithm works in a way that it helps in the renegotiations of the risk knowledge.
Merits and Demerits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the catchphrase of the decade and many companies are moving to it every day. While switching to cloud is making computing much easier but it's not great to run into. Before rushing to it we should see the pros and cons of cloud computing [32] [33]. Merits of Cloud Computing:
Merits of Cloud Computing:
- Cost Saving: It is the best model for all the companies in terms of cost as compared to the traditional model they used to follow. In a traditional model, the cost for buying the software and harware is very high. Thus cloud provides with the ability to pay as per usage, hence offering the servise at a reasonable price.
- Usability: Accesing the services and data on cloud is very user friendly. We can easily copy and paste the data from cloud storage to our local storage.
- Easy Implementation: Cloud providers helps the client to hang on to their applications and processes without being them concerned of the background technical knowledge.
- Easy access: All the information and data on cloud is easily accessible despite of the geographical location. All the registered consumerscan use the data whenever they want and from wherever they want.
- Reliability: Cloud computing infrastructure offers a reliable and steady information as compared to traditional infrastructure. Cloud providers offers with a SLA that gives 24/7/365 availability. If any server fails, then the organiszation can contact any other available server for their information.
- Managebility: It is the duty of the service provider to offer the customers with all the updated and properly maintained applications. Customers are having the preference to enjoy a web based user friendly interface without thinking of the installation or upgradationof any of the services..
- New Services: Service provider offers a large variety of data used by all the different consumers.
- Backup and Recovery: As all the data and information is stored on cloud so it is easy to backup and recover data when needed.
- Quick Deployment: All the data and application are deployment very quickly on cloud.
- Automatic Software Integratation: Consumers using the softwares on cloud are not bothered about upgrading or degrading the software as per therir need.
- Data security, Scalable service and huge amount of storage.
Demerits of Cloud Computing
- Security Issues: Security is the main concern for any of the organization who is opting for cloud. Secret and confidential data is being shared with the cloud provider, so companies should analyze carefully before selecting any cloud provider.
- Constant Monitoring: Sometimes customers have to monitor the services constantly thus becoming a burden.
- Prone to attacks: Confidential and sensitive data is on cloud and thus can be affected by the external attacks.
- Technical Issues: Though the network is managed and maintained regularly but a single technical issue leads to a great loss for both the customer and service provider. Any kind of technical failure will degrade the performance of the cloud [33].
- High Cost: Cloud computing is cheaper than the in house computing. But it should provide all the features required by the customers.
- Inflexibility: Sometimes consumers have to get bond to a particular format. Application in one design cannot be written in any other design.
- Possible Downtime: For accessing anything on cloud, we need internet connection. So in case of internet failure, even the smallest organizations work will be on hold, affecting the business process.
- Limited Control: All the services and applications are provided by the cloud service provider, thus they are the only people who controlled and managed the data. The customer has right to manage or control the data which are used and operated by them. All the important and critical assignments are not given to the customers.
- Bandwidth: Some of the cloud providers offers a limited bandwidth to the consumers and if the bandwidth is crossed than the customers have to pay the additional charges. While choosing a provider, customers should think of the bandwidth they are getting as certain providers are there in the market which offers you with unlimited bandwidth.
 Figure 28 Advantages and disadvantages of cloud [34]
Figure 28 Advantages and disadvantages of cloud [34]
Challenges of Cloud Computing
Following are the challenges associated with cloud computing [9]:- Security and Privacy: Main concern for cloud computing is how to maintain the security and privacy of the companies who are adopting this infrastructure. Virus on one site can affect all the clients on that particular network. These risks can be lessen by adopting security measures like using encrypted file system, security applications and having transparency in their operations. Features like pooled computing resources and multi-tenancy have establish more security issues that needs to be handle through new and innovative techniques.
- Cost: Infrastructure cost has been reduced after moving to cloud services but the cost of communication has increased. Consumers have to invest more on transferring the data to and from the public and community cloud.
