Blockchain and Smart Contracts in Healthcare
Info: 5700 words (23 pages) Dissertation
Published: 9th Dec 2019
Tagged: HealthBlock Chains
Abstract: Looking to the current technology trend, we examine whether the healthcare blockchain will be beneficial to the health industry or not. We also review the current challenges in this industry and how the blockchains can help to overcome this problem.
We then move in to the standard followed by healthcare industry (FHIR) and how this FHIR is linked with blockchains. Further we also describe how blockchain works and what does block contain in it. We also point out the advantages and issues to be considered before deploying this technology. Our conclusion is that blockchain-healthcare combination is very strong technology and it will be proved very fruitful in the entire healthcare industry. Though it has some challenges and issues, there are ways to overcome it.
Keywords: Blockchains, Smart contracts, FHIR, Telemedicine, Artificial Intelligence
- INTRODUCTION
For years innovation and medical records keeping have been held back by the need for compliance.
Electronic health records can be difficult to access, impart because the ability to view and change them
abides by several laws and confidentiality rules. As your personal health data grows overtime and the
number of healthcare services you received increases, it can be hard to keep track of records that are
being made in past. Smart contracts can streamline ownership and access to health information for both
patients and health providers. Storing medical records on blockchain allows those with viewing permissions to securely access them at any time. The smart contract functionality means that authorized
parties can easily receive and make changes to the record.
- CURRENT CHALLENGES
Healthcare industry keeps utilizing old inflexible frameworks for working with individual information and exchanges. It doesn’t give security to patient’s records. The Healthcare business is identified with the printed material like wellbeing records, restorative history, lab tests, diagnostic exams and so on.There are numerous examples like if patient wants to change the doctor for any reason, he must fill out forms again. Another example is patient having chronic diseases and need care 24/7, their care team does not have any efficient way to access healthcare information.[1]
Currently as the smart contracts and blockchain technology is not fully developed, there are lot of problems associated with it. Issues like improper treatment, conflicts between pharmacies and doctors, illegal drug sales could be eliminated with the use of blockchain. Patient records could be made available in a secure manner to all doctors in all hospitals in case of emergencies. Information related to the patients’ medical history, past treatment, current immunizations given is critical to ensure that the best care is given to the patient. With proper authentication to monitor the records, doctors can make sure the proper workflow is followed and the process becomes easy.[2]
1.2 PROBLEM SOLVER – BLOCKCHAIN HEALTHCARE
Blockchain Healthcare Smart Contracts permit having a computerized stockpiling of all patient’s wellbeing records. Subsequently, it will totally evacuate the need of filling data over and over. It will likewise help insurance agencies and healing facilities. The points of interest of the arrangement get connected to the profile inside the blockchain [1]When a patient experiences a restorative technique, which is secured by strategy then the savvy contract will naturally be activated and the right installment from the insurance agency to the clinic will be consequently made. This will have positive. This will have positive impact on the execution of the person’s insurance policy. It will reduce inefficiencies that come to complete insurance claims forms.[3]
1.3 OPPURTUNITIES FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
One of the main essentials of blockchains would be interoperability. With interoperability in blockchain, a provider could send or receive patient data to another provider in any location in a secure way. Blockchain would also allow betterment and savings in cost in healthcare processes. Blockchain and smart contracts would help in improving the processes for all stakeholders. As per some of the surveys, blockchains could be the solution to healthcare interoperability problem. The interoperability problem leads the healthcare payers and the providers open to compliance vulnerabilities. Providers are required to comply with the HIPAA compliance and provide report on the patient data. The providers and payers also mitigate from the increasing risk of false claims as every updating of information in the blockchain is automatically recorded ensuring transparency. It can also lead to an improvement in planning as more strategies are carried out for risk management. As transactions are accessible in real time, smart contracts and blockchain technology can help improve the quality of healthcare audit process. It can also lead to faster execution and automation in the processed leading to successful testing and validation of information.
1.4 FHIR- Standard for healthcare
FHIR stands for Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources. new standard for trading electronic human services data and replaces more unbending and entangled heritage groups. It is based on current web advances that are utilized by sites you use as Facebook and so forth. It enables implementers to proficiently incorporate, demand and exchange information between different human services systems. [1]
The basic building blocks of FHIR are resources. Resources are categorized into various groups like
Clinical Resources
- Allergies
- Care plans
- Medications
Identification Resources
- Patient demographics
- Device information
Financial Resources
- Insurance coverage
- Eligibility information
- Billing
The FHIR characterizes the way assets can be traded between various frameworks and every asset design is characterized by the rest call for trading the information.
