Role of Cryptocurrencies and their Advantages and Disadvantages
Info: 7377 words (30 pages) Dissertation
Published: 14th Dec 2021
Tagged: Cryptocurrency
Executive summary
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum have changed the way people and organisations operate in everyday life and have posed several questions for the current monetary system which is in place in almost every country in the world. As the popularity of cryptocurrencies reach staggering heights to people everywhere, we must consider the implication it can have in many different aspects. The very nature of these currencies makes the use of third-parties and many financial institutions less significant. It’s revolutionary blockchain technology has demanded the attention of IT people and opportunists alike due to major increases in value and the different perspective it offers us in terms of privacy, swiftness and efficiency when sending and receiving money.
The system which involves these currencies being stored on decentralized exchanges has posed many questions. Such as is this a safe way to make transactions and store money, are the proper regulations in place to operate with safety and anonymity and is this just a way for scammers and cyber criminals to operate without being caught by law enforcement.
This year is also looking like the year that proper regulations for cryptocurrency will be quite apparent. Countries around the world are now grappling with cryptocurrencies as they learn how they are going to treat them. While some are more accepting, others tend to be suspicious of the new currency format while countries such as China refuse to acknowledge cryptocurrency altogether.
Table of Contents
Executive summary..…………….……………………………….……..2
What is Cryptocurrency…….………………………………………….3
How does cryptocurrency work……………………………………4
The role of cryptography………………………………………………7
Public key cryptography……………………………………….8
The role of decentralized exchanges…………………………..10
The merits and shortcomings of major cryptocurrencies and decentralized exchanges…………………12
Anonymization and cryptocurrencies…………………………14
The economic and regulatory implications and challenges of cryptocurrencies…………………………16
What is a Cryptocurrency?
The last decade has seen the emergence of several virtual currencies, including the most well-known currency Bitcoin, as well as Ethereum (ETH), LiteCoin (LTC), Zcash (ZEC), Dash, Ripple (XRP), and Monero (XMR). Financial experts, investors, cyber professionals, and the scientific community have various opinions, both positive and negative, on the future of cryptocurrency. Government officials are unsure on the necessary regulations which may be needed for economic stability. Further research of this technology and the technology that is needed to use it, Blockchain, must be conducted and evaluated.

In 2009 the world was first introduced to the cryptocurrency, Bitcoin. While Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have taken years to become popular they have since rapidly grown. As cryptocurrencies continue to grow so do possible risks and threats to financial institutions, law enforcement and the public. Another kind of cryptocurrency is Litecoin which was released in 2011, three years after Bitcoin. It uses the same structure as Bitcoin but has a higher limit of 84 million units to Bitcoins 21 million. It also has a shorter target blockchain creation time. Ethereum is another noteworthy cryptocurrency as it made improvements on Bitcoins architecture. It uses “smart contracts” that enforce the performance of a transaction as it compels parties not to go back on arrangements and contains refund mechanisms if there were a violation of the agreement by one of the parties.
Only a small number of people in the crypto-communities knew what they were, and many thought that it was another fad which would come and go like so many others. The value of Bitcoin was just a few cents which is obviously not much. There were far more profitable investments at the time, and for this reason it was ignored by many. This new digital currency was founded by an unknown person or group of people who go by the name Satoshi Nakamoto. There is a lot of speculation as to the identity of Satoshi Nakatomo, but to this day people can still only speculate. However, the Japanese to English translation of the name is considered to be too perfect in its possibilities in relation to Bitcoin and blockchain to not be a made-up name. Possible translations referring to a “Sugar city” possibly referring to the wealth that may come from the new digital currency and a “Clever heir” which may imply that the creator(s) knew that this new system would essentially replace old systems. The people who invested in the new digital currency either had faith in its founder or simply wanted to see how it worked.
Importantly, cryptocurrencies can be exchanged for fiat currencies in special online markets such as Bitfinex, Kraken and Coinone. A fiat currency is a currency than a government has declared as legal tender, such as the US dollar, European euro or British pound sterling. However, Cryptocurrency exchanges are somewhat vulnerable to hacking and represent the most common location for cryptocurrency theft by hackers. A notable difference between cryptocurrency and fiat currencies is that most, but not all, cryptocurrencies are characterized by finite supply.