- Automated Service Provisioning: Main feature of a cloud computing system is to assign and reassign the resources to consumers as per demand. It is a big challenge for the providers to manage this feature and provide QoS to their consumers [14].
- Reliability: Sometimes service providers are not able to provide 24/7 support, which results in a breakdown. Computing environment should always be reliable and consistent. In case of any failure, all possible solutions should be taken smoothly.
- Interoperability and Portability: Consumers should have the power to move in and out of the cloud or to change the service provider when they want, without any bond [35].
- Performance: Cloud service providers should provide the required performance and bandwidth to the consumers as required. It is the responsibility of both the parties to mention the requirements on the SLA contract before signing for a particular provider. Most of the problems in cloud are related to performance issues like capability, capacity, availability etc.
- Technical and operational loss of control: Consumers don’t have access to software versions and their updates and neither they have any control on the technical operations such as data backup and restore. To overcome this issue, providers should give access to the consumers on the data which is relevant to their own organization.
- Integration: Companies using hybrid cloud have their data extended to both public and private cloud thus facing integration issues.
Impact of cloud Computing
With both advantages and disadvantages, cloud computing has its own impact on the organizations and society. Two basic benefits that cloud brings are:- It allows organization to use resources that they do not own and maintain, thus helps in reducing cost.
- Supports with prebuilt components so organization don’t have to build anything from scratch
- Students now have the ability to access data and information from any part of the world and can register themselves for any online course and indulge themselves in any group activities.
- Institutions can store huge amount of data on cloud instead of going for a complicated infrastructure [37].
- Benefits of per as per usage also helps the students to use cloud as per their needs.
- By automating stuff like enrollment for classes, assignments submission etc also helps in reducing the overhead.
- Provides benefits to student from developing country as well.
Cloud Computing Security
Security is one of the major concern in cloud computing. The biggest issue is that once you upload your information or data on the cloud then you won't have any control over it. The cloud will allow you to access the information/data but you can't stop anyone else from accessing the same data. Though cloud computing helps the users with large number of benefits like data availability, unlimited number of software applications, unlimited storage and ease of access but there are many security issues related to it as well. Some of the security issues are because of the inclusion of various technologies such as virtualization, transaction management, memory management, load balancing, network management etc. The network that connects all the different system needs to be safe and sound. Virtualization in cloud computing leads to various security issues. Foe ex: Connection of the virtual machine to the physical machine needs to be done safely. Data security helps in encrypting the information and makes sure that all the policies are followed for data sharing. Algorithms like memory and resource management needs to be secure. Keeping your data, accessing software on someone's else machine and using others CPU can be risky at times. Some of the known issues are phishing, data loss, software issues, etc. Multi tenancy and sharing resources on cloud has introduced many security related issues that requires a fresh methods to deal with.Flooding Attack Problem
In cloud, servers work in an interactive way. Whenever a server reaches to maximum limit, it will transfer some of its job to the nearby server to reduce some of its load. This helps in making the cloud more efficient and able to execute the request faster. Whenever anyone is authorized to make a request to the cloud, then that person is capable of creating a fake data on the cloud. Before processing any request, the server checks the accuracy of the request. This uses CPU utilization, memory and make the IaaS busy which results in offloading the load from one server to another. Repetition of the same process will result in interrupting the server by involving the whole cloud system, thus flooding the system [40].Browser Security
In cloud, the user will send the request and stop for the result, whereas whole computation processing occurs at the server end. We can connect to the cloud with the help of a web browser. Before making any request on the cloud, the customer has to verify whether he is eligible to access services on the cloud or not. These days browsers mostly depends upon SSL/TLS with respect to security point of view. They are not capable to use WS Security to confirm the process. To authenticate the client, the browser will use SSL/TLS to encrypt the credentials. As SSL/TLS maintain point to point communication, so if any tier is in between the server and customer, the data needs to be decrypted.Confidentiality