The objective is to illuminate an extensive variety of clinical and regulatory social insurance issues by making medicinal services data more compact and improving interoperability.
1.5 A Healthcare Blockchain
A blockchain is a universally useful information structure so it is conceivable to apply it to spaces other than digital cash. The prospect of chronicled mind influencing present decisions fits well into the blockchain show, where the character of a present event is dependent on each past event.
Our piece in healthcare is tree-based structure. The leaf hubs of the tree speak to quiet record exchanges and depict the expansion of an asset to the official patient record. FHIR in conjunction with the blockchain can serve to protect the uprightness and related setting of information exchanges[4]
A transaction contains following things:
Hash: The SHA256 hash of the resource payload
Contributor Signature: The digital Signature of the originating node
FHIR URL: A reference to the actual FHIR resource location.
FHIR Profile: The URL of the FHIR Profile to which this resource confirms.
Secure Index: Index allowing for data discovery without leaking information about the record


Block Header
Hash
Previous block hash
Contributor signature
Transaction 2
Transaction 1
Hash
FHIR URL
FHIR profile
Secure Index
1.6 Two Approaches for creating blockchain solutions
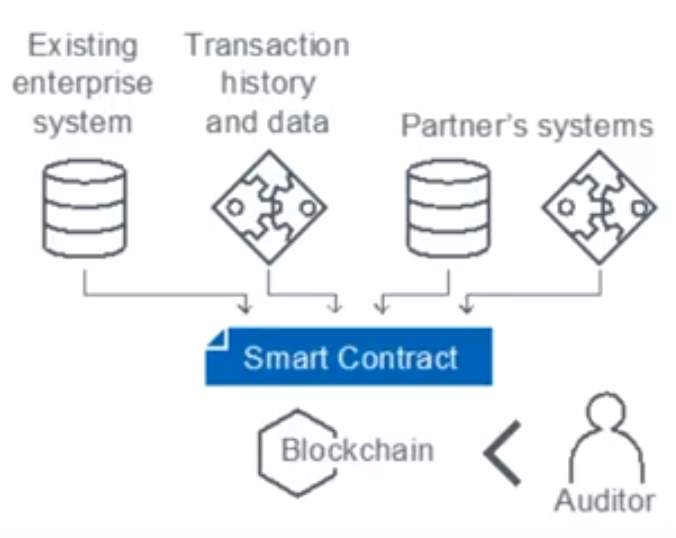
- Simple augmentation of existing solutions: Similar to shadow chain. Runs on top of systems to leverage blockchain principles, to reducing inefficiency in process through transparency across business with partners.
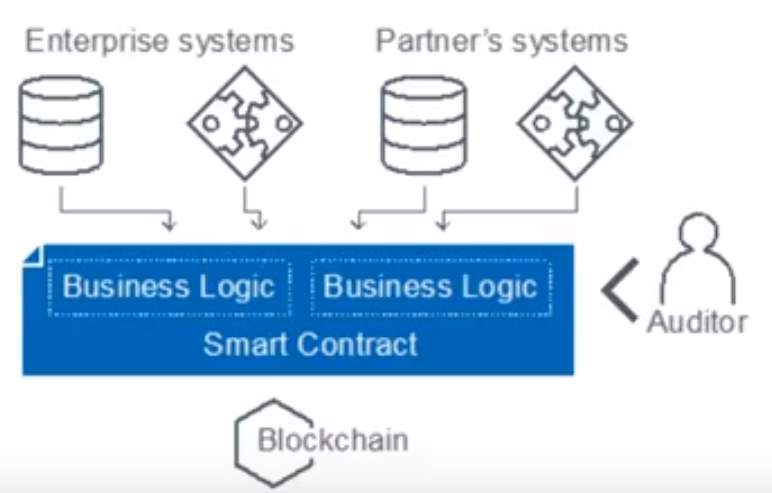
- Creating a new function or solution with Blockchain and smart contracts for business logic: Business logic is combined with enterprise and partner systems to form a new solution which can enhance the productivity and reduce the time spent in a process.