Let’s take Bitcoin for example, there is a limit of 21 million Bitcoin ever allowed to be in circulation, but what happens after all 21 million are mined? Bitcoin in many ways is like gold as it cannot simply be created from nothing like a euro or dollar can. Gold must be mined from the ground and Bitcoin must be mined digitally. Once miners have unlocked 21 million Bitcoin the planets supply will be dry unless the protocol for it can change to a larger supply. People who support Bitcoin say the limit on Bitcoin will keep banks in check and not allow them to issue its own Bitcoin. The individuals who are most effected by the limit of Bitcoin are the people who mine it. There will be people who are against the Bitcoin limit who say miners will be forced away from their block rewards they receive for their work once the Bitcoin supply has reached its 21 million limit. When and if this happens, miners may need to rely on the transaction fees to keep working. A transaction fee is the cost of labour for required to bring a good or service to market, a Bitcoin in this case. According to Bitcoin.com, miners will eventually find the process unaffordable, leading to a decrease in miners in operation, and many negative effects on the Bitcoin system. This only assumes that transaction fees will not be enough for miners to keep financially stable once the Bitcoin limit has been reached. However, there are also reasons to believe that transaction fees and the cost of mining will even out in the future.
Looking towards the future, it is not hard to imagine that mining chips will become small and more efficient. This would result in a lower threshold of initial cost for miners and reduce the burden placed on miners. It is likely that transaction fees would increase also, and this would help keep miners afloat. The limit on the number of Bitcoin allowed in circulation will also likely have an adverse effect on the price of Bitcoin. The price of Bitcoin has seen massive hikes in the last couple of months and while nobody is quite certain if it will spread to the wider financial world, it seems likely that the limit on Bitcoin may see prices continue to increase. There are also stockpiles of Bitcoin around the world and, unsurprisingly, the largest of which belongs to its founder, Satoshi Nakamoto. His supply consists of roughly one million Bitcoins and that is currently equal to approximately five and a half billion euros.
There have been many attempts to create digital cash before especially during the tech boom in the 90s with systems like Flooz, Beenz and DigiCash emerging and ultimately failing. The biggest problem any network had to solve is double-spending. It is the fraudulent act of spending the same amount twice meaning there would have to be a trusted third party, a central server, that kept records of the transactions and balances. The most important part of Satoshi’s invention was that he found a way to build a decentralized cash system. Many have tried to do this before, but they all failed until now. Satoshi witnessed all the other digital cash systems failed and all these failed systems were centralized, so he decided to create one with no central entity. Like a peer-to-peer network for file sharing.
How does cryptocurrency work?
The base behind cryptocurrency is something called Blockchain. Blockchain is a public ledger of all transactions that ever happened within the network. This ledger is available to everyone meaning that everyone on the network can see everyone else’s account balance. Every transaction is a file that consists of the sender and the recipient’s public keys and the quantity of coins that is transferred. The sender also needs to use their public key to sign off on the transaction. Then the transaction will be broadcast to the network after it has been confirmed.
The process by which transactions are verified and added to the public ledger is known as Bitcoin mining and the public ledger is known as the blockchain, Bitcoin mining the means through which Bitcoin are released. All that is needed to mine Bitcoin is the suitable hardware and access to the internet. The process of mining involves compiling recent transactions into blocks and trying to solve a difficult computational puzzle. He who solves the first puzzle gets to place the next block on the blockchain and claim the reward. The reward is the transaction fee as associated with the transaction which has been compiled as well as the newly released Bitcoin. The amount of new Bitcoin released with each block that has been mined is known as the ‘block reward’ which is halved every 210,000 blocks, or approximately every 4 years. The difficulty of the computational puzzles depends on the effort which is being put into mining across the network. The difficulty can be adjusted by the protocol every 2016 blocks, or roughly every two weeks. The change in difficulty intends to keep the rate of discovery constant. The more computational power employed in mining will result in a higher level of difficulty and if computational power is taken off the network it will become simpler. During the days of Bitcoins infancy, mining was done using normal desktop computers. GPUs became dominant for mining Bitcoin as it gained popularity. In 2013, hardware known as ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) was created which is designed specifically to be used for mining Bitcoin and have been improved and upgraded since. Mining is currently competitive and can only be reasonably profitable when using ASIC.