Keeping the user data secret is the major concern. Confidentiality is a concern for users to use cloud as they will be keeping their secret data in the cloud. Isolation between customers and controllers should ensure data confidentiality. It is advisable to keep encrypted data on the cloud instead of unencrypted as it will be more secure [13].Integrity
Data integrity main goal is to keep information safe from the unauthorized users. As data plays the most important role in cloud computing, keeping it secure is the most essential task. A system designed by Zetta known as the Zetta system is responsible for keeping data secure with respect to the corruption factor.Availability
Resources are accessible to anyone from any location and at any time point of time. As the concept of cloud is totally based on internet, so the users are allow to use applications and data from wherever and whenever they want. Cloud serves all its users with the data they requested. It is done by two main thing : redundancy and hardening. It is used to progress the availability of cloud resources and data.Service Provider Security Issues
Public cloud supplied by the service provider makes sure that the cloud satisfies the security and privacy needs of an organization. The Cloud provider should define rules to protect the customers information and data and also give proofs of effectiveness regarding the migration of data on the cloud.Malware-injection attack problem
Client requests are entirely based on authentication and authorization, there is a likelihood that Meta data exchange may occur between web browser and server. This could be advantageous to any attacker who has his eyed on this Meta data. The attacker will try to break in with nasty code. This malicious code will appear as a valid service operating in the cloud. If this process gets succeeded, then cloud will get stuck in deadlock and the users then have to wait for the job to get finished which was started by the attacker. This type of attack is called as the Meta-data Spoofing attack.Accountability check problem
The payment method in cloud depends upon pay as per you go. When customer uses the cloud services, all its usage is recorded. Based on the recording, customers are billed. But when an attacker executes a malicious code on cloud, which uses a lot of cloud services, then the legal account owner is charged. As a result, misunderstanding is created and service provider name is affected.Securing Data in Transmission
Transmission of data is done by different types of encryption techniques. Data is protected during transmission by using integrity and authentication policy and cannot be modified in between. This is implemented with the help of SSL/TLS protocols.. For processing data, it should be unencrypted. Cryptography is one of the technique which allows data and information to be processed without being decrypted.Cloud Computing Security benefits
Highlevel of security is one of the main benefit offered by the cloud computing as compared to traditional system. In addition to this, a response to security occurrence is much faster as the service provider security experts are highly knowledgeable to handle issues like this. Easy security patch management is offered by the centralized cloud security, resulting in advanced security structure. Being the main concern of the consumers, security is a business differentiator. Any cloud user will choose a service provider based on the status of its privacy, confidentiality, flexibility and security offered by him. This is used as a motivational thing for the providers to improve its security to get more users. Flexibility or resilience is one of the feature that provides gives along with security. It is known as the ability if reallocating the data and information for authentication, traffic control, encryption, etc. This helps in reduce cost of access control, with easy and cheap usage of many security related processes [41]. Security also helps in providing benefits in the economic terms of cloud computing. If executed on a large level, security can be treated as a way cheaper and cost effective feature. The money the provider will like to invest on capital expense can be spend for the renewal of security services which further helps in the execution of state of the art security technologies.Grid Computing
Grid computing is a structure which joins the resources from different domains to arrive at a important objective. In this, different computers making the network are allowed to work together on a job, thus working as a super computer [42]. Usually , a grid is capable of working on a several different task in a network but is also capable of doing a specific application. They are created to provide solutions to problems that are big for a supercomputer while preserving the flexibility require to solve smaller problems. Few years back, Ian Foster gave some points to describe Grid [43]:- Manages resources that are not concerned to centralized control.