- BACKGROUND
Studies have revealed that more than 15% of healthcare costs are illicit which results in excessive billing.
Factors related to healthcare are countering counterfeit drugs, protecting data from hackers, data leaks,
privacy and security, health data availability is driving the performance of this sector. Blockchain and
smart contracts have a major role to play in drugs supply due to the problem of counterfeit drugs.
Counterfeit medicines are a huge risk globally. It also leads to decrease in revenue and trust of health
systems and healthcare providers. Blockchains can increase drug traceability by tracing all the
transactions of all users involved in the drug supply chain. By making sure each user has access to what
information is updated in the blockchain, blockchain enforces transparency and can trace the user at any given point of time. It can also help in the identification of users who are accountable, and proof of
ownership can be known for the counterfeit drug supply.[5]
Using smart contracts in blockchain can eliminate the fraudulent practices and automate the processes.
Patients would be able to see the information on the blockchain and know what exactly they are charged for Administrative costs could also be reduced as it removed the middleman from the chain of processes. Since the surge for electronic data which is being available in an increased pace than before, it is essential to find secure ways to use it. With the rise in technological innovations in healthcare and the global hacking attack gave prominence to the need of the health security for all sectors.[6] Blockchain would allow only authorized personnel to have access to information. In fact, an advantage of using blockchain and smart contracts would be patients can exchange data to the physician and the issue of gathering information from all physicians while moving to another city could be resolved. This ensures a higher level of privacy. Blockchain will allow the new physician to access all the patients’ medical history.
Smart contracts can be used along with blockchain in healthcare as it would solve the data manipulation
problem. It acts as trusted parties and delivers immutable record of trial history. Smart contracts can lead to exchanging any type of dealings related to healthcare in a transparent and conflict-free manner.
Blockchain could signal a innovative model to the entire clinical research by ensuring transparency to
patients and traceability to stakeholders.
For example, patient consent forms can be stored in a secure way and enable sharing of information real time preventing posteriori reconstruction. With smart contracts in blockchain the history of workflows in a clinical trial can be located and is possible due to the ability of blockchain to handle complex workflows.[7]. The electronic sharing of patient imaging data is a vital component of healthcare, but current foundation for cross-site picture exchange relies upon third parties. With blockchain technology, it enables parties to reach consensus without relying on a central authority. [12]
Hyperledger, an open source blockchain has a separate dedicated branch for healthcare which works on
open source software development projects and could change the way in which healthcare currently
works.[8] Technical solutions such as integrity and confidentiality of data can lead to the formation of
movable user owned data. Also, it can ease the establishment of a cryptographically secured data exchange that could be useful in real time access to patient’s medical record.
Currently, medical records of patients are stored in a closed database called practice management suites. All hospitals use different vendors for their electronic medical software. Recently, there has been a trend to push data into cloud format called Electronic Health Records (EHRs). By pushing data in cloud, it allows better interoperability among health organizations. This make processes simpler as for example if the patient wants access to their own medical data, the administrator can generate a link and share it to them. The blockchain can be used to maintain the sharing of those encrypted datalinks per patient based on addresses. Transactions are managed on each block in the blockchain. Once the data is in the cloud, computations can be performed.
3. Operations with Healthcare Blockchain
- How does blockchain and smart contract fit with healthcare?
One of the most important aspect of a healthcare system is how data is shared across the chain. Blockchain supports seamless information that can eliminate the duplication, errors and inconsistency in data that can arise with data centric and traditional data storage. Smart contract eliminates the need for intermediaries to manage and execute the contract. [9]
Blockchain can provide solutions to many health care industries challenges listed below.
- Timely Access to Patient Data: Blockchain provides distributed, secure access to patient health data across the distributed ledger and distributed data enables real-time updates over the networks.
- System Interoperability: Blockchain gives opportunities to decentralized internet and computer networks across geographies and enables authenticity.
- Data Security: It is used for data security of transaction and digital identity guard’s patient care.
- Fragmented Data: It is a decentralized storage, uses computer networks for patient data.
- Cost Effectiveness: By this transaction costs are reduced and real-time processing to make the system more efficient. It also provides elimination of third-party applications which removes time lag in data access.
3.2 How Blockchain and smart contracts remove middleman?
Figure 1 shows the current healthcare system model.