Figure 1: ASIC
If you think about Bitcoin as a decentralized network or peers which keep a ledger of accounts and balances, it is more than merely the figures you see in a bank account. Cryptocurrencies have crypto in their name because the consensus-keeping process uses cryptography to secure it. While normal currencies are secured by people or by trust, cryptocurrency is secured by math. The probability of a Bitcoins address being compromised is less likely than that of a meteor hitting your house.
To understand how cryptocurrency works it is important to understand its properties and for this they must be split up into transactional and monetary properties. The first transactional property we will look at is that it is irreversible. This means that a transaction cannot be reversed after it has been confirmed. Not one person on the planet can do this, not even the parties involved in the transaction. If you’ve sent money to a scammer or a hacker there is no going back. Another transactional property is that neither transactions or accounts are connected to real-world people or identities. Bitcoins are received on addresses which are seemingly random chains of characters. While it is possible to analyse the transaction flow, it is not possible to connect users addresses to real-world individuals.
Cryptocurrencies are permissionless. You do not need permission to use cryptocurrency. The software can be downloaded freely by anyone and after that you can send and receive cryptocurrencies as you please. Cryptocurrencies are also very secure. The funds of a cryptocurrency are locked in a public key cryptography system and the owner of the key is the only one who can send cryptocurrency. Cryptography makes it impossible to break. The address of a Bitcoin is one of the safest things in the world. The final transactional property is that cryptocurrencies are fast and global. Once a transaction has begun it is nearly instantly in the network and can be confirmed within minutes. Since these transactions happen on a global network of computers they are indifferent of your actual location. It makes no matter if you send a Bitcoin to someone across the road or someone on the other side of the world.
The monetary properties of Bitcoin are that they are a controlled supply and the should reach they’re max of 21 million somewhere around 2140. All cryptocurrencies control the supply by a schedule written in the code. This means the supply of a cryptocurrency in the future can be calculated at any given moment. The other monetary property is that there is no debt. The fiat-money in a bank account exists because of debt and the numbers you see represent debts. Cryptocurrencies do not represent debt. It is a money that is as hard as a coin of gold. To understand cryptocurrencies both properties must be considered. Bitcoin, being permissionless, irreversible and pseudonymous means of payment, challenges the control of governments and banks of the monetary transactions of the people. You can’t stop someone using Bitcoin, you can’t stop someone accepting a payment through Bitcoin and you can’t undo a transaction. It is money with a limited, controlled supply that is not changeable by a central institution, government or bank.
The role of cryptography
Cryptography is essentially the practice of encrypting certain data or information so that it can be kept secret from third parties. Cryptography has been used for everything from Julius Ceaser using ciphers to send secret messages to his generals during ancient times to the allied forces during WW2 sending messages back and forth. Cryptography is needed to prevent private data from being compromised and taken by people who are not meant to see it. This data can be medical, financial, mathematical etc. in origin. There are many reasons as to why people would want to keep data private. Some information, if exposed can pose a threat to national security in some countries. Cryptography makes it possible to that only the appropriate people have access to certain sensitive information. There are many ways cryptography is applied to pieces of data. Before modern day technology existed, transposition cyphers were used to arrange and rearrange the letters in a message. The methods have become a lot more complex since then. Now, incredibly complex computers and mathematical technology can be used to encrypt data in more complex ways than ever and cryptography is the science of applying mathematical functions to pieces of data to guarantee its security.

Figure 2: Enigma decryption machine used for decoding secret messages during WW2
It is claimed in movies and television that anything can be hacked, however in the real world this is simply not true. Cryptography itself cannot be hacked to generate a forged cryptographic signature, just as math can’t be hacked to make 3+3=5. However, both cryptography and math can be used incorrectly. If a system which is using cryptography fails, it is because the designer has incorrectly applied the cryptography. It is never because the cryptography didn’t work, just as it’s not the moneys fault if your bank handles your account incorrectly. This is important because cryptocurrency is an application of cryptography. Cryptography is not a new technology, it has been not only used by Bitcoin but used since the very beginning of the internet and is as important as many other common internet protocols we use every day. Cryptographic technology is as essential and reliable to computer scientists as rocket science is considered essential and reliable to NASA.