- Uses open purpose procedure and rules
- Delivers qualities of service
Comparison between Cloud and Grid Computing
Below we have done the comparison of cloud computing with grid computing [44].| Features | Grid | Cloud |
| Resource sharing | Collaboration (VOs, fair share). | Allocated resources are not shared |
| Security | Security via credentials allocation | Via isolation |
| Virtualization | Virtualization of data and computing resources | Virtualization of hardware and software platforms |
| Resource Heterogeneity | Aggregation of heterogeneous resources | Aggregation of heterogeneous resources |
| Platform Awareness | Software must be grid enabled | The SP software works on a modified environment |
| Software Dependencies | Application domain dependent | Application domain independent |
| Architecture | Service Oriented | User chosen Architecture |
| High Level Services | Abundance of high level services | No high level services defined till now |
| Usability | Hard to manage | User friendliness |
| Scalability | Nodes and Sites scalability | Nodes, hardware and Sites scalability |
| Software Workflow | Applications require a predefined workflow of services | Workflow is not required for most of the services. |
| User Access | Access transparency for the end user | Access transparency for the end user |
| Payment Model | Rigid | Flexible |
| QoS Guarantees | Limited support, often best effort only | Limited support, focused on availability and uptime |
| Standardization | Standardization and interoperability | Lack of Standards for clouds interoperability |
| Centralization Degree | Decentralized Control | Centralized control |
| Self Management | Re-configurability | Re-configurability and Self healing |
Mobile Cloud Computing(MCC)
There has been a tremendous growth in mobile applications across a large number of categories like games, social media, entertainment, business, news and travel. The popularity of these applications is because of the independence in users location, but they also face problems in low connectivity, shortage of resources, etc. This issue can be solved to an extent by using resources which are external to the mobile device. The processing and data storage going outside the mobile gave rise to MCC [18].Importance of Mobile Cloud Computing
MCChas turned into one of the most significant technology for the mobile users as it combines mobile technology with cloud computing benefits. Combination of both helps in providing the best services for the users. Several mobile applications are taking benefits from MCC [45]. Some of these are discussed below: Mobile Banking: It is related to any task that involves banking services like checking the balance, transferring funds, generating OTP's, payments of bill, receiving SMS related to bank services through a mobile device. Nowadays banking is done through mobile internet or messages. Banking apps on cloud deals with concerns like storage and speed. Mobile Commerce: This application is mostly used in everyday jobs which involves mobility like mobile payments, ticketing, socializing, messaging, transactions, etc. This has lead to several problems like security, privacy, low bandwidth, complexity of device configuration. Thus with the integration of cloud computing and M-commerce applications these issues can be handle. Mobile Learning: It can be defined as the combination of electronic learning with mobility. Tradition learning have many issues like high network cost, limited amount of resources and device cost. Mobile learning with combination to clouds provide users with large amount of resources, high processing abilities and large storage space. Mobile Healthcare: In contrast with the traditional medical treatment, cloud based mobile healthcare decreases the problems like small physical storage, security, privacy and medical errors. It supports mobile users to easily access resources like staff data, status of the tests, medical records of the patients. Mobile cloud computing also helps to provide access to hospitals and other health care organization with on demand services. Mobile Government: It is the extension of eGovernment with mobile that provides access to government services and applications using mobile combined with wireless internet structure. It helps to use the government services and application from anywhere and anytime. Mobile Gaming: It is one the biggest market nowadays that is giving a huge profit to the service providers. With MCC, we can offload the game engine on the mobile cloud which requires large amount of computing. This will help in saving energy and will increase game playing time.Advantages of Mobile Cloud Computing
- Storage: Helps user to store large amount of data. So applications in mobile are not restricted to certain amount of storage as their data is stored on cloud.
- Multi-tenancy: Service provide can share the data and applications to large number of users at the same time.
- Ease of Integration: Users demands can be met by integrating different service from different service providers with the help of cloud and internet.
- Cost Efficiency
- Mobility and availability: With the ability of storing data on cloud, chances of losing data is reduced. It can be defined as an information security model for users and providers. Due to cloud storage we can access the data from any location we want.
- Backup and disaster recovery
- Redundancy and Flexibility
- Scalability and Performance: Applications can be enhanced as per users requirements. Any app can be easily added or enhanced by the service providers.
- Easy Integration and quick deployment
- Environmentally friendly and dynamic provisioning
Disadvantage of Mobile Cloud Computing
- Information Flow Control
- Security and Privacy
- Compatibility
- Dependency
- Unpredicted Cost
- Limited Control
Open Challenges in Mobile Cloud Computing
There are many challengesrelated to mobile cloud computing. We have listed some major issues below:- Due to an increase number of users, bandwidth is a major concern in cloud computing.