Consumers/patients:
They pay monthly premiums to health payers.
They also pay co-pays to providers and pharmacies.
Health Payers:
They receive claims from healthcare providers.
Reimburse providers for care and Pharmacy Benefit Managers for drug prescriptions.
Pharmacy Benefit Managers:
Reimburse pharmacies for drug prescriptions.
Negotiate prices with drug manufactures and places drugs on a health plan’s formulary.
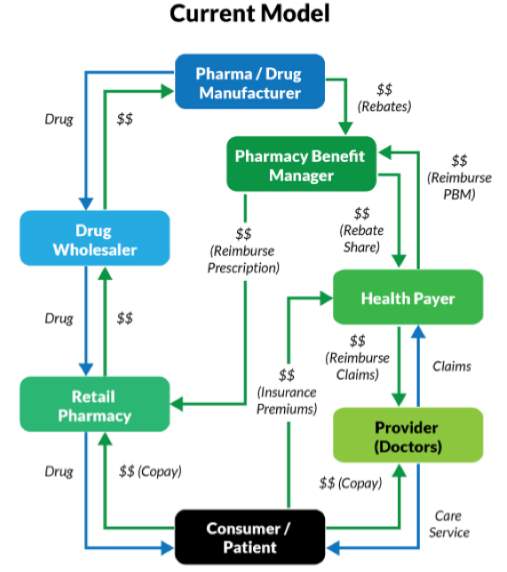
Figure 1
Figure 2 shows the blockchain model in healthcare:
Blockchain has the capacity to significantly cut the cost for the end customer.
- Multiple parties need to be able to view and sometimes edit the same data.
- Several of the transactions are sequential, and all the parties conducting the transactions need to know the interdependencies of those transactions.
- Middlemen are in the ecosystem mainly because of the lack of trust amongst the parties.
- Financial gains to be made in the ecosystem with reduced transaction times.[10]
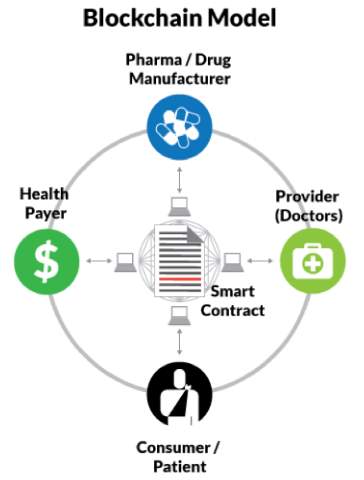
Figure 2
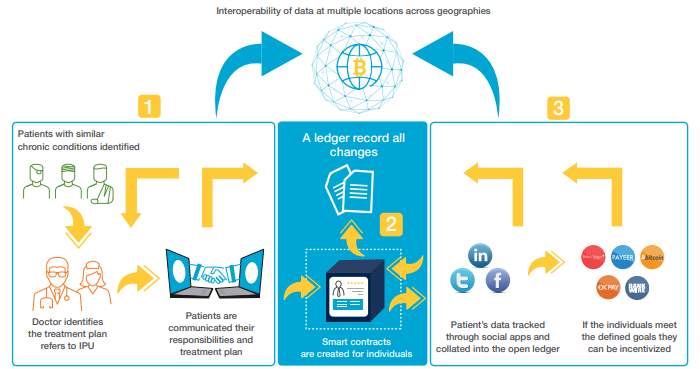
3.3 Blockchain for health payer
High trustworthiness records related with a patient in spite of their traveling through various social insurance spaces and frameworks is one of the considerable difficulties of medicinal services IT. Blockchain turns into the bringing together magic that binds an exceptionally divided medicinal services record.
The assortment of blockchain for social insurance ideas can be thought of as spreading along a range from techno-idealistic dream to convincing close term utilize mind. One approach towards the last 50% of the range is the production of a blockchain-based Master Patient Index Block 1: In the case management scenario, a patient’s initial encounter with the care provider, that treatment plan becomes a medical record for the patient and it is added to the blockchain ledger and provides the basis of patient attribution in case management.
Block 2: Then a smart contract is being created containing all the attributes for the patient’s case management. The contract defines the key parameters, wellness goals and business rules that are defined to evaluate the patient’s progress. This file is added to blockchain.