Public key cryptography
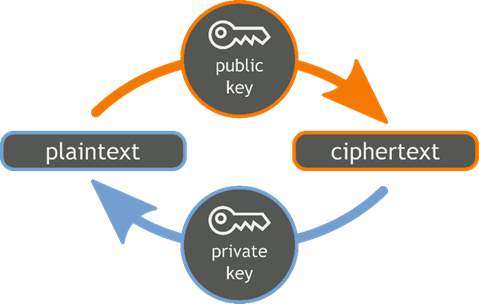
Cryptocurrencies use cryptography to secure transactions, to control the creation of additional units and to verify the transfer of assets. Cryptocurrencies use public key cryptography to accomplish these things. Public key cryptography involves the user having a private key and a public key which is collectively called a keypair. They are both encrypted and involve having a random assortment of upper and lowercase numbers and letters which is known as ciphertext and would look something like this: YKdxmAQBur3W6IF1fjvneydZ09Pr93. The keys would usually be around 30 characters in length. The decoded message is known as the plaintext. The reason of having the private key is to unlock the public key which would allow a user to receive the money that has been sent. The public key then allows people to receive an address to send the money to. This means that only the person who has the private key would be allowed to unlock the public key. It is quite like a postman with a postbox, anyone in the public can put letters in the postbox but only the postman can unlock in and take the mail within. Any person can deposit money to a public key, but only those who have the private key can access the money. This allows users to have access to and receive money but not allowing other people access to that money. Public key technology has been a huge development for the e-payment industry in recent times.
In order to work, private keys need to be able to authenticate transactions without going anywhere. It is only ever stored or used on your local device. This allows the user to stay in control of its security. It does this using cryptographic digital signatures. There are a few different ways of generating and validating cryptographic signatures. The mathematical theorems that make them work are extremely complex. For a user to generate a signature, they will use a computer’s signature generation algorithm, which takes the users private key and the message, and finally generates the digital signature. Both the message and the signature are together sent to the person on the other end of the transaction but crucially not the private key. When the signature is received there is a full signature validation algorithm to employ. The algorithm will take the message and signature and use these to determine the public key that was used to create the message, but the private key will always remain unknown.
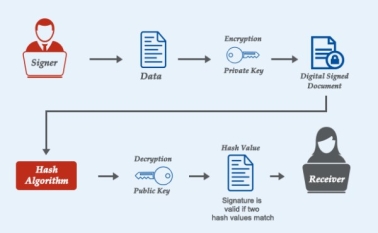
The cryptographic signature process will allow the user to be sure that a message hadn’t been created or tampered with by an unknown or third party and must have been generated by a user with the correct private key, without knowing the private key itself. All that is needed is the combination of the message and the signature and the public key. Cryptographic signatures are so rock solid because of the size of the numbers used in a private key. Private keys in Bitcoin are 256-bit integers, which gives up a number that is seventy-six digits long. This size of this number allows it to be incredibly powerful and impossible for any computer on the planet to hack. In fact, it would require a computer with the power of three hundred sextillion suns for a year to even count through the private keys, let alone test or use them. It is a technique that is known to be incredibly trustworthy in the technological community as the complexity of the mathematics behind it is already outside the scope of most people.
Public key cryptography does have its vulnerabilities. This includes people accidentally losing their keys or accidentally showing their private key to other individuals. There may be no way of recovering any of the money taken if a person was to lose their private key. If a person accidentally revealed their private key information to a third party, that third party could access the users account and steal any Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies that may be in that person’s wallet. However, there are ways to protect private key information. Most importantly, a user should never share their private key information with anyone besides someone they truly trust like a spouse for example.