- Problems such as network blocking, disconnection of network and signal issues can reduce the quality of service considerably.
- Pricing issue such as how to divide the bill between different components, how much price needs to set and what will be the mode of payment by the customers.
- Interoperability and standard layout are also among the concerns related to of mobile cloud computing.
- Managing wireless connectivity with a heterogeneous network can be a difficult thing.
- Computing offload is also one of the major concern. It can be difficult to determine whether to offload and what potion to offload.
2017 Cloud Computing Trends
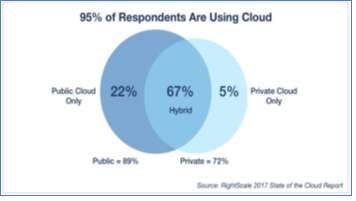
Figure 29 [46]
Sixth annual State of the cloud survey was conducted by Rightscale in January,2017 discussing the latest 2017 cloud trends [46]. In this survey, professionals from several different organizations were questioned about their adoption of cloud. These professionals include managers, practitioners, and technical executives from different organizations. Their thoughts gave a broad point of view on the status of cloud. The finding of that survey are given below.Organization depends more on Hybrid cloud
- Multi cloud strategy is followed by 85% of the organizations, which is increased slightly from last year which was 82%.
- The number of organizations planning to use hybrid cloud has increased from 55% to 58% as compared to last year
- There was a 9% decrease of usage private cloud among the companies from last year(23%).
- There was increase of 4% in the usage of public cloud in 2017, 20% from 16% last year.
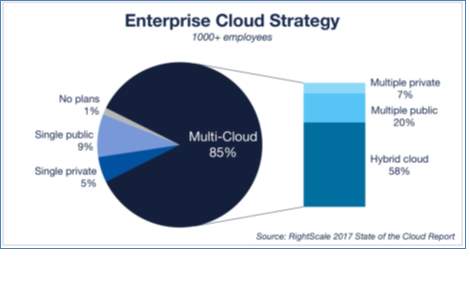
Optimizing Cloud Costs Becomes a Top Initiative
- Cost optimization is one of the biggest plan for cloud users(53%), slightly higher of moving workload to cloud(52%)
- As per reports, very less enterprises are taking actions for cloud cost optimization.
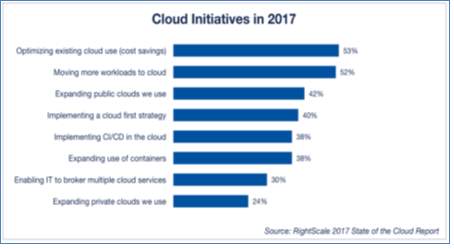 Figure 31 [46]
Figure 31 [46]
Enterprise Central IT Teams Take a Stronger Cloud Role
- Many central IT teams are shifting to centralization with a wide role in cloud in 2017.
- IT teams looks for their job in selecting private cloud(63%), public cloud(65%) and deciding on which apps to move to cloud(63%).
Future of cloud
The future of cloud computing is very bright because of its numerous advantages. Some of the new development trends are listed below [47]:- The huge demand of resources on the internet will encourage the growth of market oriented computing services. Number of services and applications will be introduced that will focus on a particular area.
- With the increase number of applications from the consumers will result in the increase number of service providers thus raising the competition among the service providers. New ways of utilizing services and applications may be created or discovered in this process.
- New international models for small and large multinational companies will be enabled with the help of cloud based teleconferencing system and cloud based customer relationship management.
- Will help in scientific experiments because of it's completely runtime experimental settings.
- Cloud computing network is likely to widen in order to achieve global market support.
- Advance level of interoperability is required in order to cope up with the global market and large amount of requirements.