Block 3: the process in patient’s health and wellness data is collected from wearable devices and social media applications. This data is added to the next block in blockchain in an open ledger.
The main advantage of this process is that each entity in the network has access to the open ledger, but patient’s data can only be viewed to the authorized patients only. This removes the need of the central authority. This medical data can be referenced to create a personalized care for the patients. [10]
Figure 2 shows how a chronic-care patient’s data can be enhanced to make a medical-history records available on a global network. This would enable any doctor, any patient, any hospital regardless of the country in which it is located, to access this data.
The shared ledger capability of a healthcare blockchain can provide complete transparency to all parties regardless of the location. This would allow payers and providers to negotiate complex bundle claims that are tied to value and move away from the fee-for-service model. Also, the smart contracts would make the claims adjudication process seamless. [10]

One of the most prominent cost loads hiding in the procedures of US medicinal services is the persistent following of the stream of administrations and cash: The huge intricacy and conveyed nature of our wellbeing framework implies that billions of dollars are used every year attempting to comprehend which quiet got what benefit from which administrations supplier and by whose expert. [10]
Question emerge, and both the protection business and the suppliers of medicinal services at that point use a lot of extra time and cash arbitrating these contradictions. As a result of its autonomous design, blockchain could possibly shape the establishment of a high respectability following ability that is refreshed in a close momentary way.
3.4 Med Token – The chain of medical
Med tokens are intended to be the money related ointment that keeps the blockchain running. They will be used to compensate the center points who support the record. Patients will use the tokens to pay masters for telemedicine gatherings and these authorities would then have the capacity to exchange them for level cash.
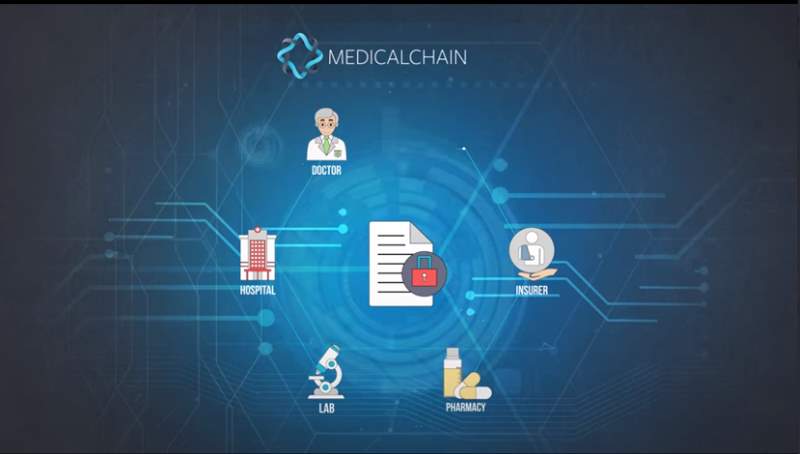
Medicalchain gives the system whereupon electronic prosperity applications and organizations are to be collected. It uses the blockchain development, smart contracts and computerized cash.
It is a decentralized stage that empowers secure, quick and straightforward trade and utilization of therapeutic information. This chain will empower diverse human services specialists, for example, specialists, doctor’s facilities, labs, drug specialists and back up plans to ask for consent to get to and communicate with therapeutic records. Medicinal chain is based on the consent based Hyperledger Fabric design which permits fluctuating access levels.[1]
3.5 Smart contracts and EHR (Electronic health records)
Smart contracts are code held and executed on the Ethereum blockchain. Procedures that ordinarily require an expert or public accountant can be mechanized and approved by brilliant contracts in an entirely straightforward and secure way. For instance, a doctor burns through 3-4 hours week by week on charging and protection if they begin utilizing keen gets their procedures are mechanized and approved by Ethereum organize. In addition, Patient possessed electronic wellbeing records will empower a few highlights to be utilized as a part of conjunction with medicinal chain stage[3]
- Telemedicine
Telemedicine is an online communication between a specialist and patient utilizing a webcam interface.
It discredits the time and calculated problem required to visit the specialist’s office and gives a remote varying media conference. Specialists additionally advantage from connecting with this innovation. It empowers adaptable working hours and the capacity to work from any area. Medicalchain empowers the specialist to communicate live with the patient’s longitudinal wellbeing records amid the counsel.