Some users take protecting their private key very seriously and purchase hardware wallets. A hardware wallet is a device something like a memory stick that provides cold storage for a person’s cryptocurrencies. They remove the cryptocurrencies from the internet and remove them from the internet in the same way a memory stick removes files from a computer. These hardware wallets can add an extra layer of security by requiring passwords themselves. Although it is very unlikely that a hardware wallet is ever compromised there is still the possibility of losing the password to the wallet or the wallet itself, which can result in the cryptocurrencies being lost indefinitely. The wallets sometimes come with anti-theft features which can punish a person for incorrectly entering the password multiple times and locking the user out for potentially a couple of hours initially and with more failed attempts the user can be locked out for weeks and possible months. Another popular measure in protecting against loss of theft is insurance. Some major cryptocurrency exchanges are now advertising insurance for all their accounts. This can be extremely beneficial to both parties, as it adds another level of security. Many cryptocurrency exchanges keep a large percentage of their assets in cold storage facilities. This means only a small amount of their assets are vulnerable to cyber-attacks while it is true that these assets can be subject to a physical attack, it would be extremely difficult for any person to do this.

Figure 3: A branded hardware wallet.
Despite cryptography being around for quite a long time now, being used in very different ways, public key cryptography is still quite new and because Bitcoin has only been around for roughly ten years now the potential for public key cryptography is only beginning to be realized. More and more people all over the world are starting to understand and use cryptocurrencies which means a larger amount of people will begin to understand the value of public key cryptography and cryptocurrencies. A huge reason that cryptography technology is being developed is because there is a huge need to store, send and receive money securely over the internet. Online banking has become extremely relevant in recent years and driving the need for cryptography technology. Public key cryptography is making money exchange and storing safer. It is likely that cryptocurrencies will continue to become rise in popularity in the coming years since public key cryptography and cryptography are helping to improve digital money use and storage. It is likely we will see less and less major hacks as cryptography improves.
The role of decentralized exchanges
The greatest need in the cryptocurrency system is that is operates in a truly decentralized exchange. It is estimated that one in sixteen Bitcoins have been stolen. Exchanges make it easier to keep track of what and who have been hacked, stolen and defrauded. The need to trust a third party with your money has been an obvious weak point in the world of cryptocurrency and cryptocurrencies cannot achieve their purpose of being a decentralized currency without having decentralized exchanges. If one is required to trust the traditional, centralized businesses to purchase or sell cryptocurrencies, it would have to have not been disintermediated. A decentralized exchange or DEX allows peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies without the need for an intermediary or third party. They are transactions which do not require trust meaning you do not have to give your crypto coins to a third party, bank or intermediary. The user maintains full control of their account and digital currency.
Decentralized exchanges are still only in their youthful stages. Launching a DEX is difficult technically, expensive, and requires some development before we see changes from the masses. As it is with any exchange, there are pros and cons that come with each DEX, however, it is obvious that decentralized is gaining popularity and the likelihood the world shifts to a decentralized economy is becoming ever more likely. There are many notable differences between a centralized and decentralized exchange, one being the control of funds. Users of centralized exchange platforms make deposits to facilitate the exchange transaction. The centralized exchange service is in control of these funds. This means that the power is firmly in the hands of the centralized service. However, in a decentralized cryptocurrency exchange platform, users make transactions directly with their pees without any need for a central server. Funds are in the control of the people and users in the platform. It is quite difficult to trade anonymously of centralized platforms due to government regulations and adherence with strict KYC and AML laws. Decentralized cryptocurrency is very much about the anonymity of the user. This is also apparent when is comes to authentication. Users of centralized crypto exchanges must heavily rely on the platform service to authenticate transactions. In the case of decentralized exchanges, users do not have to count on third-party intermediaries. By means of smart contracts and several blockchain protocols, the entire system provides authentication and authorization of crypto exchange transactions that does not require trust.
Figure 4: Altcoin.io is a popular decentralized exchange.
A capacity for an exchange to deal with demand is quite important if downtime is to be avoided. In many cases, the profits which centralized exchanges make from transaction fees goes back into the exchange to cover the running costs and into their profits. Ut despite the millions that some exchanges take on a daily basis, they are often unable to scale quickly enough to deal with the amount of traffic and prevent downtime from occurring. The problem is not money rather the centralization of these exchanges. The nature of centralized infrastructure and service provision results in downtime and no amount of money can solve this and make it quick enough to keep up with demand. Exchanges must be able to grow as their user bases grow, regardless of how rapidly or massive it grows. Decentralized exchanges have a solution to this issue as there is no central hub that can be overloaded with traffic or user request and there are no bottlenecks other than the ones that lie with the users and specifically their local internet connections. A truly decentralized exchange’s broadcast system should have a shared capacity, and with order broadcasts and order matching also being decentralized, there would be no existing point of failure.