- Combination of grid and cloud will come into picture in order to optimize grid services, cloud services and infrastructure.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is locating itself as a novel stage for providing information and a variety of computer resources for government, businesses, education and individual as IT services. Customers can install the services in a pay as per usage fashion and in a easy way thus saving large amount of money. Clouds are bringing a high level of interest for both the developed and emerging markets. Though some of the challenges related to security, performance and privacy of the data remains to be addressed properly. This paper gives the basic knowledge of cloud computing which includes its architecture, service layers, deployment models, types of cloud and so on. It includes the discussion related to some of the recent growth of cloud market and also elaborates the emerging trends in cloud. The integration of cloud computing with mobile technology has also provide network as a service known as mobile cloud computing. It is one of the new trends as it combined the mobile services with cloud thus providing better services to the individuals. This paper also discussed the concept of mobile cloud computing, along with its advantages and disadvantages and the challenges related to this new technology. Cloud computing and other related models need to join so as to create an unified and interoperable platforms for providing IT services to companies, government, individuals and corporations.Bibliography
- M. Singh, "Study on cloud computing and cloud database," pp. 708-713, 2015.
- M. P and G. T, "The NIST definition of Cloud Computing," 2009.
- Y. Jadeja and K. Modi, "Cloud computing - concepts, architecture and challenges," 2012 International Conference on Computing, Electronics and Electrical Technologies (ICCEET), pp. 877880, 2012.
- L. Quan, L. Zhiguo, G. Leitao and D. Yujian, "Cloud Computing: An Overview," pp. 626-631, 2009.
- "Greatcloudmigration," 3 March 2014. [Online]. Available:
- Chandana, "Simplilearn," 13 April 2013. [Online]. Available: https://www.simplilearn.com/cloudcomputing-architecture-article.
- cloudadmin, "cloudcomputingnet," 26 May 2015. [Online]. Available:
- J. Strickland, "Cloud Computing Architecture," 2008.
- V. Saxena and S. Pushkar, "Cloud computing challenges and implementations," in Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques (ICEEOT), International Conference on, 2016, pp. 25832588.
- B. Golden, "cio," 20 January 2014. [Online]. Available: http://www.cio.com/article/2379480/cloudcomputing/the-new-cloud-application-design-paradigm.html.
- L. Columbus, "By 2018, 62% Of CRM Will Be Cloud-Based, And The Cloud Computing Market Will Reach $127.5B," Forbes, 2015.
- T. Wei-Tek, S. Xin and B. Janaka, "Service-Oriented Cloud Computing Architecture," 2010 Seventh International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations, pp. 684-689, 2010.
- K. I. H., K. A. and E. M. M., "A taxonomy and survey of Cloud computing," 2013 National Security Days (JNS3), pp. 1-13, 2013.
- M. Almubaddel and A. M. Elmogy, "Cloud Computing Antecedents, Challenges, and Direction," in Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet of things and Cloud Computing, ACM, 2016, p. 16.
- M. Lenz, "Everything as a Service – Introduction," 2012.
- M. Ali, "Mazikglobal," 16 June 2014. [Online]. Available: http://www.mazikglobal.com/blog/cloudcomputing-stack-saas-paas-iaas/.
- K. Combs, "blogs.technet.microsoft.com," 4 April 2012. [Online]. Available:
- S. Wattal and A. Kumar, "Cloud computing - An emerging trend in information technology," pp. 168173, 2014.
- K. So, "Cloud Computing Security Issues and Challenges," International Journal of Computer Networks, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 247-255, 2011.
- V. C, "Linkedin," 30 January 2017. [Online]. Available: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/2017-publiccloud-computing-growing-phenomenal-rates-c-vishal.
- admin, "Xyfon.com," 14 June 2014. [Online]. Available: http://xyfon.com/public-vs-private-vshybrid-cloud/.
- G. Motta, N. Sfondrini and D. Sacco, "Cloud Computing: An Architectural and Technological Overview," pp. 23-27, 2012.
- N. Jain and S. Choudhary, "Overview of virtualization in cloud computing," in Colossal Data Analysis and Networking (CDAN), Symposium on, 2016, pp. 1-4.
- D. S. Linthium, "Connecting Fog and Cloud Computing," IEEE Cloud Computing, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 1820, 2017.