Predictable with the establishing standards of Medicalchain, patients ought to have control over their wellbeing records and they ought to likewise profit by the potential esteem that they have. Medicalchain will associate research foundations with clients willing to have their wellbeing information utilized as a part of concentrates in a wellbeing information commercial center. Clients will be given data with reference to how their information is being utilized and what information will be required. Consequently, members will be repaid in digital money. Patients will be enabled to open the fiscal esteem that their wellbeing information holds and conceivably be more drawn in with their wellbeing conditions.[9]
Pharmaceutical and research companies
They will also benefit from engaging with the technology of medical chain. They will be ready to search out patients who have selected in to being reached – never again expecting to approach a healing center or facility for tolerant data. This will expand productivity and process will be more straightforward. It will likewise urge patient to assume a part in investigate about their own wellbeing problems [3]
3.7 Security
Data security is the main priority of healthcare system. The approach which we proposed includes:
Blockchain Encryption: – Public information is expected to be encrypted by a network shared key while sensitive information should be encrypted by originating node.
Smart contracts: – Patients may approve access to their record just under specific conditions or for a reason. The expectation is to guarantee that patient approval is systematized and executable. The brilliant contracts can be set specifically on the blockchain as exchanges giving affirmations of legitimacy as well as a review component too[11]
Since the distributed system technology is different from existing healthcare technology, its structure and functionality could create unexpected problems. For example
Human error: – Blockchain innovation can be confounded to see, along these lines any worker in charge of working with the framework ought to be prepared to comprehend its usefulness and related dangers. An inadequately oversaw blockchain framework can turn into a security chance. [2]
Government Regulations: – Blockchain creates massive hurdles when complying with government regulations such as HIPPAA. Since blockchain is still emerging into commercial use, there is regulatory uncertainty which could cause severe noncompliant damages.[2]
3.8 Business perspective
The patient and provider both are benefited from this robust data exchange platform.
- Patient Perspective
Patients never again need to organize the dull assignment of get-together records from different suppliers to send them. Rather, they would give the authority access to the blockchain empowering them access to the information as they fit.
Patients hold control of their information. They never again should invest time and vitality keeping their information oversaw and up and coming.
Therefore, this will prompt better watch over the patient.[3]
- Doctors and Organization perspective
This approach would take out numerous difficulties of existing wellbeing data trades. Human services association will now approach a similar data. Presently they don’t have stress over information driven preferred standpoint as they will approach a similar data.
Through contracts with patients and doctor’s facilities, hubs can communicate alarms or dangers. Information can likewise be shared for different research exercises like clinical trials and so forth.[4]
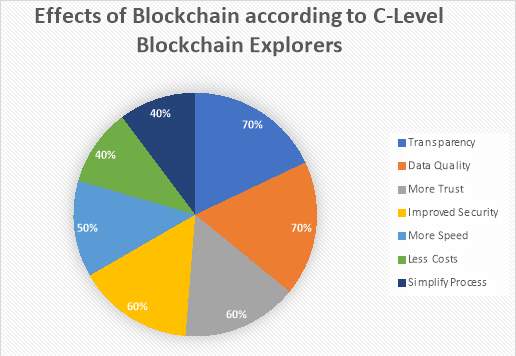
3.9 Effects of Blockchains according to C-level Blockchain Explorers
The figure shows the effects of blockchain in various entities. As healthcare is all about transparency, data quality and security, Blockchain will turn out to be basic in building a worldwide exactness drug biological community that ideally interfaces patients, clinicians, scientists, safety net providers and clinical research centers to each other. Blockchain will enhance information security, information sharing, interoperability, persistent commitment, huge information investigation, wellbeing data trade, battling fake medications, R&D forms, AI-based diagnostics and cultivating vertical plans of action.
Blockchain will improve transparency to 70% and quality to 60% which would be very helpful in healthcare sector.
4. Future work
Blockchain technology along with smart contracts in healthcare can undoubtedly transform healthcare. Healthcare sectors can make the best use of this technology to help patients and health professionals anytime. Researches from researchers and scientists reveal that blockchain will prove to be a revolutionary in drastically transforming healthcare.