An important advancement in the use of decentralized exchanges is the atomic swap. It is when two simultaneous events occur at the same time, such that they could be referred to as one single event. The atomic swap refers to two events happening at the same time, so in simple terms if Tim is shaking Fred’s hand then Fred must be shaking Tim’s hand, so these single events with two people has occurred simultaneously. In cryptography, an atomic swap is the exchange of different cryptocurrencies on different blockchains, without the need to trust an intermediary. It utilizes something called a hash time locked contract which is a specific type of smart contract that enables people to exchange different kinds of cryptocurrencies in a manner that is trust less, without the risk of one person backing out of the contract.
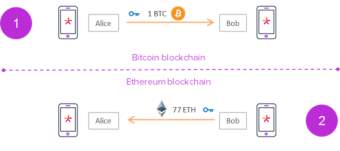
Figure 5: Diagram of an atomic swap.
A hash time locked contract is the smart contract underneath which is used to facilitates atomic swaps. It is what makes sure that both parties hold up their end of the agreement, if not the entire thing is abandoned, and the cryptocurrencies are returned to each user. For example, if Tim was to exchange 1 Bitcoin for 1’000 of Fred’s Ethereum. Tim would have to create a specific hash which represents the amount of Bitcoin he will pay Fred. To accept the payment, Fred will create a cryptographic proof of payment, and this will have to be done by both parties within a specific amount of time. They can both see each other’s cryptocurrencies but can unlock them by entering the secret key. When Tim enters the secret key and claims the Ethereum, it will be sent to the blockchain and Fred will be able to claim the Bitcoin.
The merits and shortcomings of major cryptocurrencies and decentralized exchanges
Blockchain technology is a relatively new concept and has proven to be extremely useful to businesses and has many advantages. One of its major advantages is Fraud prevention. Blockchains are open-sourced ledgers, and due to the fact that every single transaction is recorded on them, it is quite easy to tell if fraud has taken place. A blockchains system is monitored and maintained by miners who validate each transaction around the clock. The number of miners who are validating blockchains are in the thousands all over the world at any given moment in time. This allows decentralized blockchain-based coins a hug amount of oversight and makes them nearly invulnerable to fraud. This is a huge benefit of decentralized blockchains.
Decentralized cryptocurrencies are not controlled by any government or bank which means they cannot be meddled with by governments. Interference by governments is a problem that has led to the devaluation of many cryptocurrencies throughout history. A frequently recurring problem with government currency meddling is that they end up creating too much inflation by printing too much or devaluing currency in a short period of time. Decentralized blockchains make it impossible for governments to meddle with currency because, just like everybody else, they have absolutely no control over them whatsoever. This is because cryptocurrencies are simply put just software that have a limited amount of coins resulting in them being resistant to inflation, which is unlike normal currencies printed by banks.
Blockchain cryptocurrencies have transaction times which are quite a lot faster than that of banks. Some bank transfers can take up to a couple of days at a time whereas transactions made on a blockchain usually only take a matter of minutes. The speed of transfer on the blockchain can be beneficial to countless numbers of people around the world. If money moves faster, then decisions can be made faster and all process are conducted more efficiently which can only be a good thing for the world economy.
Bitcoin, which is a cryptocurrency that runs on the blockchain is regularly referred to as digital gold. This has come about due to the amount of similarities between the two entities. Similarities such as the fact that there is only a finite amount of both, it must be mined and that it is very valuable around the world. Due to it being referred to as digital gold and because of it’s qualities, Bitcoin and blockchain technology can be a very effective way to store value. A few people have made this realisation and is partly the reason that the value of Bitcoin has risen so sharply over the last few months. However, Bitcoin has one crucial advantage over gold and other physical entities. This advantage is that they can be stored on computer hardware and can be sent safely over the internet. This means that people do not have to store the physical substance of gold in a bank or a safe.