- K. Akherfi, M. Gerndt and h. Harroud, "Mobile cloud computing for computation offloading: Issues and challenges," Applied Computing and Informatics, 2016.
- D. Assante, M. Castro, I. Hamburg and S. Martin, "The Use of Cloud Computing in SMEs," Procedia Computer Science, vol. 83, pp. 1207-1212, 2016.
- B. K. Rani, P. B. Rani and D. B. A. Vinaya, "Cloud Computing and Inter-Clouds - Types, Topologies and Research Issues," Procedia Computer Science, vol. 50, pp. 24-29, 2015.
- D. Bernstein, ""Intercloud" - Not all the same! Federation versus Multicloud," 2013.
- L. Y. Astri, "A Study Literature of Critical Success Factors of Cloud Computing in Organizations," Procedia Computer Science, vol. 59, pp. 18-194, 2015.
- Y. Chaowei, Y. Manzhu, h. Fei, J. Yongyao and L. Yun, "Utilizing Cloud Computing to address big geospatial data challenges," Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, vol. 61, pp. 120-128, 2017.
- J. Mouna and A. B. Latifa, "Comparative Study of Information Security Risk Assessment Models for Cloud Computing systems," Procedia Computer Science, vol. 83, pp. 1084-1089, 2016.
- "Stratosphere Networks," [Online]. Available: http://www.stratospherenetworks.com/advantagesand-disadvantages-of-cloud.html.
- S. Kamboj and N. S. Ghumman, "A survey on cloud computing and its types," Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), 2016 3rd International Conference on, pp. 2971-2974, 2016.
- Nastya, "Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing," 2015.
- J. Rosenblum, "Top Five Challenges Of Cloud Computing," Cloudtweaks, 2012.
- K. Gai and S. Li, "Towards Cloud Computing: A Literature Review on Cloud Computing and Its Development Trends," in Multimedia Information Networking and Security (MINES), 2012 Fourth International Conference on, IEEE, 2012, pp. 142-146.
- M. Ferkoun, "How cloud computing is impacting everyday life," 4 April 2013.
- A. K. Pathak, "Impact of cloud computing in education, e governance," 7 May 2015. [Online]. Available: https://www.slideshare.net/asimkumarpathak/impact-of-cloud-computing-in-educatione-governance-47864353.
- M. Rowland, "Technoweb," 6 April 2017. [Online]. Available: http://www.technobeep.com/cloudcomputing-future-what-will-be-its-impact-on-the-industry/.
- G. Kulkarni, N. Chavan, R. Chandorkar, R. Waghmare and R. Palwe, "Cloud security challenges," in Telecommunication Systems, Services, and Applications (TSSA), 2012 7th International Conference on, IEEE, 2012, pp. 88-91.
- S. Barakovic and J. H. Barakovic, "Short and sweet: Cloud computing and its security," Telecommunications (BIHTEL), 2016 XI International Symposium on, pp. 1-5, 2016.
- "Techopedia," [Online]. Available: https://www.techopedia.com/definition/87/grid-computing.
- I. Foster, Y. Zhao, I. Raicu and S. Lu, "Cloud Computing and Grid Computing 360-Degree Compared," pp. 1-10, 2008.
- A. H. a. Aldabas, T. and A. a. Hamza, "Comparison between cloud and grid computing: review paper," International journal on cloud computing: services and architecture (IJCCSA), vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 1-21, 2012.
- Alzaharani, A. a. Alalwan, M. and N. a. Sarrab, "Mobile Cloud Computing: Advantage, Disadvantage and Open Challenge," Proceedings of the 7th Euro American Conference on Telematics and Information Systems, p. 21, 2014.
- 2017 Cloud Trends, Right Scale, 2017.
- K. Gai and S. Li, "Towards Cloud Computing: A Literature Review on Cloud Computing and Its Development Trends," in Multimedia Information Networking and Security (MINES), 2012 Fourth International Conference on, 2012, pp. 142-146.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Computing"
Computing is a term that describes the use of computers to process information. Key aspects of Computing are hardware, software, and processing through algorithms.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