4.1 Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Blockchain technology can help facilitate a mechanism to AI provider for the development and execution of machine learning algorithms in healthcare industry. For example, an algorithm that can look at a CT scan or any Imaging and make diagnosis predictions. The radiologist could use this result as an independent reference to compare his or her own diagnosis. This technology will ensure accuracy and will be proved helpful in entire industry.[1]
4.2 Organ donation via blockchain
There is plausibility of making organ contributor and beneficiary holding up list where they can be straightforwardly combined up. Utilizing this innovation, it is anything but difficult to comprehend what your spot in the holding up rundown and you can be ensured that you will remain on that spot and won’t be kicked out and expelled from that point.[2]
4.3 Data creation by improving quality measurement
As of now, doctor’s facilities gather PRO (patient- reported outcomes) measures through reviews or surveys, however blockchain offers the potential for a quick paced elective that coordinates wellbeing data from cell phones and mHealth apps opening a strong new informational index for suppliers
In our proposed models of blockchain in healthcare, the accompanying are the destinations that show blockchain is an innovation of future:
1. Improve the trustworthiness and security of patient information.
2. Aim to lessen administrative and legal costs.
3. Advancing the connections between the patients, healthcare providers and insurance agencies.
4. Empowering patients through technology.
5. Conclusion:
There are some major issues to be tackled to use this technology. Firstly, lack of investment which is crucial to blockchains development. Secondly, healthcare professionals and patients should be trained properly on how to use this technology and be completely aware of the benefits. Finally, as every country’s rules regulations are different, all technology providers must work together with the government to have confidence among the stakeholders. Blockchain may be encouraging for the future healthcare, but there have been innumerable questions on its long-term usability. Despite the challenges, blockchain is a magnificent possibility for the expansion of healthcare in a transparent, secure and confidential way. Moreover, Smart contracts of blockchain are used to authorize each patient with governor over their personal data. It also helps to simplify the process of interaction between various parties. Nevertheless, the methodologies and possibilities of blockchain are still obscure all through society.
REFERENCES
1. Balyuk, I. IMPLEMENTATION OF BLOCKCHAIN HEALTHCARE SMART CONTRACTS. Jan 2016; Available from: https://applicature.com/blog/blockchain-healthcare-smart-contracts-2.
2. Southey, S., Blockchain – the future of healthcare? 2014.
3. Randy Bean, G.S. How Blockchain Is Impacting Healthcare And Life Sciences Today. April 2018; Available from: https://www.forbes.com/sites/ciocentral/2018/04/02/how-blockchain-is-impacting-healthcare-and-life-sciences-today/#436918a6738f.
4. Kevin Peterson, R.D., Pradip Kanjamala, and Kelly Boles, A Blockchain-Based Approach to Health Information Exchange Networks.
5. Dyrda, L. Blockchain in healthcare: Identifying the biggest and best opportunities with Change Healthcare. August 21, 2017 Available from: https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/healthcare-information-technology/blockchain-in-healthcare-identifying-the-biggest-and-best-opportunities-with-change-healthcare-cto-aaron-symanski.html.
6. Space-o-Technologies. 3 Benefits of Blockchain in Healthcare And How It Will Revolutionize the Industry. 2015; Available from: https://www.upwork.com/hiring/for-clients/3-benefits-of-blockchain-in-healthcare/.
7. Mehdi Benchoufi, P.R., Blockchain technology for improving clinical research quality. 2017 Jul 19.
8. O’Dowd, E. New Hyperledger Project Fuels Healthcare Blockchain Development. October 18, 2017; Available from: https://hitinfrastructure.com/news/new-hyperledger-project-fuels-healthcare-blockchain-development.
9. Mamoshina, P., et al., Converging blockchain and next-generation artificial intelligence technologies to decentralize and accelerate biomedical research and healthcare. Oncotarget, 2018. 9(5): p. 5665-5690.
10. Capgemini. Blockchain: A healthcare Industry view. 2012; Available from: https://www.capgemini.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/blockchain-a_healthcare_industry_view_2017_web.pdf.
11. Wabo, B. Security Considerations for Using Blockchain Technology in Healthcare. March 28,2018; Available from: https://a-lign.com/security-considerations-using-blockchain-technology-healthcare.
12. Patel, V.A framework for secure and decentralized sharing of medical imaging data via blockchain consensus. April 2018:Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29692204
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Block Chains"
Blockchain is a system that has the ability to hold transactional data, without the potential to be hacked. Records are held essentially in block form and don't require a central authority to control it.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