But we know that cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology is not perfect. There are still a few drawbacks worth mentioning. One of it’s biggest drawbacks is crime. Cybercriminals have become fond of cryptocurrencies since its users can retain a level of anonymity. For example, the dark net based digital black market known as the Silk Road was heavily reliant on the use of Bitcoin for transactions. People could buy illicit goods such as weapons and drugs on this site using blockchain-based cryptocurrencies. But as soon as the FBI became aware of the Silk Roads existence it was shut down, just a couple of years after it had been started. This was a giant leap forward for preventing criminals that were making use of cryptocurrencies. There are people who believe that criminals will still take advantage of cryptocurrencies, so it is likely that there will be heavy regulations put in place in attempt of preventing this outcome. However, it will not be the first currency used for illegal transactions, such as that of the infamous drug lord Pablo Escobar, who made so much money he had to bury some American dollars under the ground. However, if he had Bitcoin he would have had a much easier job storing it.
Another disadvantage of cryptocurrencies that use a decentralized blockchain is that they can be extremely volatile at times. It is still quite common if Bitcoin prices were to fluctuate by 20% in one day. A reason for this could be that cryptocurrencies are new which means businesses, investors and even governments are still making their mind up on weather or not to adopt them which can cause these fluctuations. In early 2017, China attempted to outlaw cryptocurrency exchanges which resulted in a drop in the price of Bitcoin of roughly 40%. This kind of volatility can result in groups considering adopting of the cryptocurrency in being extremely concerned. But even with this kind of price uncertainty Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies have had an upward trend over the last few years. The market cap for cryptocurrencies may one day find an equilibrium which may result in a decreased amount of volatility. This may not be until the market cap has possibly reaches trillions of dollars but now it is only a few hundred billion for every cryptocurrency.
Storing cryptocurrencies which are blockchain-based can result in problems for people who are not very tech savvy, but it is quite simple for those who are. For example, transferring Bitcoin from a computer onto a cold storage wallet may seem simple to an IT person but could possibly prove to be a challenge for the regular person. This might result in people holding their cryptocurrencies on the exchange itself. These exchanges can be something of a target for cybertheft. An example of this is the infamous Mt. Gox which was the largest cryptocurrency exchange in the technologies infancy years. The exchange was hacked and everyone of its Bitcoins had been stolen resulting in the biggest case of cryptocurrency theft to date and the loss of hundreds of millions of dollars. Today exchanges claim to have better security and offer insurance to make cryptocurrency more appealing. However, nobody is quite sure as to the perfect safe storage of cryptocurrencies.
Anonymization and cryptocurrencies
A main feature that usually links people to Bitcoin is its anonymity. In one respect it is completely anonymous and in another it is enterable trackable and transparent because of all transactions being recorded in a public ledger. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are pseudonymous. Making Bitcoin transactions are like writing under a pseudonym. Your pseudonym is the address where use receive Bitcoin. If the link between your address and your identity is revealed, then your anonymity is lost. Because all transactions are recorded on the blockchain other users will know exactly what and how many cryptocurrencies you own.
There are many reasons as to why to stay anonymous when it comes your cryptocurrencies. If your address is well known it can leave you subject to risk when it comes to hackers, cybercriminals and scammers. You also may be trying to avoid law enforcement and conduct in illegal activities on dark net markets such as Alphabay and Hansa, which usually only accept Bitcoin in their transactions. However according to the European Cybercrime Centre Internet Organised Crime Threat Assessment report there ae a lot of markets starting to accept other currencies such as Ethereum and Zcash. Not only this but attempts at extortion through ransomware are now accepting cryptocurrencies as payment. For the people who conduct these crimes, it is important that they stay anonymous. Staying anonymous can be tough due to attacks against the network which are made to deanonymize users. This can lead to a reveal of identity which can hinder the law enforcement and result in them not catching criminal, or even reveal the identity of the criminal and get them arrested.
The blockchains visible nature allows anyone to analyse and match up addresses with names of individuals and if they do this correctly, they can connect all payments sent and received with a certain individual. This allows the attacker to perform a taint analysis. The taint of a Bitcoin evaluates the link between an address and previous transaction addresses. The more taint results in a bigger connection between two addresses. A great way of securing anonymity is to not give out information which can make you personally identifiable. This can be done by avoiding linking your personal or organisations information with your cryptocurrency address. A big party of anonymity is trusting the person you are making the transaction with, this way you can make trades in person.
But there are techniques which can raise your level of privacy and spreading these techniques to the entire crypto community will help in nulling the effects of coin predators. When it comes to the blockchain, it’s solid cryptography is only affecting to fraud and counterfeit until human intervention is present. Although it is considered an anonymous monetary system there are many ways in linking a persons Bitcoin address to their real address. When users need to make business transactions this can make anonymity difficult and numerous Bitcoin wallets will broadcast your actual IP address, and if the right person wanted to, could link that to your actual address. However, Bitcoin is still far more private than credit cards and not as private as cash. This raises quite a few issues for businesses and individuals who take their personal privacy seriously. Your Bitcoin address does reveal information without having been linked to any individual or groups personal information. These pieces of info are:
- How much currency you hold in your address.
- When you received each coin.
- The address you received those coins from.
- The address of the user you sent those coins.
These reveal a lot of information and may be quite daunting to a person who is conscious with their information. But there are technical ways for a person to become more anonymous while using cryptocurrency. These might include using a VPN which is designed to protect the user and their privacy. You could also use a new Bitcoin address for each transaction which would make it difficult for anyone to make connections between addresses. However, if you do this and your identity is compromised, it is likely that the connection to all the addresses would be too. Using a service known as tumblers or mixers which are services that can mix up a trail of transactions by associating funds which are not related.
The economic and regulatory implications and challenges of cryptocurrencies
The emergence of cryptocurrencies in different geographic market has been apparent in not only huge economies like the US and EU but also countries which have less developed financial institutions. In Kenya for example, half of the countries GDP is fulfilled by a digital currency. Countries that have had notable devaluation of currencies should consider cryptocurrencies when making transactions between countries. Signs of countries adopting Bitcoin, as it is the most popular cryptocurrency to date, is growing as there are over 14 million Bitcoins in circulation.
More and more financial institutions have been considering sing blockchain technology to increase efficiency and gain a leg into markets which had not previously been utilised. However, many financial institutions have seemed against taking currencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum on board as they believe they will lose a certain degree of control over their ledger and transaction process. This could prove to be a stumbling block in the development of cryptocurrencies. It is likely that cryptocurrencies will be adopted by certain banks and other financial institutions, it is unlikely that it will be taken on by major financial organisations.
In countries on the western side of the world Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have been extremely successful and taken on by the masses. However, in countries with stricter regulations such Asian countries. In 2017, China made a ban on Bitcoin which led to a major decline in the price Bitcoin all over the world. This shows just how important the involvement of each major country is with cryptocurrencies. While a complete ban seemed sufficient in China, the rest of the world will likely see regulations put in as to ensure safe transactions of Bitcoins and other cryptocurrencies between users. This would be likely to impact prices initially but may be beneficial in the long run as people will see cryptocurrency as a safer and more reliable means of transactions.
As Bitcoin is only a digital currency, it can often go in the opposite direction as the world wide economy due to locations which lack developed financial institutions taking it into adoption. Ethereum should too but not as much due to it’s wide range of uses and innovative nature. As Bitcoin is more of a commodity like gold, Ethereum would be linked more with the places introducing its smart contracts and overall network.
Unstable exchange rates are not easily avoided when it comes to cryptocurrencies. But the innovative nature of cryptocurrencies just comes hand in hand with the way they were created and removing currency from control of the state is gaining major support from people around the world. This sort of widespread change is bound to have social and economic consequences. To make the masses confident in cryptocurrency, regulations and a framework for the use of Bitcoins, Ethereum etc is quite necessary.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
Related Services
View allRelated Content
All TagsContent relating to: "Cryptocurrency"
Cryptocurrency is digital currency that can be used to pay for goods and services, using blockchain technology to ensure secure transactions. Bitcoin is almost certainly the most commonly known Cryptocurrency, though others such as Dogecoin, Ethereum and more are now seeing increased popularity.
Related Articles
DMCA / Removal Request
If you are the original writer of this dissertation and no longer wish to have your work published on the UKDiss.com website then please:




